Abstract
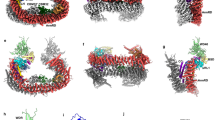
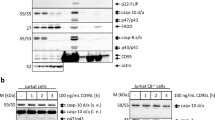
ARTS (Sept4_i2), is a pro-apoptotic protein localized at the mitochondria of living cells. In response to apoptotic signals, ARTS rapidly translocates to the cytosol where it binds and antagonizes XIAP to promote caspase activation. However, the mechanism of interaction between these two proteins and how it is regulated remained to be explored. In this study, we show that ARTS and XIAP bind directly to each other, as recombinant ARTS and XIAP proteins co-immunoprecipitate together. We also show that over expression of ARTS alone is sufficient to induce a strong down-regulation of XIAP protein levels and that this reduction occurs through the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS). Using various deletion and mutation constructs of XIAP we show that ARTS specifically binds to the BIR3 domain in XIAP. Moreover, we found that ARTS binds to different sequences in BIR3 than other IAP antagonists such as SMAC/Diablo. Computational analysis comparing the location of the putative ARTS interface in BIR3 with the known interfaces of SMAC/Diablo and caspase 9 support our results indicating that ARTS interacts with residues in BIR3 that are different from those involved in binding SMAC/Diablo and caspase 9. We therefore suggest that ARTS binds and antagonizes XIAP in a way which is distinct from other IAP-antagonists to promote apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267(5203):1456–1462
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281(5381):1309–1312
Nicholson DW (1999) Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 6(11):1028–1042. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400598
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281(5381):1312–1316
Yuan JY, Shaham S, Ledoux S, Ellis HM, Horvitz HR (1993) The C-elegans cell-death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1-beta-converting enzyme. Cell 75(4):641–652
Xue D, Shaham S, Horvitz HR (1996) The Caenorhabditis elegans cell-death protein CED-3 is a cysteine protease with substrate specificities similar to those of the human CPP32 protease. Genes Dev 10(9):1073–1083
Degterev A, Boyce M, Yuan J (2003) A decade of caspases. Oncogene 22(53):8543–8567. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207107
Shi Y (2002) Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9(3):459–470
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1999) Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J 18(19):5242–5251. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.19.5242
Roy N, Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1997) The c-IAP-1 and c-IAP-2 proteins are direct inhibitors of specific caspases. EMBO J 16(23):6914–6925. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.23.6914
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(6):401–410. doi:10.1038/nrm830]
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13(3):239–252
Takahashi R, Deveraux Q, Tamm I, Welsh K, Assa-Munt N, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1998) A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J Biol Chem 273(14):7787–7790
Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD (2008) IAPs: what’s in a name? Mol Cell 30(2):123–135. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.008
Hu S, Yang X (2003) Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2 are ubiquitin ligases for the apoptosis inducer Smac/DIABLO. J Biol Chem 278(12):10055–10060. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207197200
Schile AJ, Garcia-Fernandez M, Steller H (2008) Regulation of apoptosis by XIAP ubiquitin-ligase activity. Genes Dev 22(16):2256–2266. doi:10.1101/gad.1663108
Yang YL, Li XM (2000) The IAP family: endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities. Cell Res 10(3):169–177. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290046
Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG (2003) The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene 22(53):8568–8580. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207101
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1997) X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature 388(6639):300–304. doi:10.1038/40901
Sun C, Cai M, Meadows RP, Xu N, Gunasekera AH, Herrmann J, Wu JC, Fesik SW (2000) NMR structure and mutagenesis of the third Bir domain of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP. J Biol Chem 275(43):33777–33781. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006226200
