Abstract
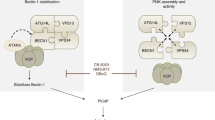
DAP-kinase (DAPK) is a Ca2+-calmodulin regulated kinase with various, diverse cellular activities, including regulation of apoptosis and caspase-independent death programs, cytoskeletal dynamics, and immune functions. Recently, DAPK has also been shown to be a critical regulator of autophagy, a catabolic process whereby the cell consumes cytoplasmic contents and organelles within specialized vesicles, called autophagosomes. Here we present the latest findings demonstrating how DAPK modulates autophagy. DAPK positively contributes to the induction stage of autophagosome nucleation by modulating the Vps34 class III phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase complex by two independent mechanisms. The first involves a kinase cascade in which DAPK phosphorylates protein kinase D, which then phosphorylates and activates Vps34. In the second mechanism, DAPK directly phosphorylates Beclin 1, a necessary component of the Vps34 complex, thereby releasing it from its inhibitor, Bcl-2. In addition to these established pathways, we will discuss additional connections between DAPK and autophagy and potential mechanisms that still remain to be fully validated. These include myosin-dependent trafficking of Atg9-containing vesicles to the sites of autophagosome formation, membrane fusion events that contribute to expansion of the autophagosome membrane and maturation through the endocytic pathway, and trafficking to the lysosome on microtubules. Finally, we discuss how DAPK's participation in the autophagic process may be related to its function as a tumor suppressor protein, and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A (1995) Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev 9(1):15–30
Bialik S, Kimchi A (2006) The death-associated protein kinases: structure, function and beyond. Annu Rev Biochem 75:189–210
Inbal B, Bialik S, Sabanay I, Shani G, Kimchi A (2002) DAP kinase and DRP-1 mediate membrane blebbing and the formation of autophagic vesicles during programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 157(3):455–468
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Kimchi A (2011) PKD is a kinase of Vps34 that mediates ROS-induced autophagy downstream of DAPk. Cell Death Differ 19(5):788–797
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Mizrachy L, Idelchuk Y, Koren I, Eisenstein M, Sabanay H, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Kimchi A (2009) DAP-kinase-mediated phosphorylation on the BH3 domain of Beclin 1 promotes dissociation of Beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and induction of autophagy. EMBO Rep 10(3):285–292. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.246
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ (2010) Mammalian autophagy: core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22(2):124–131
Mizushima N, Levine B (2010) Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):823–830
Qu X, Zou Z, Sun Q, Luby-Phelps K, Cheng P, Hogan R, Gilpin C, Levine B (2007) Autophagy gene-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells during embryonic development. Cell 128(5):931–946
Al Rawi S, Louvet-Vall S, Djeddi A, Sachse M, Culetto E, Hajjar C, Boyd L, Legouis R, Galy V (2011) Postfertilization autophagy of sperm organelles prevents paternal mitochondrial DNA transmission. Science 334(6059):1144–1147. doi:10.1126/science.1211878
Mizushima N, Komatsu M (2011) Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 147(4):728–741
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P, Levine B (2012) Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(9):709–730. doi:10.1038/nrd3802
Rubinstein AD, Kimchi A (2012) Life in the balance—a mechanistic view of the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 22):5259–5268. doi:10.1242/jcs.115865
Basit F, Cristofanon S, Fulda S (2013) Obatoclax (GX15-070) triggers necroptosis by promoting the assembly of the necrosome on autophagosomal membranes. Cell Death Differ 20(9):1161–1173. doi:10.1038/cdd.2013.45
Denton D, Nicolson S, Kumar S (2012) Cell death by autophagy: facts and apparent artefacts. Cell Death Differ 19(1):87–95. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.146
