Abstract
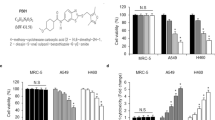
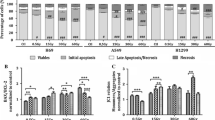
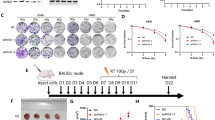
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in modulating the radiation responsiveness of tumors. We determined that an inflammation response prior to irradiation contributes to radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. In the clonogenic survival assay, activation of the inflammation response by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) decreased the degree of radiosensitivity in NCI-H460 cells (relatively radiosensitive cells), but had no effect in A549 cells (relatively radioresistant cells). LPS-induced radioresistance of NCI-H460 cells was also confirmed with a xenograft mouse model. The radioresistant effect observed in NCI-H460 cells was correlated with inhibition of apoptotic cell death due to reduced Caspase 3/7 activity. Moreover, we found that the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were synergistically elevated in NCI-H460 cells by treatment with LPS and radiation. Increased ROS generation negatively affected the activity of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Decreased PP1 activity did not lead to Bad dephosphorylation, consequently resulting in the inhibition of irradiation-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss and apoptosis. We confirmed that pre-treatment with a PP1 activator and LPS sensitized NCI-H460 cells to radiation. Taken together, our findings provided evidence that PP1 activity is critical for radiosensitization in NSCLC cells and PP1 activators can serve as promising radiosensitizers to improve therapeutic efficacy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koh PK, Faivre-Finn C, Blackhall FH, De Ruysscher D (2012) Targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): clinical developments and rationale for the combination with thoracic radiotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev 38:626–640
Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ, Kaanders JH (2008) Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol 9:288–296
Wang L, Yang H, Palmbos PL, Ney G, Detzler TA, Coleman D et al (2014) ATDC/TRIM29 phosphorylation by ATM/MAPKAP kinase 2 mediates radioresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 74:1778–1788
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Zani BM, Popov VM, Fratticci A, Cerasani M et al (2014) Hypoxia sustains glioblastoma radioresistance through ERKs/DNA-PKcs/HIF-1alpha functional interplay. Int J Oncol 44:2121–2131
Multhoff G, Radons J (2012) Radiation, inflammation, and immune responses in cancer. Front Oncol 2:58
Roughton K, Andreasson U, Blomgren K, Kalm M (2013) Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation aggravates irradiation-induced injury to the young mouse brain. Dev Neurosci 35:406–415
Kim W, Youn H, Kwon T, Kang J, Kim E, Son B et al (2013) PIM1 kinase inhibitors induce radiosensitization in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Pharmacol Res 70:90–101
Li F, Sethi G (2010) Targeting transcription factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805:167–180
Sandur SK, Deorukhkar A, Pandey MK, Pabon AM, Shentu S, Guha S et al (2009) Curcumin modulates the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:534–542
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Sethi G, Shanmugam MK, Ramachandran L, Kumar AP, Tergaonkar V (2012) Multifaceted link between cancer and inflammation. Biosci Rep 32:1–15
Gonda TA, Tu S, Wang TC (2009) Chronic inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle 8:2005–2013
Xia L, Mo P, Huang W, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhu H et al (2012) The TNF-alpha/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 33:2250–2259
Zamkova M, Khromova N, Kopnin BP, Kopnin P (2013) Ras-induced ROS upregulation affecting cell proliferation is connected with cell type-specific alterations of HSF1/SESN3/p21Cip1/WAF1 pathways. Cell Cycle 12:826–836
O’Loghlen A, Perez-Morgado MI, Salinas M, Martin ME (2003) Reversible inhibition of the protein phosphatase 1 by hydrogen peroxide. Potential regulation of eIF2 alpha phosphorylation in differentiated PC12 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 417:194–202
Garcia A, Cayla X, Guergnon J, Dessauge F, Hospital V, Rebollo MP et al (2003) Serine/threonine protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A are key players in apoptosis. Biochimie 85:721–726
Li L, Ren CH, Tahir SA, Ren C, Thompson TC (2003) Caveolin-1 maintains activated Akt in prostate cancer cells through scaffolding domain binding site interactions with and inhibition of serine/threonine protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A. Mol Cell Biol 23:9389–9404
Das AK, Sato M, Story MD, Peyton M, Graves R, Redpath S et al (2006) Non-small-cell lung cancers with kinase domain mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor are sensitive to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 66:9601–9608
Kim W, Youn H, Seong KM, Yang HJ, Yun YJ, Kwon T et al (2011) PIM1-activated PRAS40 regulates radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells through interplay with FOXO3a, 14-3-3 and protein phosphatases. Radiat Res 176:539–552
Azzam EI, Jay-Gerin JP, Pain D (2012) Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged cell injury. Cancer Lett 327:48–60
