Abstract
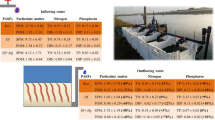
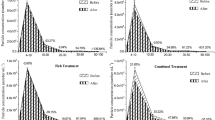
The filter feeder sabellid Sabella spallanzanii Gmelin (Polychaeta, Sabellidae) was proposed as biofilter in the treatment of wastes from intensive aquaculture. The species was previously studied concerning reproductive traits and ecological requirements; moreover, previous laboratory experiments indicated a positive action of its feeding activity on solid removal from water column coupled with an interesting microbiological activity. In the present paper data on settlement and growth rate from a natural population, together with data on the bioremediation activity of an adult population, relative to an experiment conducted in a small fish farm are reported. Results seem to encourage further studies on S. spallanzanii for a future utilization in bioremediation of fish farms with recycled water. Data from natural annual settlement indicated, however, the unreliability in obtaining settlers from natural populations, so that the artificial reproduction of the target species will be one of the main points of further investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Abeysinghe H. Shanableh A. Rigden (1996) ArticleTitleBiofilter for water reuse in aquaculture Water Science Technology 34 IssueID11 253–260
A. Cavallo A. Giangrande (2003) ArticleTitleProve di sperimentazione ai fini dell’utilizzazione di Sabella spallanzanii come biorimediatore in acquacoltura Biologia Marina Mediterranea 10 IssueID2 4–5
Chen, S. and Malone, R.F. 1991. Suspended solids in recirculating aquaculture systems. In: Engineering aspects of intensive aquaculture. Proc. from the aquaculture Symposium, Cornell University, 4–6 April 1991, Northeast Regional Agricultural Engineering Service, Ithaca, NY, pp. 170–185.
Clapin, G. 1996. The filtration rate, oxygen consuption and biomass of the introduced polychaete Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin) within Cockburn sound: can it control phytoplankton level and is it an efficient filter feeder? Honour Thesis, April 1996. Department of Environmental management, Edith Cowan Univerity, Joondalup Western Australia, 90 pp.
M. Enander M. Hasselstom (1994) ArticleTitleAn experimental waste water treatment system for a shrimp farm Infofish International 4 56–61
A. Giangrande M. Licciano P. Pagliara M.C. Gambi (2000) ArticleTitleGametogenesis and larval development in Sabella spallanzanii. (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) from the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Biology 136 847–861
M. Licciano L. Stabili Cavallo A. Giangrande (2003) ArticleTitleProve di stabulazione per la valutazione della capacità di accumulo microbiologico con il sabellidae filtratore Sabella spallanzanii (Annelida: Polychaeta) Biologia Marina Mediterranea 10 IssueID2 1–3
J.H. Ryther J.C. Goldman C.E. Gifford J.E. Huguenin A.S. Wing P.J. Clarner L.D. Williams B.E. Lapointe (1975) ArticleTitlePhysical integrated waste-recycling-marine polyculture systems Aquaculture 5 163–177
M. Shpigel A. Neori D.M. Popper H. Gordin (1993) ArticleTitleA proposed model for “environmental clean” land-based culture of fish, bivalves and seaweeds Aquaculture 117 115–128
J.D.H. Strickland T.R. Person (1992) ArticleTitleA practical handbook of seawater analisys Bullettin Fisheries Research Board of Canada 167 310
A. Trovar C. Moreno M.P. Manuel-vez M. Garcia-Vargas (2000) ArticleTitleEnvironmental impact of intensive aquaculture in marine waters Water Research 34 334–342
H. Tsutsumi T. Inoue (1996) ArticleTitleBenthic environment and macrobenthic communities in a cove with organically enriched bottom sediment due to fish farming for two decades Benthos Research 50 39–49
Twarowska, J.G., Westerman, P.W., and Losordo, T.M. 1996. Water treatment and waste characterization evalutation of an intensive recirculating fish production system. In: Aquaculture Engineering Society Proceedings II: Successes and Failures in Commercial Recirculating Aquaculture, 2. Northeast Regional Agricultural Engineering Service, pp. 447–460.
J. Van Rijn (1996) ArticleTitleThe potential for integrated biological treatment systems in recirculating fish culture A review. Aquaculture 139 181–201
R.S.S. Wu (1995) ArticleTitleThe environmental impact of marine fish culture: towards a sustainable future Marine Pollution Bulletin 31 159–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giangrande, A., Cavallo, A., Licciano, M. et al. Utilization of the filter feeder polychaete Sabella. Aquacult Int 13, 129–136 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-004-9025-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-004-9025-3