Weidberg H, Shvets E, Elazar Z (2011) Biogenesis and cargo selectivity of autophagosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 80:125–156. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-052709-094552
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM, Kim DH (2010) mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett 584(7):1287–1295. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.017
Jewell JL, Russell RC, Guan KL (2013) Amino acid signalling upstream of mTOR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14(3):133–139. doi:10.1038/nrm3522
Bar-Peled L, Chantranupong L, Cherniack AD, Chen WW, Ottina KA, Grabiner BC, Spear ED, Carter SL, Meyerson M, Sabatini DM (2013) A tumor suppressor complex with GAP activity for the Rag GTPases that signal amino acid sufficiency to mTORC1. Science 340(6136):1100–1106. doi:10.1126/science.1232044
Alers S, Loffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B (2012) Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 32(1):2–11. doi:10.1128/MCB.06159-11
Lamb CA, Dooley HC, Tooze SA (2013) Endocytosis and autophagy: shared machinery for degradation. BioEssays 35(1):34–45. doi:10.1002/bies.201200130
Tooze SA, Yoshimori T (2010) The origin of the autophagosomal membrane. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):831–835. doi:10.1038/ncb0910-831
Moreau K, Renna M, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Connections between SNAREs and autophagy. Trends Biochem Sci 38(2):57–63. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2012.11.004
Zavodszky E, Vicinanza M, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Biology and trafficking of ATG9 and ATG16L1, two proteins that regulate autophagosome formation. FEBS Lett 587(13):1988–1996. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.04.025
Russell RC, Tian Y, Yuan H, Park HW, Chang YY, Kim J, Kim H, Neufeld TP, Dillin A, Guan KL (2013) ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase. Nat Cell Biol 15(7):741–750. doi:10.1038/ncb2757
Wong PM, Puente C, Ganley IG, Jiang X (2013) The ULK1 complex: sensing nutrient signals for autophagy activation. Autophagy 9(2):124–137. doi:10.4161/auto.23323
Di Bartolomeo S, Corazzari M, Nazio F, Oliverio S, Lisi G, Antonioli M, Pagliarini V, Matteoni S, Fuoco C, Giunta L, D’Amelio M, Nardacci R, Romagnoli A, Piacentini M, Cecconi F, Fimia GM (2010) The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy. J Cell Biol 191(1):155–168. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002100
Young A, Chan E, Hu X, Kochl R, Crawshaw S, High S, Hailey D, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Tooze S (2006) Starvation and ULK1-dependent cycling of mammalian Atg9 between the TGN and endosomes. J Cell Sci 119(18):3888–3900
Tang HW, Wang YB, Wang SL, Wu MH, Lin SY, Chen GC (2011) Atg1-mediated myosin II activation regulates autophagosome formation during starvation-induced autophagy. EMBO J 30(4):636–651. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.338
Longatti A, Tooze SA (2009) Vesicular trafficking and autophagosome formation. Cell Death Differ 16(7):956–965. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.39
Bento CF, Puri C, Moreau K, Rubinsztein DC (2013) The role of membrane-trafficking small GTPases in the regulation of autophagy. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 5):1059–1069. doi:10.1242/jcs.123075
Orsi A, Polson HE, Tooze SA (2010) Membrane trafficking events that partake in autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22(2):150–156. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.11.013
Shani G, Marash L, Gozuacik D, Bialik S, Teitelbaum L, Shohat G, Kimchi A (2004) Death-associated protein kinase phosphorylates ZIP kinase, forming a unique kinase hierarchy to activate its cell death functions. Mol Cell Biol 24(19):8611–8626
Cohen O, Feinstein E, Kimchi A (1997) DAP-kinase is a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase, with cell death-inducing functions that depend on its catalytic activity. EMBO J 16(5):998–1008
Shohat G, Spivak-Kroizman T, Cohen O, Bialik S, Shani G, Berrisi H, Eisenstein M, Kimchi A (2001) The pro-apoptotic function of death-associated protein kinase is controlled by a unique inhibitory autophosphorylation-based mechanism. J Biol Chem 276(50):47460–47467