Olas B, Wachowicz B, Saluk-Juszczak J, Zielinski T, Kaca W, Buczynski A (2001) Antioxidant activity of resveratrol in endotoxin-stimulated blood platelets. Cell Biol Toxicol 17:117–125
Li P, Zhao QL, Wu LH, Jawaid P, Jiao YF, Kadowaki M et al (2014) Isofraxidin, a potent reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger, protects human leukemia cells from radiation-induced apoptosis via ROS/mitochondria pathway in p53-independent manner. Apoptosis 19:1043–1053
Kim HS, Song MC, Kwak IH, Park TJ, Lim IK (2003) Constitutive induction of p-Erk1/2 accompanied by reduced activities of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A and MKP3 due to reactive oxygen species during cellular senescence. J Biol Chem 278:37497–37510
Ayllon V, Martinez AC, Garcia A, Cayla X, Rebollo A (2000) Protein phosphatase 1alpha is a Ras-activated Bad phosphatase that regulates interleukin-2 deprivation-induced apoptosis. EMBO J 19:2237–2246
Peng A, Maller JL (2010) Serine/threonine phosphatases in the DNA damage response and cancer. Oncogene 29:5977–5988
Blume-Jensen P, Janknecht R, Hunter T (1998) The kit receptor promotes cell survival via activation of PI 3-kinase and subsequent Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Bad on Ser136. Curr Biol 8:779–782
Berry DL, Theriault RL, Holmes FA, Parisi VM, Booser DJ, Singletary SE et al (1999) Management of breast cancer during pregnancy using a standardized protocol. J Clin Oncol 17:855–861
Wu K, House L, Liu W, Cho WC (2012) Personalized targeted therapy for lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci 13:11471–11496
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9:265–273
Higashiyama M, Okami J, Maeda J, Tokunaga T, Fujiwara A, Kodama K et al (2012) Differences in chemosensitivity between primary and paired metastatic lung cancer tissues: in vitro analysis based on the collagen gel droplet embedded culture drug test (CD-DST). J Thorac Dis 4:40–47
Toulany M, Kehlbach R, Florczak U, Sak A, Wang S, Chen J et al (2008) Targeting of AKT1 enhances radiation toxicity of human tumor cells by inhibiting DNA-PKcs-dependent DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1772–1781
Chae S, Kang KA, Chang WY, Kim MJ, Lee SJ, Lee YS et al (2009) Effect of compound K, a metabolite of ginseng saponin, combined with gamma-ray radiation in human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J Agric Food Chem 57:5777–5782
Bandugula VR, N RP (2013) 2-Deoxy-d-glucose and ferulic acid modulates radiation response signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol 34:251–259
Luo H, Yount C, Lang H, Yang A, Riemer EC, Lyons K et al (2013) Activation of p53 with Nutlin-3a radiosensitizes lung cancer cells via enhancing radiation-induced premature senescence. Lung Cancer 81:167–173
Yu L, Shang ZF, Hsu FM, Zhang Z, Tumati V, Lin YF et al (2015) NSCLC cells demonstrate differential mode of cell death in response to the combined treatment of radiation and a DNA-PKcs inhibitor. Oncotarget 6:3848–3860
Mirzayans R, Andrais B, Scott A, Wang YW, Murray D (2013) Ionizing radiation-induced responses in human cells with differing TP53 status. Int J Mol Sci 14:22409–22435
Valerie K, Yacoub A, Hagan MP, Curiel DT, Fisher PB, Grant S et al (2007) Radiation-induced cell signaling: inside-out and outside-in. Mol Cancer Ther 6:789–801
Brautigan DL (2013) Protein Ser/Thr phosphatases—the ugly ducklings of cell signalling. FEBS J 280:324–345
Klumpp S, Selke D, Krieglstein J (2003) Protein phosphatase type 2C dephosphorylates BAD. Neurochem Int 42:555–560
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, Jin YW, Kim J, Youn B (2013) Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S3 and antiapoptotic TRAF2 protein mediates radioresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem 288:2965–2975
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, Yun YJ, Kim W, Kim YH et al (2011) Psoralidin, a dual inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX, regulates ionizing radiation (IR)-induced pulmonary inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 82:524–534
Kim W, Yang HJ, Youn H, Yun YJ, Seong KM, Youn B (2010) Myricetin inhibits Akt survival signaling and induces Bad-mediated apoptosis in a low dose ultraviolet (UV)-B-irradiated HaCaT human immortalized keratinocytes. J Radiat Res 51:285–296
Kim E, Youn H, Kwon T, Son B, Kang J, Yang HJ et al (2014) PAK1 tyrosine phosphorylation is required to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 74:5520–5531
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Radiation Technology R&D program through the NRF funded by the MSIP (2013M2A2A7042502), a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, MOHW (1320100), Basic Science Research Program through the NRF funded by the MSIP (2014R1A1A1A05002112), and Basic Science Research Program through the NRF funded by the MOE (2013R1A1A2059832 to W Kim and 2014R1A1A2004061 to H Youn). In addition, this research was financially supported by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Human Resource Training Project for Regional Innovation (2012H1B8A2026225).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, W., Youn, H., Kang, C. et al. Inflammation-induced radioresistance is mediated by ROS-dependent inactivation of protein phosphatase 1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Apoptosis 20, 1242–1252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1141-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1141-1