Abstract
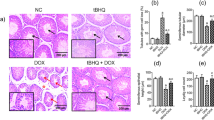
Human (HN) prevents stress-induced apoptosis in many cells/tissues. In this study we showed that HN ameliorated chemotherapy [cyclophosphamide (CP) and Doxorubicin (DOX)]-induced male germ cell apoptosis both ex vivo in seminiferous tubule cultures and in vivo in the testis. HN acts by several putative mechanisms via binding to: an IL-12 like trimeric membrane receptor; BAX; or insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3, a proapoptotic factor). To understand the mechanisms of HN on male germ cell apoptosis, we studied five HN analogues including: HNG (HN-S14G, a potent agonist), HNG-F6A (no binding to IGFBP-3), HN-S7A (no self-dimerization), HN-C8P (no binding to BAX), and HN-L12A (a HN antagonist) on CP-induced male germ cell apoptosis in mice. CP-induced germ cell apoptosis was inhibited by HN, HNG, HNG-F6A, HN-S7A, and HN-C8P (less effective); but not by HN-L12A. HN-L12A, but not HN-S7A or HN-C8P, blocked the protective effect of HN against CP-induced male germ cell apoptosis. HN, HN-S7A, and HN-C8P restored CP-suppressed STAT3 phosphorylation. These results suggest that HN: (1) decreases DOX (ex vivo) and CP (in vivo) induced male germ cell apoptosis; (2) action is mediated by the membrane receptor/STAT3 with minor contribution by BAX-binding pathway; (3) self-dimerization or binding to IGFBP-3 may not be involved in HN’s effect in testis. HN is an important molecule in the regulation of germ cell homeostasis after injury and agonistic analogues may be developed for treating male infertility or protection against chemotherapy side effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Tajima H, Yasukawa T, Sudo H, Ito Y, Kita Y, Kawasumi M, Kouyama K, Doyu M, Sobue G, Koide T, Tsuji S, Lang J, Kurokawa K, Nishimoto I (2001) A rescue factor abolishing neuronal cell death by a wide spectrum of familial Alzheimer’s disease genes and Aβ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6336–6341
Matsuoka M (2009) Humanin: a defender against Alzheimer’s disease? Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 4:37–42
Xu X, Chua CC, Gao J, Hamdy RC, Chua BH (2006) Humanin is a novel neuroprotective agent against stroke. Stroke 37:2613–2619
Bachar AR, Scheffer L, Schroeder AS, Nakamura HK, Cobb LJ, Oh YK, Lerman LO, Pagano RE, Cohen P, Lerman A (2010) Humanin is expressed in human vascular walls and has a cytoprotective effect against oxidized LDL-induced oxidative stress. Cardiovasc Res 88:360–366
Muzumdar RH, Huffman DM, Calvert JW, Jha S, Weinberg Y, Cui L, Nemkal A, Atzmon G, Klein L, Gundewar S, Ji SY, Lavu M, Predmore BL, Lefer DJ (2010) Acute humanin therapy attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:1940–1948
Eriksson E, Wickström M, Perup LS, Johnsen JI, Eksborg S, Kogner P, Sävendahl L (2014) Protective role of humanin on bortezomib-induced bone growth impairment in anticancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(3):djt459. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt459
Wang D, Li H, Yuan H, Zheng M, Bai C, Chen L, Pei X (2005) Humanin delays apoptosis in K562 cells by downregulation of P38 MAP kinase. Apoptosis 10:963–971
Ying G, Iribarren P, Zhou Y, Gong W, Zhang N, Yu ZX, Le Y, Cui Y, Wang JM (2004) Humanin, a newly identified neuroprotective factor, uses the G protein-coupled formylpeptide receptor-like-1 as a functional receptor. J Immunol 172:7078–7085
Muzumdar RH, Huffman DM, Atzmon G, Buettner C, Cobb LJ, Fishman S, Budagov T, Cui L, Einstein FH, Poduval A, Hwang D, Barzilai N, Cohen P (2009) Humanin: a novel central regulator of peripheral insulin action. PLoS ONE 4(7):e6334. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006334
Hoang PT, Park P, Cobb LJ, Paharkova-Vatchkova V, Hakimi M, Cohen P (2010) The neurosurvival factor humanin inhibits beta-cell apoptosis via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and delays and ameliorates diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Metabolism 59:343–349
Lue Y, Swerdloff R, Liu Q, Mehta H, Hikim AS, Lee KW, Jia Y, Hwang D, Cobb LJ, Cohen P, Wang C (2010) Opposing roles of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and humanin in the regulation of testicular germ cell apoptosis. Endocrinology 151:350–357
Jia Y, Lue YH, Swerdloff R, Lee KW, Cobb LJ, Cohen P, Wang C (2013) The cytoprotective peptide humanin is induced and neutralizes Bax after pro-apoptotic stress in the rat testis. Andrology 1(4):651–659. doi:10.1111/j.2047-2927.2013.00091.x (Epub 2013 May 20)
