Abstract
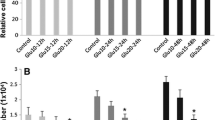
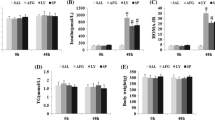
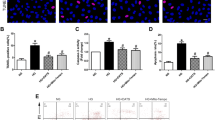
The underlying molecular mechanism whereby hyperglycemia causes endothelial cell apoptosis is not well understood. This study aims to elucidate the role of survival factor VEGF involved in the apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by elevated glucose. The present study confirmed that high concentration of glucose (25 mmol/l) significantly increased the apoptotic cell number in cultured primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Up-regulation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and activation of caspase-3 induced by high glucose suggested that mitochondria apoptosis pathway was involved. High glucose significantly reduced VEGF expression in HUVEC both at mRNA and protein levels. p42/44 MAPK phosphorylation was transitory attenuated when exposed to high glucose and preceded VEGF reduction, thus suggesting down-regulation of VEGF through inhibition of p42/44 MAPK. Addition of VEGF prevented HUVEC apoptosis from high glucose exposure. Moreover, elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, calcium overload, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, caspase-3 activation in HUVEC induced by high glucose were reversed by pre-challenge with VEGF. This may represent a mechanism for the anti-apoptotic effect of VEGF. These results suggest that down-regulation of VEGF plays a critical role in apoptosis of endothelial cells induced by high glucose and restoration of VEGF might have benefits in the early stage of diabetic endothelial dysfunction.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Glc:
-
Glucose
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Blom ML, Green WR, Schachat AP (1994) Diabetic retinopathy: a review. Del Med J 66:379–388
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications I insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309303291401
Lorenzi M, Cagliero E, Toledo S (1985) Glucose toxicity for human endothelial cells in culture: delayed replication, disturbed cell cycle, and accelerated death. Diabetes 34:621–627. doi:10.2337/diabetes.34.7.621
Baumgartner-Parzer SM, Wagner L, Pettermann M, Grillari J, Gessl A, Waldhausl W (1995) High-glucose-triggered apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes 44:1323–1327. doi:10.2337/diabetes.44.11.1323
Ceriello A, Quagliaro L, D’Amico M et al (2002) Acute hyperglycemia induces nitrotyrosine formation and apoptosis in perfused heart from rat. Diabetes 51:1076–1082. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.4.1076
Nakagami H, Morishita R, Yamamoto K et al (2001) Phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase downstream of bax-caspase-3 pathway leads to cell death induced by high D-glucose in human endothelial cells. Diabetes 50:1472–1481. doi:10.2337/diabetes.50.6.1472
Graiani G, Emanueli C, Desortes E et al (2004) Nerve growth factor promotes reparative angiogenesis and inhibits endothelial apoptosis in cutaneous wounds of Type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetologia 47(6):1047–1054. doi:10.1007/s00125-004-1414-7
Ho FM, Liu SH, Liau CS, Huang PJ, Lin-Shiau SY (2000) High glucose-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells is mediated by sequential activations of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase and caspase-3. Circulation 101(22):2618–2624
Sheu ML, Ho FM, Yang RS et al (2005) High glucose induces human endothelial cell apoptosis through a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-regulated cyclooxygenase-2 pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(3):539–545. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000155462.24263.e4
Vander Heiden MG, Plas DR, Rathmell JC, Fox CJ, Harris MH, Thompson CB (2001) Growth factors can influence cell growth and survival through effects on glucose metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 21(17):5899–5912. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.17.5899-5912.2001
Takadera T, Ohyashiki T (1997) Apoptotic cell death and caspase 3 (CPP32) activation induced by calcium ionophore at low concentrations and their prevention by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. Eur J Biochem 249:8–12. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00008.x
Lin HL, Yang JS, Yang JH et al (2006) The Role of Ca2+ on the DADS-induced apoptosis in mouse–rat hybrid retina ganglion cells (N18). Neurochem Res 31(3):383–393. doi:10.1007/s11064-005-9035-1
Shen HM, Dong SY, Ong CN (2001) Critical role of calcium overloading in cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 171:12–19. doi:10.1006/taap.2000.9092
Nicotera P, Orrenius S (1998) The role of calcium in apoptosis. Cell Calcium 23:173–180. doi:10.1016/S0143-4160(98)90116-6
Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Li W et al (1999) VEGF prevents apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells via opposing effects on MAPK/ERK and SAPK/JNK signaling. Exp Cell Res 247(2):495–504. doi:10.1006/excr.1998.4359
Grosjean J, Kiriakidis S, Reilly K, Feldmann M, Paleolog E (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor signalling in endothelial cell survival: a role for NF-κB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:984–994. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.095
Liu WL, Guo X, Chen QQ, Guo ZG (2002) VEGF protects bovine aortic endothelial cells from TNF-alpha- and H2O2-induced apoptosis via co-modulatory effects on p38-and p42/p44-CCDPK signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23(1):45–49
Moriga T, Arii S, Takeda Y et al (2000) Protection by vascular endothelial growth factor against sinusoidal endothelial cell damage and apoptosis induced by cold preservation. Transplantation 69:141–147. doi:10.1097/00007890-200001150-00024
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG, Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52:2745–2756. doi:10.1172/JCI107470
Gao G, Shao C, Zhang SX, Dudley A, Fant J, Ma JX (2003) Kallikrein-binding protein inhibits retinal neovascularization and decreases vascular leakage. Diabetologia 46:689–698
Lorenzi M, Montisano DF, Toledo S (1986) High glucose induces DNA damage in cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 77:322–325. doi:10.1172/JCI112295
Tesfamariam B, Brown ML, Cohen RA (1991) Elevated glucose impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation by activating protein kinase C. J Clin Invest 87:1643–1648. doi:10.1172/JCI115179
