Abstract
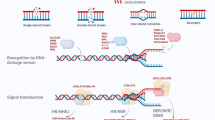
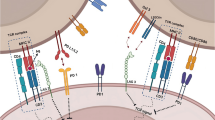
Innate immunity, which is the first line of host defense against invading microbial pathogens in multicellular organisms, occurs through germline-encoded pattern-recognition receptors. The Toll-like receptor/Interleukin (IL)-1 receptor (TLR/IL-1R) superfamily comprises proteins that contain the phylogenetically conserved Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain, which is responsible for the propagation of downstream signaling through recruitment of TIR domain containing cytosolic adaptor proteins such as MyD88, TIRAP/MAL, TRIF, TRAM and SARM. These interactions activate transcription factors that regulate the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α) and chemokines. Activation of the TLR/IL-1R signaling pathway promotes the onset of inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases and cancer; therefore, this pathway can be used for the development of therapeutic strategies against these types of pathogenesis. In this review paper, we illustrate the role of the TIR–TIR domain interaction with the TLR/IL-1R signaling pathway in inflammation and apoptosis and recent therapeutic drugs targeted to inhibit the downstream signaling cascade for treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonardi V, Cherkis K, Nishimura MT, Dangl JL (2012) A new eye on NLR proteins: focused on clarity or diffused by complexity? Curr Opin Immunol 24(1):41–50
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11(5):373–384
Eisenacher K, Krug A (2012) Regulation of RLR-mediated innate immune signaling – it is all about keeping the balance. Eur J Cell Biol 91(1):36–47
Kingeter LM, Lin X (2012) C-type lectin receptor-induced NF-κB activation in innate immune and inflammatory responses. Cell Mol Immunol 9(2):105–112
Werts C, Girardin SE, Philpott DJ (2006) TIR, CARD and PYRIN: three domains for an antimicrobial triad. Cell Death Diff 13(5):798–815
Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R (2002) Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 20:197–216
Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T (2001) Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nature Immunol 2(8):675–680
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptors signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4(7):499–511
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Medzhitov R (2009) Toll-like receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9(1):57–63
Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA (1996) The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86(6):973–983
Williams MJ, Rodriguez A, Kimbrell DA, Eldon ED (1997) The 18-wheeler mutation reveals complex anti-bacterial gene regulation in Drosophila host defense. EMBO J 16(20):6120–6130
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr (1997) A human homo-logue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 388:394–397
Kawai T, Akira S (2009) The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int Immunol 21(4):317–337
Beutler BA (2009) TLRs and innate immunity. Blood 113(7):1399–1407
Jin MS, Lee JO (2008) Structures of the Toll-like receptor family and its ligand complexes. Immunity 29(2):182–191
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R (2004) Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 5(10):987–995
Dai J, Liu B, Li Z (2009) Regulatory T cells and Toll-like receptors: what is the missing link? Int Immunopharmacol 9(5):528–533
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124(4):783–801
Miyake K (2007) Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger signals by cell surface Toll-like receptors. Semin Immunol 19(1):3–10
Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S (2009) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388(4):621–625
Kim YM, Brinkmann MM, Paquet ME, Ploegh HL (2008) UNC93B1 delivers nucleotide-sensing toll-like receptors to endolysosomes. Nature 452(7184):234–238
Bowie A, O’Neill LAJ (2000) The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal generators for pro-inflammatory interleukins and microbial products. J Leukoc Biol 67(4):508–514
Greenfeder SA, Nunes P, Kwee L, Labow M, Chizzonite RA, Ju G (1995) Molecular cloning and characterization of a second subunit of the interleukin 1 receptor complex. J Biol Chem 270(23):13757–13765
