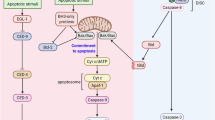
Abstract
Regulation of apoptosis is crucial to ensure cellular viability, and failure to do so is linked to several human pathologies. The apoptotic cell death programme culminates in the activation of caspases, a family of highly specific cysteine proteases essential for the destruction of the cell. Although best known for their role in executing apoptosis, caspases also play important signalling roles in non-apoptotic processes, such as regulation of actin dynamics, innate immunity, cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. Under such conditions, caspases are activated without killing the cell. Caspase activation and activity is subject to complex regulation, and various cellular and viral inhibitors have been identified that control the activity of caspases in their apoptotic and non-apoptotic roles. Members of the Inhibitor of APoptosis (IAP) protein family ensure cell viability in Drosophila by directly binding to caspases and regulating their activities in a ubiquitin-dependent manner. The observation that IAPs are essential for cell survival in Drosophila, and are frequently deregulated in human cancer, contributing to tumourigenesis, chemoresistance, disease progression and poor patient survival, highlights the importance of this family of caspase regulators in health and disease. Here we summarise recent advances from Drosophila that start to elucidate how the cellular response to caspase activation is modulated by IAPs and their regulators.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P (2007) Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 14:44–55. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402047
Leulier F, Rodriguez A, Khush RS, Abrams JM, Lemaitre B (2000) The Drosophila caspase Dredd is required to resist gram-negative bacterial infection. EMBO Rep 1:353–358. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd073
Chew SK, Akdemir F, Chen P, Lu WJ, Mills K, Daish T, Kumar S, Rodriguez A, Abrams JM (2004) The apical caspase dronc governs programmed and unprogrammed cell death in Drosophila. Dev Cell 7:897–907. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.09.016
Daish TJ, Mills K, Kumar S (2004) Drosophila caspase DRONC is required for specific developmental cell death pathways and stress-induced apoptosis. Dev Cell 7:909–915. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.09.018
Xu D, Li Y, Arcaro M, Lackey M, Bergmann A (2005) The CARD-carrying caspase Dronc is essential for most, but not all, developmental cell death in Drosophila. Development 132:2125–2134. doi:10.1242/dev.01790
Steller H (2008) Regulation of apoptosis in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 15:1132–1138. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.50
Fraser AG, McCarthy NJ, Evan GI (1997) drICE is an essential caspase required for apoptotic activity in Drosophila cells. EMBO J 16:6192–6199. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.20.6192
Muro I, Berry DL, Huh JR, Chen CH, Huang H, Yoo SJ, Guo M, Baehrecke EH, Hay BA (2006) The Drosophila caspase Ice is important for many apoptotic cell deaths and for spermatid individualization, a nonapoptotic process. Development 133:3305–3315. doi:10.1242/dev.02495
Xu D, Wang Y, Willecke R, Chen Z, Ding T, Bergmann A (2006) The effector caspases drICE and dcp-1 have partially overlapping functions in the apoptotic pathway in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ 13:1697–1706. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401920
Dorstyn L, Kumar S (2008) A biochemical analysis of the activation of the Drosophila caspase DRONC. Cell Death Differ 15:461–470. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402288
Snipas SJ, Drag M, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS (2008) Activation mechanism and substrate specificity of the Drosophila initiator caspase DRONC. Cell Death Differ 15:938–945. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.23
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, Datta P, Shiozaki E, Chai J, Lee RA, Robbins PD, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Shi Y, Alnemri ES (2001) A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature 410:112–116. doi:10.1038/35065125