Sinha Hikim AP, Wang C, Leung A, Swerdloff RS (1995) Involvement of apoptosis in the induction of germ cell degeneration in adult rats after gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist treatment. Endocrinology 136:2770–2775
Lue YH, Sinha Hikim AP, Swerdloff RS, Im P, Taing KS, Bui T, Leung A, Wang C (1999) Single exposure to heat induces stage-specific germ cell apoptosis in rats: role of intratesticular testosterone (T) on stage specificity. Endocrinology 140:1709–1717
Lue Y, Wang C, Liu YX, Hikim AP, Zhang XS, Ng CM, Hu ZY, Li YC, Leung A, Swerdloff RS (2006) Transient testicular warming enhances the suppressive effect of testosterone on spermatogenesis in adult cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:539–545
Jia Y, Sinha Hikim AP, Swerdloff RS, Lue YH, Vera Y, Zhang XS, Hu ZY, Li YC, Liu YX, Wang C (2007) Signaling pathways for germ cell death in adult cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) induced by mild testicular hyperthermia and exogenous testosterone treatment. Biol Reprod 77:83–92
Wang C, Cui YG, Wang XH, Jia Y, Sinha HA, Lue YH, Tong JS, Qian LX, Sha JH, Zhou ZM, Hull L, Leung A, Swerdloff RS (2007) Transient scrotal hyperthermia and levonorgestrel enhance testosterone-induced spermatogenesis suppression in men through increased germ cell apoptosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3292–3304
Sinha Hikim AP, Swerdloff RS (1993) Temporal and stage-specific changes in spermatogenesis of rat after gonadotropin deprivation by a potent gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist treatment. Endocrinology 133:2161–2170
Hashimoto Y, Suzuki H, Aiso S, Niikura T, Nishimoto I, Matsuoka M (2005) Involvement of tyrosine kinases and STAT3 in humanin-mediated neuroprotection. Life Sci 77:3092–3104
Hashimoto Y, Kurita M, Aiso S, Nishimoto I, Matsuoka M (2009) Humanin inhibits neuronal cell death by interacting with a cytokine receptor complex or complexes involving CNTF receptor α/WSX-1/gp130. Mol Biol Cell 20:2864–2873
Matsuoka M, Hashimoto Y (2010) Humanin and the receptors for humanin. Mol Neurobiol 41:22–28
Guo B, Zhai D, Cabezas E, Welsh K, Nouraini S, Satterthwait AC, Reed JC (2003) Humanin peptide suppresses apoptosis by interfering with Bax activation. Nature 423:456–461
Ikonen M, Liu B, Hashimoto Y, Ma L, Lee KW, Niikura T, Nishimoto I, Cohen P (2003) Interaction between the Alzheimer’s survival peptide humanin and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 regulates cell survival and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13042–13047
Terashita K, Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Tajima H, Yamagishi Y, Ishizaka M, Kawasumi M, Chiba T, Kanekura K, Yamada M, Nawa M, Kita Y, Aiso S, Nishimoto I (2003) Two serine residues distinctly regulate the rescue function of humanin, an inhibiting factor of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurotoxicity: functional potentiation by isomerization and dimerization. J Neurochem 85(6):1521–1538
Hashimoto Y, Terashita K, Niikura T, Yamagishi Y, Ishizaka M, Kanekura K, Chiba T, Yamada M, Kita Y, Aiso S, Matsuoka M, Nishimoto I (2004) Humanin antagonists: mutants that interfere with dimerization inhibit neuroprotection by humanin. Eur J Neurosci 19:2356–2364
Marcon L, Hales BF, Robaire B (2008) Reversibility of the effects of subchronic exposure to the cancer chemotherapeutics bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin on spermatogenesis, fertility, and progeny outcome in the male rat. J Andrology 29:4
Meistrich ML (2009) Male gonadal toxicity. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53:261–266
Lee SH, Shin CH (2013) Reduced male fertility in childhood cancer survivors. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 18(4):168–712. doi:10.6065/apem.2013.18.4.168
Watring WG, Byfield JE, Lagasse LD, Lee YD, Juillard G, Jacobs M, Smith ML (1974) Combination adriamycin and radiation therapy in gynecologic cancers. Gynecol Oncol 2(4):518–526
Gor PP, Su HI, Gray RJ, Gimotty PA, Horn M, Aplenc R, Vaughan WP, Tallman MS, Rebbeck TR, DeMichele A (2010) Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res 12:R26
Kunesová G, Hlavácek J, Patocka J, Evangelou A, Zikos C, Benaki D, Paravatou-Petsotas M, Pelecanou M, Livaniou E, Slaninova J (2008) The multiple T-maze in vivo testing of the neuroprotective effect of humanin analogues. Peptides 29:1982–1987
Miao J, Zhang W, Yin R, Liu R, Su C, Lei G, Li Z (2008) S14G HN ameliorates Abeta25–35-induced behavioral deficits by reducing neuroinflammatory responses and apoptosis in mice. Neuropeptides 42:557–567