Gay N, Keith F (1991) Drosophila Toll and IL-1 receptor. Nature 351(6325):355–356
Dinarello CA (2009) Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol 27:519–550
Subramaniam S, Stansberg C, Cunningham C (2004) The interleukin 1 receptor family. Dev Comp Immunol 28(5):415–428
Heguy A, Baldari CT, Macchia G, Telford JL, Melli M (1992) Amino acids conserved in interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs) and the drosophila Toll protein are essential for IL-1R signal transduction. J Biol Chem 267(4):2605–2609
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA (2005) IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 23(5):479–490
Boraschi D, Tagliabue A (2006) The interleukin-1 receptor family. Vitam Horm 74:229–254
Burns K, Janssens S, Brissoni B, Olivos N, Beyaert R, Tschopp J (2003) Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4. J Exp Med 197(2):263–268
Lord KA, Hoffman-Liebermann B, Liebermann DA (1990) Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding MyD88, a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by IL6. Oncogene 5(7):1095–1097
Kawai T, Adachi O, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Unresponsiveness of MyD88-deficient mice to endotoxin. Immunity 11(1):115–122
Takeuchi O, Takeda K, Hoshino K, Adachi O, Ogawa T, Akira S (2000) Cellular responses to bacterial cell wall components are mediated through MyD88-dependent signaling cascades. Int Immunol 12(1):113–117
Hacker H, Vabulas RM, Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Akira S, Wagner H (2000) Immune cell activation by bacterial CpG-DNA through myeloid differentiation marker 88 and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6. J Exp Med 192(4):595–600
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor-5. Nature 410(6832):1099–1103
Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Sato S, Sanjo S, Hoshino K, Horiuchi T, Tomizawa H, Takeda K, Akira S (2002) Small antiviral compounds activate immune cells via TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 3(2):196–200
Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2001) TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2(9):835–841
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Sanjo H, Uematsu S, Kaisho T, Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kobayashi M, Fujita T, Takeda K, Akira S (2002) Essential role of TIRAP/Mal for activation of the signaling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature 420(6913):324–329
Horng T, Barton GM, Flavell RA, Medzhitov R (2002) The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signaling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 420(6913):329–333
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Takeuchi O, Sugiyama M, Okabe M, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 301(5633):640–643
Hoebe K, Du X, Georgel P, Janssen E, Tabeta K, Kim SO, Goode J, Lin P, Mann N, Mudd S, Crozat K, Sovath S, Han J, Beutler B (2003) Identification of Lps2 as a key transducer of MyD88-independnet TIR signaling. Nature 424(6950):743–748
Bin LH, Xu LG, Shu HB (2003) TIRP, a novel Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adapter protein involved in TIR signaling. J Biol Chem 278:24526–245312
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Uematsu S, Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Takeuchi O, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) TRAM is specifically involved in the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated MyD88-independent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 4(11):1144–1150
Fitzgerald KA, Rowe DC, Barnes BJ, Caffrey DR, Visintin A, Latz E, Monks B, Pitha PM, Golenbock DT (2003) LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-κB involves the Toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J Exp Med 198(7):1043–1055
Oshiumi H, Sasai M, Shida K, Fujita T, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2003) TIR-containing adapter molecule (TICAM)-2: a bridging adapter recruiting to Toll-like receptor 4 TICAM-1 that induces interferon-β. J Biol Chem 278(50):49751–49762