Stennicke HR, Deveraux QL, Humke EW, Reed JC, Dixit VM, Salvesen GS (1999) Caspase-9 can be activated without proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem 274:8359–8362. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.13.8359
Yan N, Huh JR, Schirf V, Demeler B, Hay BA, Shi Y (2006) Structure and activation mechanism of the Drosophila initiator caspase Dronc. J Biol Chem 281:8667–8674. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513232200
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907. doi:10.1038/nrm1496
Salvesen GS, Riedl SJ (2008) Caspase mechanisms. Adv Exp Med Biol 615:13–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6554-5_2
Crook NE, Clem RJ, Miller LK (1993) An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol 67:2168–2174
Goyal L, McCall K, Agapite J, Hartwieg E, Steller H (2000) Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J 19:589–597. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.4.589
Lisi S, Mazzon I, White K (2000) Diverse domains of THREAD/DIAP1 are required to inhibit apoptosis induced by REAPER and HID in Drosophila. Genetics 154:669–678
Wang SL, Hawkins CJ, Yoo SJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (1999) The Drosophila caspase inhibitor DIAP1 is essential for cell survival and is negatively regulated by HID. Cell 98:453–463. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81974-1
LaCasse EC, Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, Plenchette S, Baird S, Korneluk RG (2008) IAP-targeted therapies for cancer. Oncogene 27:6252–6275. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.302
Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD (2008) IAPs: what’s in a name? Mol Cell 30:123–135. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.008
Vernooy SY, Chow V, Su J, Verbrugghe K, Yang J, Cole S, Olson MR, Hay BA (2002) Drosophila Bruce can potently suppress Rpr- and Grim-dependent but not Hid-dependent cell death. Curr Biol 12:1164–1168. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00935-1
Vernooy SY, Copeland J, Ghaboosi N, Griffin EE, Yoo SJ, Hay BA (2000) Cell death regulation in Drosophila: conservation of mechanism and unique insights. J Cell Biol 150:F69–F76. doi:10.1083/jcb.150.2.F69
Jones G, Jones D, Zhou L, Steller H, Chu Y (2000) Deterin, a new inhibitor of apoptosis from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem 275:22157–22165. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000369200
Hawkins CJ, Wang SL, Hay BA (1999) A cloning method to identify caspases and their regulators in yeast: identification of Drosophila IAP1 as an inhibitor of the Drosophila caspase DCP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2885–2890. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.2885
Kaiser WJ, Vucic D, Miller LK (1998) The Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis D-IAP1 suppresses cell death induced by the caspase drICE. FEBS Lett 440:243–248. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01465-3
Zachariou A, Tenev T, Goyal L, Agapite J, Steller H, Meier P (2003) IAP-antagonists exhibit non-redundant modes of action through differential DIAP1 binding. EMBO J 22:6642–6652. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg617
Meier P, Silke J, Leevers SJ, Evan GI (2000) The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1. EMBO J 19:598–611. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.4.598
Rodriguez A, Chen P, Oliver H, Abrams JM (2002) Unrestrained caspase-dependent cell death caused by loss of Diap1 function requires the Drosophila Apaf-1 homolog, Dark. EMBO J 21:2189–2197. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.9.2189
Tenev T, Zachariou A, Wilson R, Ditzel M, Meier P (2005) IAPs are functionally non-equivalent and regulate effector caspases through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 7:70–77. doi:10.1038/ncb1204
Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, Wang X, Shi Y (2000) Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 408:1008–1012. doi:10.1038/35050012
Wu JW, Cocina AE, Chai J, Hay BA, Shi Y (2001) Structural analysis of a functional DIAP1 fragment bound to grim and hid peptides. Mol Cell 8:95–104. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00282-9