Chai J, Shiozaki E, Srinivasula SM, Wu Q, Datta P, Alnemri ES, Shi Y (2001) Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell 104(5):769–780
Riedl SJ, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R, Zhou Q, Sun C, Fesik SW, Liddington RC, Salvesen GS (2001) Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell 104(5):791–800
Shiozaki EN, Chai J, Rigotti DJ, Riedl SJ, Li P, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Fairman R, Shi Y (2003) Mechanism of XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol Cell 11(2):519–527
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, Datta P, Shiozaki E, Chai J, Lee RA, Robbins PD, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Shi Y, Alnemri ES (2001) A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature 410(6824):112–116. doi:10.1038/35065125
Albeck JG, Burke JM, Spencer SL, Lauffenburger DA, Sorger PK (2008) Modeling a snap-action, variable-delay switch controlling extrinsic cell death. PLoS Biol 6(12):2831–2852. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060299
Hao Z, Mak TW (2009) Type I and type II pathways of fas-mediated apoptosis are differentially controlled by XIAP. J Mol Cell Biol 2(2):63–64. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjp034
Jost PJ, Grabow S, Gray D, McKenzie MD, Nachbur U, Huang DC, Bouillet P, Thomas HE, Borner C, Silke J, Strasser A, Kaufmann T (2009) XIAP discriminates between type I and type II FAS-induced apoptosis. Nature 460(7258):1035–1039. doi:10.1038/nature08229
Broemer M, Meier P (2009) Ubiquitin-mediated regulation of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 19(3):130–140. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.01.004
Potts PR, Singh S, Knezek M, Thompson CB, Deshmukh M (2003) Critical function of endogenous XIAP in regulating caspase activation during sympathetic neuronal apoptosis. J Cell Biol 163(4):789–799. doi:10.1083/jcb.200307130
Goyal L, McCall K, Agapite J, Hartwieg E, Steller H (2000) Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J 19(4):589–597. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.4.589
Ryoo HD, Bergmann A, Gonen H, Ciechanover A, Steller H (2002) Regulation of Drosophila IAP1 degradation and apoptosis by reaper and ubcD1. Nat Cell Biol 4(6):432–438. doi:10.1038/ncb795
Steller H (2008) Regulation of apoptosis in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 15(7):1132–1138. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.50
Galban S, Duckett CS (2010) XIAP as a ubiquitin ligase in cellular signaling. Cell Death Differ 17(1):54–60. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.81
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X (2000) Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102(1):33–42
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL (2000) Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102(1):43–53
Suzuki Y, Imai Y, Nakayama H, Takahashi K, Takio K, Takahashi R (2001) A serine protease, HtrA2, is released from the mitochondria and interacts with XIAP, inducing cell death. Mol Cell 8(3):613–621
van Loo G, van Gurp M, Depuydt B, Srinivasula SM, Rodriguez I, Alnemri ES, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (2002) The serine protease Omi/HtrA2 is released from mitochondria during apoptosis. Omi interacts with caspase-inhibitor XIAP and induces enhanced caspase activity. Cell Death Differ 9(1):20–26. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400970
Hegde R, Srinivasula SM, Zhang Z, Wassell R, Mukattash R, Cilenti L, DuBois G, Lazebnik Y, Zervos AS, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2002) Identification of Omi/HtrA2 as a mitochondrial apoptotic serine protease that disrupts inhibitor of apoptosis protein-caspase interaction. J Biol Chem 277(1):432–438. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109721200
Gottfried Y, Rotem A, Lotan R, Steller H, Larisch S (2004) The mitochondrial ARTS protein promotes apoptosis through targeting XIAP. EMBO J 23(7):1627–1635. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600155
Larisch S, Yi Y, Lotan R, Kerner H, Eimerl S, Tony Parks W, Gottfried Y, Birkey Reffey S, de Caestecker MP, Danielpour D, Book-Melamed N, Timberg R, Duckett CS, Lechleider RJ, Steller H, Orly J, Kim SJ, Roberts AB (2000) A novel mitochondrial septin-like protein, ARTS, mediates apoptosis dependent on its P-loop motif. Nat Cell Biol 2(12):915–921. doi:10.1038/35046566
Liu Z, Sun C, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Betz SF, Oost T, Herrmann J, Wu JC, Fesik SW (2000) Structural basis for binding of Smac/DIABLO to the XIAP BIR3 domain. Nature 408(6815):1004–1008. doi:10.1038/35050006