Gozuacik D, Bialik S, Raveh T, Mitou G, Shohat G, Sabanay H, Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Kimchi A (2008) DAP-kinase is a mediator of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase activation and autophagic cell death. Cell Death Differ 15(12):1875–1886. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.121
Guenebeaud C, Goldschneider D, Castets M, Guix C, Chazot G, Delloye-Bourgeois C, Eisenberg-Lerner A, Shohat G, Zhang M, Laudet V, Kimchi A, Bernet A, Mehlen P (2010) The dependence receptor UNC5H2/B triggers apoptosis via PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of DAP kinase. Mol Cell 40(6):863–876. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.11.021
Widau RC, Jin Y, Dixon SA, Wadzinski BE, Gallagher PJ (2010) Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) holoenzymes regulate death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) in ceramide-induced anoikis. J Biol Chem 285(18):13827–13838. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.085076
Carlessi R, Levin-Salomon V, Ciprut S, Bialik S, Berissi H, Albeck S, Peleg Y, Kimchi A (2011) GTP binding to the ROC domain of DAP-kinase regulates its function through intramolecular signalling. EMBO Rep 12(9):917–923
Shiloh R, Bialik S, Kimchi A (2013) The DAPK family: a structure-function analysis. Apoptosis. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0924-5
Shiloh R, Kimchi A (2013) The DAP-Kinase interactome. Apoptosis. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0926-3
Ling YH, Aracil M, Zou Y, Yuan Z, Lu B, Jimeno J, Cuervo AM, Perez-Soler R (2011) PM02734 (elisidepsin) induces caspase-independent cell death associated with features of autophagy, inhibition of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, and activation of death-associated protein kinase. Clin Cancer Res 17(16):5353–5366. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1948
Gandesiri M, Chakilam S, Ivanovska J, Benderska N, Ocker M, Di Fazio P, Feoktistova M, Gali-Muhtasib H, Rave-Frank M, Prante O, Christiansen H, Leverkus M, Hartmann A, Schneider-Stock R (2012) DAPK plays an important role in panobinostat-induced autophagy and commits cells to apoptosis under autophagy deficient conditions. Apoptosis 17(12):1300–1315. doi:10.1007/s10495-012-0757-7
Zhang H, Chen GG, Zhang Z, Chun S, Leung BC, Lai PB (2012) Induction of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by SB203580 requires activation of AMPK and DAPK but not p38 MAPK. Apoptosis 17(4):325–334. doi:10.1007/s10495-011-0685-y
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R, Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD, Levine B (2005) Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 122(6):927–939
Tang D, Kang R, Livesey KM, Cheh CW, Farkas A, Loughran P, Hoppe G, Bianchi ME, Tracey KJ, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT (2010) Endogenous HMGB1 regulates autophagy. J Cell Biol 190(5):881–892. doi:10.1083/jcb.200911078
Shi CS, Kehrl JH (2010) TRAF6 and A20 regulate lysine 63-linked ubiquitination of Beclin-1 to control TLR4-induced autophagy. Sci Signal 3(123):ra42. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000751
Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Carpentier S, Levade T, Levine B, Codogno P (2009) Role of JNK1-dependent Bcl-2 phosphorylation in ceramide-induced macroautophagy. J Biol Chem 284(5):2719–2728. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805920200
Wei Y, Pattingre S, Sinha S, Bassik M, Levine B (2008) JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 regulates starvation-induced autophagy. Mol Cell 30:678–688
Zalckvar E, Berissi H, Eisenstein M, Kimchi A (2009) Phosphorylation of Beclin 1 by DAP-kinase promotes autophagy by weakening its interactions with Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L). Autophagy 5(5):720–722
Gurkar AU, Chu K, Raj L, Bouley R, Lee SH, Kim YB, Dunn SE, Mandinova A, Lee SW (2013) Identification of ROCK1 kinase as a critical regulator of Beclin 1-mediated autophagy during metabolic stress. Nat Commun 4:2189. doi:10.1038/ncomms3189