Chai J, Yan N, Huh JR, Wu JW, Li W, Hay BA, Shi Y (2003) Molecular mechanism of Reaper-Grim-Hid-mediated suppression of DIAP1-dependent Dronc ubiquitination. Nat Struct Biol 10:892–898. doi:10.1038/nsb989
Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A (2000) Basic medical research award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med 6:1073–1081. doi:10.1038/80384
Haglund K, Dikic I (2005) Ubiquitylation and cell signaling. EMBO J 24:3353–3359. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600808
Tokunaga F, Sakata S, Saeki Y, Satomi Y, Kirisako T, Kamei K, Nakagawa T, Kato M, Murata S, Yamaoka S, Yamamoto M, Akira S, Takao T, Tanaka K, Iwai K (2009) Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-kappaB activation. Nat Cell Biol 11:123–132. doi:10.1038/ncb1821
Hoeller D, Hecker CM, Dikic I (2006) Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 6:776–788. doi:10.1038/nrc1994
Ditzel M, Broemer M, Tenev T, Bolduc C, Lee TV, Rigbolt KT, Elliott R, Zvelebil M, Blagoev B, Bergmann A, Meier P (2008) Inactivation of effector caspases through nondegradative polyubiquitylation. Mol Cell 32:540–553. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.025
Wilson R, Goyal L, Ditzel M, Zachariou A, Baker DA, Agapite J, Steller H, Meier P (2002) The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensable for regulating apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4:445–450. doi:10.1038/ncb799
Shapiro PJ, Hsu HH, Jung H, Robbins ES, Ryoo HD (2008) Regulation of the Drosophila apoptosome through feedback inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 10:1440–1446. doi:10.1038/ncb1803
Muro I, Hay BA, Clem RJ (2002) The Drosophila DIAP1 protein is required to prevent accumulation of a continuously generated, processed form of the apical caspase DRONC. J Biol Chem 277:49644–49650. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203464200
Herman-Bachinsky Y, Ryoo HD, Ciechanover A, Gonen H (2007) Regulation of the Drosophila ubiquitin ligase DIAP1 is mediated via several distinct ubiquitin system pathways. Cell Death Differ 14:861–871. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402079
Yan N, Wu JW, Chai J, Li W, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of DrICE inhibition by DIAP1 and removal of inhibition by Reaper, Hid and Grim. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:420–428. doi:10.1038/nsmb764
Ditzel M, Wilson R, Tenev T, Zachariou A, Paul A, Deas E, Meier P (2003) Degradation of DIAP1 by the N-end rule pathway is essential for regulating apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 5:467–473. doi:10.1038/ncb984
Muro I, Means JC, Clem RJ (2005) Cleavage of the apoptosis inhibitor DIAP1 by the apical caspase DRONC in both normal and apoptotic Drosophila cells. J Biol Chem 280:18683–18688. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501206200
Ribeiro PS, Kuranaga E, Tenev T, Leulier F, Miura M, Meier P (2007) DIAP2 functions as a mechanism-based regulator of drICE that contributes to the caspase activity threshold in living cells. J Cell Biol 179:1467–1480. doi:10.1083/jcb.200706027
Zimmermann KC, Ricci JE, Droin NM, Green DR (2002) The role of ARK in stress-induced apoptosis in Drosophila cells. J Cell Biol 156:1077–1087. doi:10.1083/jcb.20112068
Hay BA, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM (1995) Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death. Cell 83:1253–1262. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90150-7
Leulier F, Ribeiro PS, Palmer E, Tenev T, Takahashi K, Robertson D, Zachariou A, Pichaud F, Ueda R, Meier P (2006) Systematic in vivo RNAi analysis of putative components of the Drosophila cell death machinery. Cell Death Differ 13:1663–1674. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401868
Huh JR, Vernooy SY, Yu H, Yan N, Shi Y, Guo M, Hay BA (2004) Multiple apoptotic caspase cascades are required in nonapoptotic roles for Drosophila spermatid individualization. PLoS Biol 2:E15. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020015
Arama E, Agapite J, Steller H (2003) Caspase activity and a specific cytochrome C are required for sperm differentiation in Drosophila. Dev Cell 4:687–697. doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00120-5