Mink M, Fogelgren B, Olszewski K, Maroy P, Csiszar K (2001) A novel human gene (SARM) at chromosome 17q11 encodes a protein with a SAM motif and structural similarity to Armadillo/β-catenin that is conserved in mouse, Drosophila and C. elegans. Genomics 74:234–244
O’Neill LAJ, Fitzgerald KA, Bowie AG (2003) The Toll-IL-1 receptor adaptor family grows to five members. Trends in Immunol 24(6):286–289
Carty M, Goodbody R, Schroder M, Stack J, Moynagh PN, Bowie AG (2006) The human adaptor SARM negatively regulates adaptor protein TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Immunol 7(10):1074–1081
Szretter KJ, Samuel MA, Gilfillan S, Fuchs A, Colonna M, Diamond MS (2009) The immune adaptor molecule SARM modulates tumor necrosis factor alpha production and microglia activation in the brainstem and restricts west Nile virus pathogenesis. J Virol 83(18):9329–9338
Radons J, Gabler S, Wesche H, Korherr C, Hofmeister R, Falk W (2002) Identification of essential regions in the cytoplasmic tail of interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein critical for interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 277(19):16456–16463
Xu Y, Tao X, Shen B, Horng T, Medzhitov R, Manley JL, Tong L (2000) Structural basis for signal transduction by the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domains. Nature 408(6808):111–115
Nyman T, Stenmark P, Flodin S, Johansson I, Hammarstrom M, Nordlund PR (2008) The crystal structure of the human Toll-like receptor 10 cytoplasmic domain reveals a putative signaling dimer. J Biol Chem 283(18):11861–11865
Burns K, Martinon F, Esslinger C, Pahl H, Schneider P, Bodmer JL, Marco FD, French L, Tschopp J (1998) MyD88, an adapter protein involved in interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 273(20):12203–12209
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Kopp E, Stadlen A, Chen C, Ghosh S, Janeway CA Jr (1998) MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol Cell 2(2):253–258
Khan JA, Brint EK, O’Neill LAJ, Tong L (2004) Crystal structure of the Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor domain of human IL-1RAPL. J Biol Chem 279:31664–31670
Ohnishi H, Tochio H, Kato Z, Orii KE, Li A, Kimura T, Hiroaki H, Kondo N, Shirakawa M (2009) Structural basis for the multiple interactions of the MyD88 TIR domain in TLR4 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(25):10260–10265
Valkov E, Stamp A, DiMaio F, Baker D, Verstak B, Roversi P, Kellie S, Sweet MJ, Mansell A, Gay NJ, Martin JL, Kobe B (2011) Crystal structure of Toll-like receptor adaptor MAL/TIRAP reveals the molecular basis for signal transduction and disease protection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(36):14879–14884
Jang TH, Park HH (2014) Crystal structure of TIR domain of TLR6 reveals novel dimeric interface of TIR-TIR interaction for Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J Mol Biol. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2014.07.024
Zhou K, Kanai R, Lee P, Wang HW, Modis Y (2012) Toll-like receptor 5 forms asymmetric dimers in the absence of flagellin. J Struct Biol 177(2):402–409
Lin Z, Lu J, Zhou W, Shen Y (2012) Structural insignts into TIR domain specificity of the bridging adaptor Mal in TLR4 signaling. PLoS One 7(4):e34202
Loiarro M, Gallo G, Fanto N, Santis RD, Carminati P, Ruggiero V, Sette C (2009) Identification of critical residues of the MyD88 death domain involved in the recruitment of downstream kinases. J Biol Chem 284(41):28093–28103
Deng L, Wang C, Spencer E, Yang L, Braun A, You J, Slaughter C, Pickart C, Chen ZJ (2000) Activation of the IκB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell 103(2):351–361
Kanayama A, Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Hong M, Shaito A, Chiu YH, Deng L, Chen ZJ (2004) TAB 2 and TAB 3 activate the NF-κB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains. Mol Cell 15(4):535–548
Carmody RJ, Chen YH (2007) Nuclear factor-κB: activation and regulation during Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 4(1):31–41
Yao J, Tae WK, Qin J, Jiang Z, Qian Y, Xiao H, Lu Y, Qian W, Gulen MF, Sizemore N, DiDonato J, Sato S, Akira S, Su B, Li X (2007) Interleukin-1 (IL-1)-induced TAK1-dependent versus MEKK3-dependent NF κB activation pathways bifurcate at IL-1 receptor-associated kinase modification. J Biol Chem 282(9):6075–6089