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang X, Shi Y (2000) Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 408(6815):1008–1012. doi:10.1038/35050012
Martins LM (2002) The serine protease Omi/HtrA2: a second mammalian protein with a Reaper-like function. Cell Death Differ 9(7):699–701. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401044
Verhagen AM, Kratina TK, Hawkins CJ, Silke J, Ekert PG, Vaux DL (2007) Identification of mammalian mitochondrial proteins that interact with IAPs via N-terminal IAP binding motifs. Cell Death Differ 14(2):348–357. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402001
Vaux DL, Silke J (2003) Mammalian mitochondrial IAP binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304(3):499–504
Larisch S (2004) The ARTS connection: role of ARTS in apoptosis and cancer. Cell Cycle 3(8):1021–1023
Lotan R, Rotem A, Gonen H, Finberg JP, Kemeny S, Steller H, Ciechanover A, Larisch S (2005) Regulation of the proapoptotic ARTS protein by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem 280(27):25802–25810. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501955200
Edison N, Zuri D, Maniv I, Lev T, Bornshtein G, Gottfried Y, Kemeny S, Carp Nov M-J, Garcia-Fernandez M, Kagan J, Larisch S (2011) The IAP-antagonist ARTS initiates caspase activation upstream of Cytochrome C and SMAC/Diablo.Cell Death Differ (submitted for publication)
Garcia-Fernandez M, Kissel H, Brown S, Gorenc T, Schile AJ, Rafii S, Larisch S, Steller H (2010) Sept4/ARTS is required for stem cell apoptosis and tumor suppression. Genes Dev 24(20):2282–2293. doi:10.1101/gad.1970110
Kissel H, Georgescu MM, Larisch S, Manova K, Hunnicutt GR, Steller H (2005) The Sept4 septin locus is required for sperm terminal differentiation in mice. Dev Cell 8(3):353–364. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.021
Burstein E, Ganesh L, Dick RD, van De Sluis B, Wilkinson JC, Klomp LW, Wijmenga C, Brewer GJ, Nabel GJ, Duckett CS (2004) A novel role for XIAP in copper homeostasis through regulation of MURR1. EMBO J 23(1):244–254. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600031
Silke J, Hawkins CJ, Ekert PG, Chew J, Day CL, Pakusch M, Verhagen AM, Vaux DL (2002) The anti-apoptotic activity of XIAP is retained upon mutation of both the caspase 3- and caspase 9-interacting sites. J Cell Biol 157(1):115–124. doi:10.1083/jcb.200108085
Verhagen AM, Silke J, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Kaufmann H, Connolly LM, Day CL, Tikoo A, Burke R, Wrobel C, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL (2002) HtrA2 promotes cell death through its serine protease activity and its ability to antagonize inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. J Biol Chem 277(1):445–454. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109891200
Berman HM, Bhat TN, Bourne PE, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Weissig H, Westbrook J (2000) The Protein Data Bank and the challenge of structural genomics. Nat Struct Biol 7(Suppl):957–959. doi:10.1038/80734
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS (2006) The human anti-apoptotic proteins cIAP1 and cIAP2 bind but do not inhibit caspases. J Biol Chem 281(6):3254–3260. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510863200
Hunter AM, LaCasse EC, Korneluk RG (2007) The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) as cancer targets. Apoptosis 12(9):1543–1568. doi:10.1007/s10495-007-0087-3
Tamm I, Kornblau SM, Segall H, Krajewski S, Welsh K, Kitada S, Scudiero DA, Tudor G, Qui YH, Monks A, Andreeff M, Reed JC (2000) Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin Cancer Res 6(5):1796–1803
Harlin H, Reffey SB, Duckett CS, Lindsten T, Thompson CB (2001) Characterization of XIAP-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 21(10):3604–3608. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.10.3604-3608.2001
Elhasid R, Sahar D, Merling A, Zivony Y, Rotem A, Ben-Arush M, Izraeli S, Bercovich D, Larisch S (2004) Mitochondrial pro-apoptotic ARTS protein is lost in the majority of acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Oncogene 23(32):5468–5475. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207725
Okada H, Suh WK, Jin J, Woo M, Du C, Elia A, Duncan GS, Wakeham A, Itie A, Lowe SW, Wang X, Mak TW (2002) Generation and characterization of Smac/DIABLO-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 22(10):3509–3517