Hou YC, Chittaranjan S, Barbosa SG, McCall K, Gorski SM (2008) Effector caspase Dcp-1 and IAP protein Bruce regulate starvation-induced autophagy during Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. J Cell Biol 182:1127–1139. doi:10.1083/jcb.200712091
Silke J, Vaux DL (2001) Two kinds of BIR-containing protein - inhibitors of apoptosis, or required for mitosis. J Cell Sci 114:1821–1827
White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young L, Farrell K, Steller H (1994) Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science 264:677–683. doi:10.1126/science.8171319
Christich A, Kauppila S, Chen P, Sogame N, Ho SI, Abrams JM (2002) The damage-responsive Drosophila gene sickle encodes a novel IAP binding protein similar to but distinct from reaper, grim, and hid. Curr Biol 12:137–140. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00658-3
Wing JP, Karres JS, Ogdahl JL, Zhou L, Schwartz LM, Nambu JR (2002) Drosophila sickle is a novel grim-reaper cell death activator. Curr Biol 12:131–135. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00664-9
Tenev T, Zachariou A, Wilson R, Paul A, Meier P (2002) Jafrac2 is an IAP antagonist that promotes cell death by liberating Dronc from DIAP1. EMBO J 21:5118–5129. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf530
Robinow S, Draizen TA, Truman JW (1997) Genes that induce apoptosis: transcriptional regulation in identified, doomed neurons of the Drosophila CNS. Dev Biol 190:206–213. doi:10.1006/dbio.1997.8696
Wing JP, Zhou L, Schwartz LM, Nambu JR (1998) Distinct cell killing properties of the Drosophila reaper, head involution defective, and grim genes. Cell Death Differ 5:930–939. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400423
Zhou L, Schnitzler A, Agapite J, Schwartz LM, Steller H, Nambu JR (1997) Cooperative functions of the reaper and head involution defective genes in the programmed cell death of Drosophila central nervous system midline cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5131–5136. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.10.5131
Huang Y, Park YC, Rich RL, Segal D, Myszka DG, Wu H (2001) Structural basis of caspase inhibition by XIAP: differential roles of the linker versus the BIR domain. Cell 104:781–790
Hays R, Wickline L, Cagan R (2002) Morgue mediates apoptosis in the Drosophila melanogaster retina by promoting degradation of DIAP1. Nat Cell Biol 4:425–431. doi:10.1038/ncb794
Holley CL, Olson MR, Colon-Ramos DA, Kornbluth S (2002) Reaper eliminates IAP proteins through stimulated IAP degradation and generalized translational inhibition. Nat Cell Biol 4:439–444. doi:10.1038/ncb798
Ryoo HD, Bergmann A, Gonen H, Ciechanover A, Steller H (2002) Regulation of Drosophila IAP1 degradation and apoptosis by reaper and ubcD1. Nat Cell Biol 4:432–438. doi:10.1038/ncb795
Yoo SJ, Huh JR, Muro I, Yu H, Wang L, Wang SL, Feldman RM, Clem RJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (2002) Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 4:416–424. doi:10.1038/ncb793
Wing JP, Schreader BA, Yokokura T, Wang Y, Andrews PS, Huseinovic N, Dong CK, Ogdahl JL, Schwartz LM, White K, Nambu JR (2002) Drosophila Morgue is an F box/ubiquitin conjugase domain protein important for grim-reaper mediated apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4:451–456. doi:10.1038/ncb800
Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Tonoki A, Takemoto K, Tomioka T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi S, Miura M (2006) Drosophila IKK-related kinase regulates nonapoptotic function of caspases via degradation of IAPs. Cell 126:583–596. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.048
Oshima K, Takeda M, Kuranaga E, Ueda R, Aigaki T, Miura M, Hayashi S (2006) IKK epsilon regulates F actin assembly and interacts with Drosophila IAP1 in cellular morphogenesis. Curr Biol 16:1531–1537. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.032
Pan D (2007) Hippo signaling in organ size control. Genes Dev 21:886–897. doi:10.1101/gad.1536007
Bandura JL, Edgar BA (2008) Yorkie and Scalloped: partners in growth activation. Dev Cell 14:315–316. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.02.010