Sanz L, Diaz-Meco MT, Nakano H, Moscat J (2000) The atypical PKC-interacting protein p62 channels NF-κB activation by the IL-1-TRAF6 pathway. EMBO J 19(7):1576–1586
Karin M, Liu ZG, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9(2):240–246
Shaulian E, Karin M (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat Cell Biol 4(5):E131–E136
Kawai T, Akira S (2006) TLR signalling. Cell death Differ 13(5):816–825
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):537–549
Kim JY, Beg AA, Haura EB (2013) Non-canonical IKKs, IKKε and TBK1, as novel therapeutic targets in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(10):1109–1112
Doyle SE, Vaidya SA, O’Connell R, Dadgostar H, Dempsey PW, Wu T, Rao G, Sun R, Haberland M, Modlin R, Cheng G (2002) IRF3 mediates a TLR3/TLR4-specific antiviral gene program. Immunity 17(3):251–263
Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Iwabe T, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2002) Differential involvement of IFN-β in Toll-like receptor-stimulated dendritic cell activation. Int Immunol 14(10):1225–1231
Toshchakov V, Jones BW, Perera PY, Thomas K, Cody MJ, Zhang S, Williams BR, Major J, Hamilton TA, Fenton MJ, Vogel SN (2002) TLR4, but not TLR2, mediates IFN-β-induced STAT1α/β-dependent gene expression in macrophages. Nat Immunol 3(4):392–398
Kumar H, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2013) Toll-like receptors. In: Lennarz WJ, Lane MD (eds) Encyclopedia of biological chemistry, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 396–401
Salaun B, Romero P, Lebecque S (2007) Toll-like receptors’ two-edged sword: when immunity meets apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 37(12):3311–3318
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2(10):725–734
Schmidt C (2006) Immune system’s Toll-like receptors have good opportunity for cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(9):574–575
O’Neill LAJ (2006) Targeting signal transduction as a strategy to treat inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Disc 5(7):549–563
Li F, Thiele I, Jamshidi N, Palsson BO (2009) Identification of potential pathway mediation targets in Toll-like receptor signaling. PLoS Comp Biol 5(2):e1000292
Von Bernuth H, Picard C, Jin Z et al (2008) Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with MyD88 deficiency. Science 321(5889):691–696
Ku CL, von Bernuth H, Picard C et al (2007) Selective predisposition to bacterial infections in IRAK-4-deficient children: IRAK-4-dependent TLRs are otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med 204(10):2407–2422
Marsh BJ, Stenzel-Poore MP (2008) Toll-like receptors: novel pharmacological targets for the treatment of neurological diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8(1):8–13
O’Neill LAJ, Bryant CE, Doyle SL (2009) Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol Rev 61(2):177–197
Pedras-Vasconcelos J, Puig M, Verthelyi D (2009) TLRs as therapeutic targets in CNS inflammation and infection. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 1:476–487
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282(5396):2085–2088
Li C, Zienkiewicz J, Hawiger J (2005) Interactive sites in the Myd88 Toll/interleukin (IL) 1 receptor domain responsible for coupling to the IL1β signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 280:26152–26159
Toshchakov VV, Szmacinski H, Couture LA, Lakowicz JR, Vogel SN (2011) Targeting TLR4 signaling by TLR4 TIR-derived decoy peptides: identification of the TLR4 TIR dimerization interface. J Immunol 186(8):4819–4827
Loiarro M, Sette C, Gallo G, Ciacci A, Fanto N, Mastroianni D, Carminati P, Ruggiero V (2005) Peptide-mediated interference of TIR domain dimerization in MyD88 inhibits interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-κB. J Biol Chem 280(16):15809–15814
Liu Y, Yuan Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Xiao G, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Fan J (2009) Interacting neuro-endocrine, innate, and acquired immune pathways regulate neutrophil mobilization from bone marrow following hemorrhagic shock. J Immunol 182(1):572–580
Ahmad R, Sylvester J, Zafarullah M (2007) MyD88, IRAK1 and TRAF6 knockdown in human chondrocytes inhibits interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression and promoter activity by impairing MAP kinase activation. Cell Signal 19(12):2549–2557