Hagerty L, Weitzel DH, Chambers J, Fortner CN, Brush MH, Loiselle D, Hosoya H, Haystead TA (2007) ROCK1 phosphorylates and activates zipper-interacting protein kinase. J Biol Chem 282(7):4884–4893. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609990200
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Kimchi A (2007) DAP-kinase regulates JNK signaling by binding and activating protein kinase D under oxidative stress. Cell Death Differ 14:1908–1915
Bialik S, Bresnick AR, Kimchi A (2004) DAP-kinase-mediated morphological changes are localization dependent and involve myosin-II phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ 11(6):631–644
Stevens C, Lin Y, Harrison B, Burch L, Ridgway RA, Sansom O, Hupp T (2009) Peptide combinatorial libraries identify TSC2 as a death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) death domain-binding protein and reveal a stimulatory role for DAPK in mTORC1 signaling. J Biol Chem 284(1):334–344. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805165200
Kuo JC, Lin JR, Staddon JM, Hosoya H, Chen RH (2003) Uncoordinated regulation of stress fibers and focal adhesions by DAP kinase. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 23):4777–4790
Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Yao CC, Chen RH (2002) DAP-kinase induces apoptosis by suppressing integrin activity and disrupting matrix survival signals. J Cell Biol 159(1):169–179
Kuo J, Wang W, Yao C, Wu P, Chen R (2006) The tumor suppressor DAPK inhibits cell motility by blocking the integrin-mediated polarity pathway. J Cell Biol 172(4):619–631
Bialik S, Pietrokovski S, Kimchi A (2011) Myosin drives autophagy in a pathway linking Atg1 to Atg9. EMBO J 30(4):629–630. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.8
Graves PR, Winkfield KM, Haystead TA (2005) Regulation of zipper-interacting protein kinase activity in vitro and in vivo by multisite phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 280(10):9363–9374
Wu PR, Tsai PI, Chen GC, Chou HJ, Huang YP, Chen YH, Lin MY, Kimchi A, Chien CT, Chen RH (2011) DAPK activates MARK1/2 to regulate microtubule assembly, neuronal differentiation, and tau toxicity. Cell Death Differ 18(9):1507–1520. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.2
Drewes G, Ebneth A, Mandelkow EM (1998) MAPs, MARKs and microtubule dynamics. Trends Biochem Sci 23(8):307–311
Harrison B, Kraus M, Burch L, Stevens C, Craig A, Gordon-Weeks P, Hupp T (2008) DAPK-1 binding to a linear peptide motif in MAP1B stimulates autophagy and membrane blebbing. J Biol Chem 283:9999–10014
Yue Z (2007) Regulation of neuronal autophagy in axon: implication of autophagy in axonal function and dysfunction/degeneration. Autophagy 3(2):139–141
Wang QJ, Ding Y, Kohtz DS, Mizushima N, Cristea IM, Rout MP, Chait BT, Zhong Y, Heintz N, Yue Z (2006) Induction of autophagy in axonal dystrophy and degeneration. J Neurosci 26(31):8057–8068. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2261-06.2006
Capoccia BJ, Jin RU, Kong YY, Peek RM Jr, Fassan M, Rugge M, Mills JC (2013) The ubiquitin ligase Mindbomb 1 coordinates gastrointestinal secretory cell maturation. J Clin Invest 123(4):1475–1491. doi:10.1172/JCI65703
Pelkmans L, Fava E, Grabner H, Hannus M, Habermann B, Krausz E, Zerial M (2005) Genome-wide analysis of human kinases in clathrin- and caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis. Nature 436(7047):78–86. doi:10.1038/nature03571
Tian JH, Das S, Sheng ZH (2003) Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of syntaxin-1A by the death-associated protein (DAP) kinase regulates its interaction with Munc18. J Biol Chem 278(28):26265–26274
Lorin S, Hamai A, Mehrpour M, Codogno P (2013) Autophagy regulation and its role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2013.06.007
Degenhardt K, Mathew R, Beaudoin B, Bray K, Anderson D, Chen G, Mukherjee C, Shi Y, Gelinas C, Fan Y, Nelson DA, Jin S, White E (2006) Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 10:51–64
Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O, Chen G, Mathew R, Jin S, White E (2007) Autophagy mitigates metabolic stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 21(13):1621–1635
Mathew R, Kongara S, Beaudoin B, Karp C, Bray K, Degenhardt K, Chen G, Jin S, White E (2007) Autophagy suppresses tumor progression by limiting chromosomal instability. Genes Dev 21(11):1367–1381
Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N, Chen G, Chen HY, Bray K, Reddy A, Bhanot G, Gelinas C, Dipaola RS, Karantza-Wadsworth V, White E (2009) Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62. Cell 137(6):1062–1075. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.048
White E, Karp C, Strohecker AM, Guo Y, Mathew R (2010) Role of autophagy in suppression of inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22(2):212–217. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.008
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K, Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H, Levine B (1999) Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by Beclin 1. Nature 402(6762):672–676
Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh H, Troxel A, Rosen J, Eskelinen E, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Cattoretti G, Levine B (2003) Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the Beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest 112(12):1809–1820
Bialik S, Kimchi A (2008) Autophagy and tumor suppression: recent advances in understanding the link between autophagic cell death pathways and tumor development. Adv Exp Med Biol 615:177–200
Liu J, Xia H, Kim M, Xu L, Li Y, Zhang L, Cai Y, Norberg HV, Zhang T, Furuya T, Jin M, Zhu Z, Wang H, Yu J, Li Y, Hao Y, Choi A, Ke H, Ma D, Yuan J (2011) Beclin1 controls the levels of p53 by regulating the deubiquitination activity of USP10 and USP13. Cell 147(1):223–234. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.037
Raveh T, Droguett G, Horwitz MS, DePinho RA, Kimchi A (2001) DAP kinase activates a p19ARF/p53-mediated apoptotic checkpoint to suppress oncogenic transformation. Nat Cell Biol 3(1):1–7
Inbal B, Cohen O, Polak-Charcon S, Kopolovic J, Vadai E, Eisenbach L, Kimchi A (1997) DAP kinase links the control of apoptosis to metastasis. Nature 390(6656):180–184
Mor I, Carlessi R, Ast T, Feinstein E, Kimchi A (2011) Death-associated protein kinase increases glycolytic rate through binding and activation of pyruvate kinase. Oncogene 31(6):683–693. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.264
Li Y, Grupe A, Rowland C, Nowotny P, Kauwe JSK, Smemo S, Hinrichs A, Tacey K, Toombs TA, Kwok S, Catanese J, White TJ, Maxwell TJ, Hollingworth P, Abraham R, Rubinsztein DC, Brayne C, Wavrant-De Vrieze F, Hardy J, O’Donovan M, Lovestone S, Morris JC, Thal LJ, Owen M, Williams J, Goate A (2006) DAPK1 variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease and allele-specific expression. Human Mol Gen 15(17):2560–2568. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl178.
Henshall DC, Schindler CK, So NK, Lan JQ, Meller R, Simon RP (2004) Death-associated protein kinase expression in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann Neurol 55(4):485–494
Velentza AV, Wainwright MS, Zasadzki M, Mirzoeva S, Schumacher AM, Haiech J, Focia PJ, Egli M, Watterson DM (2003) An aminopyridazine-based inhibitor of a pro-apoptotic protein kinase attenuates hypoxia-ischemia induced acute brain injury. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13(20):3465–3470
Pelled D, Raveh T, Riebeling C, Fridkin M, Berissi H, Futerman AH, Kimchi A (2002) Death-associated protein (DAP) kinase plays a central role in ceramide-induced apoptosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 277(3):1957–1961
Schori H, Yoles E, Wheeler LA, Raveh T, Kimchi A, Schwartz M (2002) Immune-related mechanisms participating in resistance and susceptibility to glutamate toxicity. Eur J Neurosci 16(4):557–564
Tu W, Xu X, Peng L, Zhong X, Zhang W, Soundarapandian MM, Belal C, Wang M, Jia N, Zhang W, Lew F, Chan SL, Chen Y, Lu Y (2010) DAPK1 Interaction with NMDA Receptor NR2B Subunits Mediates Brain Damage in Stroke. Cell 140(2):222–234
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the Flight Attendants Medical Research Institute (FAMRI) and the European Research Council (ERC) FP7. AK is the incumbent of the Helena Rubinstein Chair of Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levin-Salomon, V., Bialik, S. & Kimchi, A. DAP-kinase and autophagy. Apoptosis 19, 346–356 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0918-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0918-3