Abstract
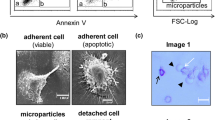
Microparticles (MPs) are small membrane-bound vesicles released from cells undergoing activation or cell death. These particles display potent biological activities that can impact on physiologic and pathologic processes. Previous studies with the Jurkat T leukemia cell line demonstrated that staurosporine (STS) induces the release of MPs as cells undergo apoptosis. To investigate further this process, we tested the effects of STS, its analogue, 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01), and other protein kinase C (PKC) and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors. FACS analysis was used to assess MP release. Results of these studies indicate that STS and UCN-01 induce MP release by Jurkat cells; in contrast, other PKC and CDK inhibitors failed to induce comparable release, suggesting that release does not result from simple inhibition of either kinase alone. Time course experiments indicated that STS-induced particle release occurred as early as 2 h after treatment, with the early release MPs displaying low levels of binding of annexin V and propidium iodide (PI). Early-release MPs, however, matured in culture to an annexin V- and PI-positive phenotype. Together, these results indicate that STS and UCN-01 induce MPs that are phenotypically distinct and reflect specific patterns of kinase inhibition during apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Distler JH, Pisetsky DS, Huber LC, Kalden JR, Gay S, Distler O (2005) Microparticles as regulators of inflammation: novel players of cellular crosstalk in the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 52:3337–3348
Ratajczak J, Wysoczynski M, Hayek F, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak MZ (2006) Membrane-derived microvesicles: important and underappreciated mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Leukemia 20:1487–1495
Piccin A, Murphy WG, Smith OP (2007) Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev 21:157–171
Del Conde I, Shrimpton CN, Thiagarajan P, Lopez JA (2005) Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 106:1604–1611
Distler JHW, Jungel A, Huber LC et al (2005) The induction of matrix metalloproteinase and cytokine expression in synovial fibroblasts stimulated with immune cell microparticles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2892–2897
Chironi G, Simon A, Hugel B et al (2006) Circulating leukocyte-derived microparticles predict subclinical atherosclerosis burden in asymptomatic subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:2775–2780
Kalinkovich A, Tavor S, Avigdor A et al (2006) Functional CXCR4-expressing microparticles and SDF-1 correlate with circulating acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res 66:11013–11020
Mesri M, Altieri DC (1998) Endothelial cell activation by leukocyte microparticles. J Immunol 161:4382–4387
Shah MD, Bergeron AL, Dong JF, López JA (2008) Flow cytometric measurement of microparticles: pitfalls and protocol modifications. Platelets 19:365–372
Mostefai HA, Andriantsitohaina R, Martínez MC (2008) Plasma membrane microparticles in angiogenesis: role in ischemic diseases and in cancer. Physiol Res 57:311–320
Pihusch R, Höhnberg B, Salat C, Pihusch M, Hiller E, Kolb H (2002) Platelet flow cytometric findings in patients undergoing conditioning therapy for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol 81:454–461
Carr JM, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF (1985) Circulating membrane vesicles in leukemic blood. Cancer Res 45:5944–5951
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J et al (2005) Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer 113:752–760
Hron G, Kollars M, Webber H et al (2007) Tissue factor-positive microparticles: cellular origin and association with coagulation activation in patients with colorectal cancer. Thromb Haemost 97:119–123
Helley D, Banu E, Bouziane A et al (2009) Platelet microparticles: a potential predictive factor of survival in hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients treated with docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Eur Urol 56:479–485
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH (1994) Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84:1415–1420
Reich CF III, Pisetsky DS (2009) The content of DNA and RNA in microparticles released by Jurkat and HL-60 cells undergoing in vitro apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 315:760–768
Bell CW, Jiang W, Reich CF III, Pisetsky DS (2006) The extracellular release of HMGB1 during apoptotic cell death. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291:C1318–C1325
Diaz-Padilla I, Siu LL, Duran I (2009) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors as potential targeted anticancer agents Invest New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-009-9236-6
Lapenna S, Giordano A (2009) Cell cycle kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:547–566
Distler JHW, Huber LC, Hueber AJ et al (2005) The release of microparticles by apoptotic cells and their effects on macrophages. Apoptosis 10:731–741
Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L, Ahearn J (1995) Novel packages of viral and self-antigens are generated during apoptosis. J Exp Med 181:1557–1561
Hagmann J, Burger MM, Dagan D (1999) Regulation of plasma membrane blebbing by the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biochem 73:488–499
Gescher A (2000) Staurosporine analogues—pharmacological toys or useful antitumour agents? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 34:127–135
Mizuno K, Noda K, Ueda Y et al (1995) UCN-01, an anti-tumor drug, is a selective inhibitor of the conventional PKC subfamily. FEBS Lett 359:259–261
Mackay HJ, Twelves CJ (2003) Protein kinase C: a target for anticancer drugs? Endocr Relat Cancer 10:389–396
Senderowicz AM (2003) Novel small molecule cyclin-dependent kinase modulators in human clinical trials. Cancer Biol Ther 2:S84–S95
Monaco EA III, Beaman-Hall CM, Mathur A, Vallano ML (2004) Roscovitine, olomoucine, purvalanol: inducers of apoptosis in maturing cerebellar granule neurons. Biochem Pharmacol 67:1947–1964
Zwaal RFA, Comfurius P, Bevers EM (2005) Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine in pathological cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:971–988
Franz S, Herrmann K, Fuhrnrohr B et al (2006) After shrinkage apoptotic cells expose internal membrane-derived epitopes on their plasma membranes. Cell Death Differ 14:733–742
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Soderland C, Horstman LL, Ahn YS (2003) Endothelial cells release phenotypically and quantitatively distinct microparticles in activation and apoptosis. Thromb Res 109:175–180
Biggiogera M, Bottone MG, Pellicciari C (1998) Nuclear RNA is extruded from apoptotic cells. J Histochem Cytochem 46:999–1006
Lane JD, Allan VJ, Woodman PG (2005) Active relocation of chromatin and endoplasmic reticulum into blebs in late apoptotic cells. J Cell Sci 118:4059–4071
Coleman ML, Sahai EA, Yeo M, Bosch M, Dewar A, Olson MF (2001) Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat Cell Biol 3:339–345
Sebbagh M, Renvoize C, Hamelin J, Riche N, Bertoglio J, Breard J (2001) Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat Cell Biol 3:346–352
Shiratsuchi A, Mori T, Nakanishi Y (2002) Independence of plasma membrane blebbing from other biochemical and biological characteristics of apoptotic cells. J Biochem 132:381–386
Langer F, Spath B, Haubold K et al (2008) Tissue factor procoagulant activity of plasma microparticles in patients with cancer-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation. Ann Hematol 87:451–457
Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M et al (2006) Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 20:847–856
Garcia JM, Garcia V, Pena C et al (2008) Extracellular plasma RNA from colon cancer patients is confined in a vesicle-like structure and is mRNA-enriched. RNA 14:1424–1432
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X et al (2008) Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS ONE 3:e3694
Bebawy M, Combes V, Lee E et al (2009) Membrane microparticles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to drug sensitive cancer cells. Leukemia 23:1643–1649
Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Podini P, Meldolesi J (2007) Enlargeosome traffic: exocytosis triggered by various signals is followed by endocytosis, membrane shedding or both. Traffic 8:742–757
Mirnikjoo B, Balasubramanian K, Schroit AJ (2009) Suicidal membrane repair regulates phosphatidylserine externalization during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 284:22512–22516
Mannherz HG, Gonsior SM, Wu X et al (2006) Dual effects of staurosporine on A431 and NRK cells: microfilament disassembly and uncoordinated lamellipodial activity followed by cell death. Eur J Cell Biol 85:785–802
Yang R, Fu W, Wang S, Liu T, Lin-Shiau S (1997) Mechanism of the morphological changes induced by staurosporine in rat osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int 61:68–73
Hotte SJ, Oza A, Winquist EW et al (2006) Phase I trial of UCN-01 in combination with topotecan in patients with advanced solid cancers: a Princess Margaret Hospital Phase II Consortium study. Ann Oncol 17:334–340
Jimeno A, Rudek MA, Purcell T et al (2008) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61:423–433
Stepczynska A, Lauber K, Engels IH et al (2001) Staurosporine and conventional anticancer drugs induce overlapping, yet distinct pathways of apoptosis and caspase activation. Oncogene 20:1193–1202
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by grants from the VA Merit Review program, Alliance for Lupus Research and NIH grant AI082402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullal, A.J., Pisetsky, D.S. The release of microparticles by Jurkat leukemia T cells treated with staurosporine and related kinase inhibitors to induce apoptosis. Apoptosis 15, 586–596 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0470-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0470-3