Jones JM, Datta P, Srinivasula SM, Ji W, Gupta S, Zhang Z, Davies E, Hajnoczky G, Saunders TL, Van Keuren ML, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Meisler MH, Alnemri ES (2003) Loss of Omi mitochondrial protease activity causes the neuromuscular disorder of mnd2 mutant mice. Nature 425(6959):721–727. doi:10.1038/nature02052
Martins LM, Morrison A, Klupsch K, Fedele V, Moisoi N, Teismann P, Abuin A, Grau E, Geppert M, Livi GP, Creasy CL, Martin A, Hargreaves I, Heales SJ, Okada H, Brandner S, Schulz JB, Mak T, Downward J (2004) Neuroprotective role of the Reaper-related serine protease HtrA2/Omi revealed by targeted deletion in mice. Mol Cell Biol 24(22):9848–9862. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.22.9848-9862.2004
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S, Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Korneluk RG (2001) Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase activity. Nat Cell Biol 3(2):128–133. doi:10.1038/35055027
Burri L, Strahm Y, Hawkins CJ, Gentle IE, Puryer MA, Verhagen A, Callus B, Vaux D, Lithgow T (2005) Mature DIABLO/Smac is produced by the IMP protease complex on the mitochondrial inner membrane. Mol Biol Cell 16(6):2926–2933. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-12-1086
Vande Walle L, Lamkanfi M, Vandenabeele P (2008) The mitochondrial serine protease HtrA2/Omi: an overview. Cell Death Differ 15(3):453–460. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402291
Yang QH, Du C (2004) Smac/DIABLO selectively reduces the levels of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 but not that of XIAP and livin in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem 279(17):16963–16970. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401253200
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P, Zobel K, Dynek JN, Elliott LO, Wallweber HJ, Flygare JA, Fairbrother WJ, Deshayes K, Dixit VM, Vucic D (2007) IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131(4):669–681. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.030
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau D, Ahmed AU, Benetatos CA, Chunduru SK, Condon SM, McKinlay M, Brink R, Leverkus M, Tergaonkar V, Schneider P, Callus BA, Koentgen F, Vaux DL, Silke J (2007) IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131(4):682–693. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.037
Morizane Y, Honda R, Fukami K, Yasuda H (2005) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis functions as ubiquitin ligase toward mature caspase-9 and cytosolic Smac/DIABLO. J Biochem 137(2):125–132. doi:10.1093/jb/mvi029
Yang Y, Fang S, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Ashwell JD (2000) Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteasomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 288(5467):874–877
Yoo SJ, Huh JR, Muro I, Yu H, Wang L, Wang SL, Feldman RM, Clem RJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (2002) Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 4(6):416–424. doi:10.1038/ncb793
Garrison JB, Correa RG, Gerlic M, Yip KW, Krieg A, Tamble CM, Shi R, Welsh K, Duggineni S, Huang Z, Ren K, Du C, Reed JC (2010) ARTS and Siah collaborate in a pathway for XIAP degradation. Mol Cell 41(1):107–116. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.12.002
Mace PD, Linke K, Feltham R, Schumacher FR, Smith CA, Vaux DL, Silke J, Day CL (2008) Structures of the cIAP2 RING domain reveal conformational changes associated with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2) recruitment. J Biol Chem 283(46):31633–31640. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804753200
Meng EC, Pettersen EF, Couch GS, Huang CC, Ferrin TE (2006) Tools for integrated sequence-structure analysis with UCSF Chimera. BMC Bioinformatics 7:339. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-339
Acknowledgments
We thank Herman Steller, John Silke, Colin Duckett, Chunying Du and Krishnaraj Rajalingam for generously providing us with constructs, antibodies and MEFs used in this manuscript. This work was supported by funds from US Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF) grant# 2003085 (to S.L), Israel Science Foundation (ISF) Grant # 1264/06 (to S.L) and a grant from Israel Cancer Association (ICA) (to S.L).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bavat Bornstein and Yossi Gottfried contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bornstein, B., Gottfried, Y., Edison, N. et al. ARTS binds to a distinct domain in XIAP-BIR3 and promotes apoptosis by a mechanism that is different from other IAP-antagonists. Apoptosis 16, 869–881 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0622-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-011-0622-0