Abstract
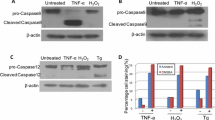
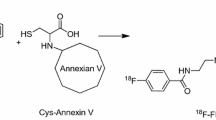
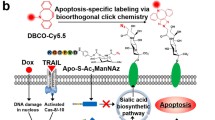
In vivo imaging of apoptosis in a preclinical setting in anticancer drug development could provide remarkable advantages in terms of translational medicine. So far, several imaging technologies with different probes have been used to achieve this goal. Here we describe a bioluminescence imaging approach that uses a new formulation of Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin, a caspase 3/7 substrate, to monitor in vivo apoptosis in tumor cells engineered to express luciferase. Upon apoptosis induction, Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin is cleaved by caspase 3/7 releasing aminoluciferin that is now free to react with luciferase generating measurable light. Thus, the activation of caspase 3/7 can be measured by quantifying the bioluminescent signal. Using this approach, we have been able to monitor caspase-3 activation and subsequent apoptosis induction after camptothecin and temozolomide treatment on xenograft mouse models of colon cancer and glioblastoma, respectively. Treated mice showed more than 2-fold induction of Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin luminescent signal when compared to the untreated group. Combining D-luciferin that measures the total tumor burden, with Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin that assesses apoptosis induction via caspase activation, we confirmed that it is possible to follow non-invasively tumor growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis after treatment in the same animal over time. Moreover, here we have proved that following early apoptosis induction by caspase 3 activation is a good biomarker that accurately predicts tumor growth inhibition by anti-cancer drugs in engineered colon cancer and glioblastoma cell lines and in their respective mouse xenograft models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Fulda S (2003) Tumor resistance to apoptosis. Int J Cancer 124:511–515
Roos WP, Batista LFZ, Naumann SC et al (2007) Apoptosis in malignant glioma cells triggered by the temozolomide-induced DNA lesion O6-methylguanine. Oncogene 26:186–197
Xu Y, Villalona-Calero MA (2002) Irinotecan: mechanisms of tumor resistance and novel strategies for modulating its activity. Ann Oncol 13:1841–1851
Jin Z, El Deiry WS (2005) Overview of cell death signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther 4:139–163
Kiechle FL, Zhang X (2002) Apoptosis: biochemical aspects and clinical implications. Clin Chim Acta 326:27–45
Rotonda J, Nicholson DW, Fazil KM et al (1996) The three-dimensional structure of apopain/CPP32, a key mediator of apoptosis. Nat Struct Biol 3:619–625
Grutter MG (2000) Caspases: key players in programmed cell death. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:649–655
Lee BW, Olin MR, Johnson GL, Griffin RJ (2008) In vitro and in vivo apoptosis detection using membrane permeant fluorescent-labeled inhibitors of caspases. Methods Mol Biol 414:109–135
Kuzelová K, Grebenová D, Hrkal Z (2007) Labeling of apoptotic JURL-MK1 cells by fluorescent caspase-3 inhibitor FAM-DEVD-fmk occurs mainly at site(s) different from caspase-3 active site. Cytometry A 71:605–611
Barnett EM, Zhang X, Maxwell D et al (2009) Single-cell imaging of retinal ganglion cell apoptosis with a cell-penetrating, activatable peptide probe in an in vivo glaucoma model. PNAS 106:9391–9396
Ray P, De A, Patel M, Gambhir SS (2008) Monitoring caspase-3 activation with a multimodality imaging sensor in living subjects. Clin Cancer Res 14:5801–5809
Troy T, Jekic-McMullen D et al (2004) Quantitative comparison of the sensitivity of detection of fluorescent and bioluminescent reporters in animal models. Mol Imaging 3:9–29
Tuchin VV, Wang RK, Yeh AT (2008) Optical clearing of tissues and cells. J Biomed Opt 13:021101
Yang Y, Hong H, Zhang Y, Cai W (2009) Molecular imaging of proteases in cancer. Pubmed Central. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2838618/. Accessed in PMC 2010 March 15
Laxman B, Hall DE, Bhojani MS et al (2002) Noninvasive real-time imaging of apoptosis. PNAS 99:16551–16555
Liu JJ, Wang W, Dicker DT et al (2005) Bioluminescent imaging of TRAIL-induced apoptosis through detection of caspase activation following cleavage of Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin. Cancer Biol Ther 4:885–892
Kizaka-Kondoh S, Itasaka S et al (2009) Selective killing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1-active cells improves survival in a mouse model of invasive and metastatic pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:3433–3441
Hickson J, Ackler S, Klaubert D et al (2010) Noninvasive molecular imaging of apoptosis in vivo using a modified firefly luciferase substrate, Z-DEVD-aminoluciferin. Cell Death Differ 17:1003–1010
Zeng L, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Itasaka S et al (2007) Hypoxia inducible factor-1 influences sensitivity to paclitaxel of human lung cancer cell lines under normoxic conditions. Cancer Sci 98:1394–1401
Del Bene F, Germani M, De Nicolao G et al (2009) A model-based approach to the in vitro evaluation of anticancer activity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63:827–836
Friedman HS, Kerby T, Calvert H (2000) Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 6:2585–2597
Nair JS, de Stanchina E, Schwartz GK (2009) The topoisomerase I poison CPT-11 enhances the effect of the Aurora B kinase inhibitor AZD1152 both in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 15:2022–2030
Shah K, Tung CH, Breakefield XO et al (2005) In vivo imaging of S-TRAIL-mediated tumor regression and apoptosis. Mol Ther 11:926–931
Lindner D, Raghavan D (2009) Intra-tumoural extra-cellular pH: a useful parameter of response to chemotherapy in syngeneic tumour. lines Br J Cancer 100:1287–1291
Tiefenthaler M, Amberger A, Bacher N et al (2001) Increased lactate production follows loss of mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis of human leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 114:574–580
Tisi L et al. (2010). PH tolerant luciferase. US Patent 68,739. Washington, DC. US Patent and Trademark Office http://ip.com/patapp/US20100068739. 18 May 2010
Ekert PG, Silke J, Vaux DL (1999) Caspase inhibitors. Cell Death Differ 6:1081–1086
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bedner E, Smolewski P et al (2002) Detection of caspases activation in situ by fluorochrome-labeled inhibitors of caspases (FLICA). Meth Molec Biol 203:289–299
Tan DS, Thomas GV, Garrett MD et al (2009) Biomarker-driven early clinical trials in oncology: a paradigm shift in drug development. Cancer J 15:406–420
Hurko O (2009) The uses of biomarkers in drug development. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1180:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Matteo Scabini and Fabio Stellari equally contributed to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scabini, M., Stellari, F., Cappella, P. et al. In vivo imaging of early stage apoptosis by measuring real-time caspase-3/7 activation. Apoptosis 16, 198–207 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0553-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0553-1