Yamada M, Chiba T, Sasabe J, Terashita K, Aiso S, Matsuoka M (2008) Nasal colivelin treatment ameliorates memory impairment related to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmaco 33:2020–2032
Yamagishi Y, Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Nishimoto I (2003) Identification of essential amino acids in Humanin, a neuroprotective factor against Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults. Peptides 24(4):585–595
Erkkila K, Henriksen K, Hirvonen V, Rannikko S, Salo J, Parvinen M, Dunkel L (1997) Testosterone regulates apoptosis in adult human seminiferous tubules in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2314–2321
Jia Y, Castellanos J, Wang C, Sinha-Hikim I, Lue Y, Swerdloff RS, Sinha-Hikim AP (2009) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in male germ cell apoptosis in the rat. Biol Reprod 80:771–780
Sinha Hikim AP, Rajavashisth TB, Sinha Hikim I, Lue Y, Bonavera JJ, Leung A, Wang C, Swerdloff RS (1997) Significance of apoptosis in the temporal and stage-specific loss of germ cells in the adult rat after gonadotropin deprivation. Biol Reprod 57:1193–1201
Russell L (1977) Movement of spermatocytes from the basal to the adluminal compartment of the rat testes. Am J Anat 148:313–328
Delbes G, Vaisheva F, Luu T, Marcon L, Hales BF, Robaire B (2010) Reversibility of the effects of the chemotherapeutic regimen for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone, on the male rat reproductive system and progeny outcome. Reprod Toxicol 29:332–338
Dohle GR (2010) Male infertility in cancer patients: review of the literature. Int J Urol 17(4):327–331. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2010.02484.x
Trost LW, Brannigan RE (2012) Oncofertility and the male cancer patient. Curr Treat Options Oncol 13(2):146–160
Cai L, Hales BF, Robaire B (1997) Induction of apoptosis in the germ cells of adult male rats after exposure to cyclophosphamide. Biol Reprod 56(6):1490–1497
Kuliawat R, Klein L, Gong Z, Nicoletta-Gentile M, Nemkal A, Cui L, Bastie C, Su K, Huffman D, Surana M, Barzilai N, Fleischer N, Muzumdar R (2013) Potent humanin analog increases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through enhanced metabolism in the β cell. FASEB J 27(12):4890–4898. doi:10.1096/fj.13-231092 (Epub 2013 Aug 30)
Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Ito Y, Sudo H, Hata M, Arakawa E, Abe Y, Kita Y, Nishimoto I (2001) Detailed characterization of neuroprotection by a rescue factor humanin against various Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults. J Neurosci 21(23):9235–9245
Sponne I, Fifre A, Koziel V, Kriem B, Oster T, Pillot T (2004) Humanin rescues cortical neurons from prion-peptide-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 25(1):95–102
Zhai D, Luciano F, Zhu X, Guo B, Satterthwait AC, Reed JC (2005) Humanin binds and nullifies Bid activity by blocking its activation of Bax and Bak. J Biol Chem 280:15815–15824
Arakawa T, Kita Y, Niikura T (2008) A rescue factor for Alzheimer’s diseases: discovery, activity, structure, and mechanism. Curr Med Chem 15(21):2086–2098
Arakawa T, Niikura T, Kita Y (2011) The biological activity of humanin analogs correlates with structure stabilities in solution. Int J Biol Macromol 49(1):93–97. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.04.003
Yen K, Lee C, Mehta H, Cohen P (2013) The emerging role of the mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin in stress resistance. J Mol Endocrinol 50(1):R11–R19. doi:10.1530/JME-12-0203 Print 2013 Feb
Jia Y, Lee KW, Swerdloff R, Hwang D, Cobb LJ, Sinha Hikim A, Lue YH, Cohen P, Wang C (2010) Interaction of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and BAX in mitochondria promotes male germ cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem 285:1726–1732
Cohen P (2014) New role for the mitochondrial peptide humanin: protective agent against chemotherapy-induced side effects. J Natl Cancer Inst 106:dju006
Acknowledgments
This study supported by the Endocrinology, Metabolism and Nutrition training Grant (T32 DK007571) and UCLA Clinical and Translational Science Institute (UL1TR000124) at Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute and Harbor-UCLA Medical Center and Grants to P.C. (1R01AG034430, 1R01GM090311, P01AG034906 and 1R01ES020812). We thank Vince Atienza for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Ohanyan, A., Lue, YH. et al. The effects of humanin and its analogues on male germ cell apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic drugs. Apoptosis 20, 551–561 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1105-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1105-5