Yin VP, Thummel CS, Bashirullah A (2007) Down-regulation of inhibitor of apoptosis levels provides competence for steroid-triggered cell death. J Cell Biol 178:85–92. doi:10.1083/jcb.200703206
Reuveny A, Elhanany H, Volk T (2009) Enhanced sensitivity of midline glial cells to apoptosis is achieved by HOW(L)-dependent repression of Diap1. Mech Dev 126:30–41. doi:10.1016/j.mod.2008.10.004
Geisbrecht ER, Montell DJ (2004) A role for Drosophila IAP1-mediated caspase inhibition in Rac-dependent cell migration. Cell 118:111–125. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.020
Gesellchen V, Kuttenkeuler D, Steckel M, Pelte N, Boutros M (2005) An RNA interference screen identifies inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 as a regulator of innate immune signalling in Drosophila. EMBO Rep 6:979–984. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400530
Huh JR, Foe I, Muro I, Chen CH, Seol JH, Yoo SJ, Guo M, Park JM, Hay BA (2007) The Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) DIAP2 is dispensable for cell survival, required for the innate immune response to gram-negative bacterial infection, and can be negatively regulated by the reaper/hid/grim family of IAP-binding apoptosis inducers. J Biol Chem 282:2056–2068. doi:10.1074/jbc.M608051200
Kleino A, Valanne S, Ulvila J, Kallio J, Myllymaki H, Enwald H, Stoven S, Poidevin M, Ueda R, Hultmark D, Lemaitre B, Ramet M (2005) Inhibitor of apoptosis 2 and TAK1-binding protein are components of the Drosophila Imd pathway. EMBO J 24:3423–3434. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600807
Leulier F, Lhocine N, Lemaitre B, Meier P (2006) The Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis protein DIAP2 functions in innate immunity and is essential to resist gram-negative bacterial infection. Mol Cell Biol 26:7821–7831. doi:10.1128/MCB.00548-06
Gaither A, Porter D, Yao Y, Borawski J, Yang G, Donovan J, Sage D, Slisz J, Tran M, Straub C, Ramsey T, Iourgenko V, Huang A, Chen Y, Schlegel R, Labow M, Fawell S, Sellers WR, Zawel L (2007) A Smac mimetic rescue screen reveals roles for inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Cancer Res 67:11493–11498. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5173
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P, Zobel K, Dynek JN, Elliott LO, Wallweber HJ, Flygare JA, Fairbrother WJ, Deshayes K, Dixit VM, Vucic D (2007) IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:669–681. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.030
Varfolomeev E, Goncharov T, Fedorova AV, Dynek JN, Zobel K, Deshayes K, Fairbrother WJ, Vucic D (2008) c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 are critical mediators of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)-induced NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 283:24295–24299. doi:10.1074/jbc.C800128200
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau D, Ahmed AU, Benetatos CA, Chunduru SK, Condon SM, McKinlay M, Brink R, Leverkus M, Tergaonkar V, Schneider P, Callus BA, Koentgen F, Vaux DL, Silke J (2007) IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131:682–693. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.037
Gyrd-Hansen M, Darding M, Miasari M, Santoro MM, Zender L, Xue W, Tenev T, da Fonseca PC, Zvelebil M, Bujnicki JM, Lowe S, Silke J, Meier P (2008) IAPs contain an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitin-binding domain that regulates NF-kappaB as well as cell survival and oncogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 10:1309–1317. doi:10.1038/ncb1789
Acknowledgments
We would like to apologise to our colleagues for omitting many relevant publications due to space limitation. We are grateful to Meike Broemer for critical reading of the manuscript and helpful comments, and we would like to thank Marketa Zvelebil for help with structural modelling. This work was supported by Breakthrough Breast Cancer and Association for International Cancer Research (AICR). We acknowledge NHS funding to the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orme, M., Meier, P. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in Drosophila: gatekeepers of death. Apoptosis 14, 950–960 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0358-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0358-2