Uto T, Wang X, Sato K, Haraguchi M, Akagi T, Akashi M, Baba M (2007) Targeting of antigen to dendritic cells with poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanoparticles induces antigen-specific humoral and cellular immunity. J Immunol 178(5):2979–2986
Toshchakov VY, Fenton MJ, Vogel SN (2007) Cutting edge: differential inhibition of TLR signaling pathways by cell-permeable peptides representing BB loops of TLRs. J Immunol 178(5):2655–2660
Toshchakov VU, Basu S, Fenton MJ, Vogel SN (2005) Differential involvement of BB loops of Toll-IL-1 resistance (TIR) domain-containing adapter proteins in TLR4- versus TLR2-mediated signal transduction. J Immunol 175(1):494–500
Bartfai T, Behrens MM, Gaidarova S, Pemberton J, Shivanyuk A, Rebek J Jr (2003) A low molecular weight mimic of the Toll/IL-1 receptor/resistance domain inhibits IL-1 receptor-mediated responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(13):7971–7976
Cao Z, Hu Y, Wu W, Ha T, Kelley J, Deng C, Chen Q, Li C, Li J, Li Y (2009) The TIR/BB-loop mimetic AS-1 protects the myocardium from ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res 84(3):442–451
Davis CN, Mann E, Behrens MM, Gaidarova S, Rebek M, Rebek J Jr, Bartfai T (2006) MyD88-dependent and –independent signaling by Il-1 in neurons probed by bifunctional Toll/IL-1 receptor domain/BB-loop mimetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2953–2958
Fanto N, Gallo G, Ciacci A, Semproni M, Vignola D, Quaglia M, Bombardi V, Mastroianni D, Zibella MP, Basile G, Sassano M, Ruggiero V, De Santis R, Carminati P (2008) Design, synthesis, and in vitro activity of peptidomimetic inhibitors of myeloid differentiation factor 88. J Med Chem 51(5):1189–1202
Loiarro M, Capolunghi F, Fanto N, Gallo G, Campo S, Arseni B, Carsetti R, Carminati P, De Santis R, Ruggiero V, Sette C (2007) Pivotal advance: inhibition of Myd88 dimerization and recruitment of IRAK1 and IRAK4 by a novel peptidomimetic compound. J Leukoc Biol 82(4):801–810
Travis S, Yap LM, Hawkey C, Warren B, Lazarov M, Fong T, Tesi RJ (2005) RDP58 is a novel and potentially effective oral therapy for ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11(8):713–719
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26(4):239–257
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357:539–545
Thorburn A (2004) Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 16(2):139–144
Kaiser WJ, Offermann MK (2005) Apoptosis induced by the Toll-like receptor adaptor TRIF is dependent on its receptor interacting protein homotypic interaction motif. J Immunol 174(8):4942–4952
Fekonja O, Avbelj M, Jerala R (2012) Suppression of TLR signaling by targeting TIR domain-containing proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 13(8):776–788
Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Weiss DS, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A (2000) The apoptotic signaling pathway activated by Toll-like receptor-2. EMBO J 19(13):3325–3336
Colomar A, Marty V, Medina C, Combe C, Parnet P, Amedee T (2003) Maturation and release of interleukin-1β by lipopolysaccharide-primed mouse Schwann cells require the stimulation of P2X7 receptors. J Biol Chem 278(33):30732–30740
Barshes NR, Wyllie S, Goss JA (2005) Inflammation-mediated dysfunction and apoptosis in pancreatic islet transplantation: implications for intrahepatic grafts. J Leukoc Biol 77(5):587–597
Sjoholm A (1998) Aspects of the involvement of interleukin-1 and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Cell Death Differ 5(6):461–468
Rothwell N, Allan S, Toulmond S (1997) The role of interleukin 1 in acute neurodegeneration and stroke: pathophysiolocial and therapeutic implications. J Clin Invest 100(11):2648–2652
Shaulian E, Karin M (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20(19):2390–2400
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012R1A2A2A01010870).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, K.B., Park, H.H. Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-mediated cellular signaling pathways. Apoptosis 20, 196–209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1073-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1073-1