Hsueh WA, Anderson PW (1992) Hypertension, the endothelial cell, and the vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 20:253–263
Williams B, Gallacher B, Patel H, Orme C (1997) Glucose-induced protein kinase C activation regulates vascular permeability factor mRNA expression and peptide production by human vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Diabetes 46(9):1497–1503. doi:10.2337/diabetes.46.9.1497
el-Remessy AB, Bartoli M, Platt DH, Fulton D, Caldwell RB (2005) Oxidative stress inactivates VEGF survival signaling in retinal endothelial cells via PI 3-kinase tyrosine nitration. J Cell Sci 118:243–252. doi:10.1242/jcs.01612
Kim NH, Jung HH, Cha DR, Choi DS (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in response to high glucose in rat mesangial cells. J Endocrinol 165(3):617–624. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1650617
Knott RM, Pascal MM, Ferguson C et al (1999) Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta, basic fibroblast growth factor, and vascular endothelial cell growth factor mRNA in peripheral blood leukocytes in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Metabolism 48:1172–1178. doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(99)90134-8
Singh AK, Gudehithlu KP, Pegoraro AA et al (2004) Vascular factors altered in glucose-treated mesangial cells and diabetic glomeruli. Changes in vascular factors impair endothelial cell growth and matrix. Lab Invest 84(5):597–606. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3700082
Pinter E, Haigh J, Nagy A, Madri J (2001) Hyperglycemia-induced vasculopathy in the murine conceptus is mediated via reductions of VEGF-A expression and VEGF receptor activation. Am J Pathol 158:1199–1206
Milanini J, Viñals F, Pouysségur J, Pagès G (1998) p42/p44 MAP kinase module plays a key role in the transcriptional regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 273(29):18165–18172. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.29.18165
Sodhi A, Montaner S, Patel V et al (2000) The Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus G protein-coupled receptor up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression and secretion through mitogen-activated protein kinase and p38 pathways acting on hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Cancer Res 60(17):4873–4880
Xu H, Czerwinski P, Hortmann M et al (2008) Protein kinase C alpha promotes angiogenic activity of human endothelial cells via induction of vascular endothelial growth factor. Cardiovasc Res 78(2):349–355. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvm085
Takahashi T, Ueno H, Shibuya M (1999) VEGF activates protein kinase C-dependent, but Ras-independent Raf-MEK-MAP kinase pathway for DNA synthesis in primary endothelial cells. Oncogene 18(13):2221–2230. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202527
Gao G, Li Y, Gee S, Dudley A, Fant J, Crosson C et al (2002) Down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and up-regulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor: a possible mechanism for the anti-angiogenic activity of plasminogen kringle 5. J Biol Chem 277(11):9492–9497. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108004200
Nakagami H, Morishita R, Yamamoto K et al (2002) Hepatocyte growth factor prevents endothelial cell death through inhibition of bax translocation from cytosol to mitochondrial membrane. Diabetes 51(8):2604–2611. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.8.2604
Zhang Z, Lapolla SM, Annis MG et al (2004) Bcl-2 homodimerization involves two distinct binding surfaces, a topographic arrangement that provides an effective mechanism for Bcl-2 to capture activated Bax. J Biol Chem 279(42):43920–43928. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406412200
Tan C, Dlugosz PJ, Peng J et al (2006) Auto-activation of the apoptosis protein Bax increases mitochondrial membrane permeability and is inhibited by Bcl-2. J Biol Chem 281(21):14764–14775. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602374200
Kim WU, Kang SS, Yoo SA et al (2006) Interaction of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 with neuropilin-1 protects rheumatoid synoviocytes from apoptotic death by regulating Bcl-2 expression and Bax translocation. J Immunol 177(8):5727–5735
Munshi N, Fernandis AZ, Cherla RP, Park IW, Ganju RK (2002) Lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells and its inhibition by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Immunol 168(11):5860–5866
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ (1997) Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139(5):1281–1292. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.5.1281
Goping IS, Gross A, Lavoie JN et al (1998) Regulated targeting of BAX to mitochondria. J Cell Biol 143(1):207–215. doi:10.1083/jcb.143.1.207
Hsu YT, Wolter KG, Youle RJ (1997) Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of bax and bcl-xL during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3668–3672. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.8.3668
Gross A, Jennifer J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ (1998) Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J 17:3878–3885. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.14.3878
Ho FM, Lin WW, Chen BC et al (2006) High glucose-induced apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells is mediated through NF-kappaB and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway and prevented by PI3 K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal 18(3):391–399. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.05.009
Vanden Abeele F, Skryma R, Shuba Y et al (2002) Bcl-2 dependent modulation of Ca2+ homeostasis and store-operated channels in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell 1:169–179. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00034-X
Vindis C, Elbaz M, Escargueil-Blanc I et al (2005) Two distinct calcium-dependent mitochondrial pathways are involved in oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 5(3):639–645. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000154359.60886.33
Tamareille S, Mignen O, Capiod T, Rucker-Martin C, Feuvray D (2006) High glucose-induced apoptosis through store-operated calcium entry and calcineurin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cell Calcium 39:47–55
Brock TA, Dvorak HF, Senger DR (1991) Tumor-secreted vascular permeability factor increases cytosolic Ca2+ and von Willebrand factor release in human endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 138(1):213–221
Gifford SM, Grummer MA, Pierre SA, Austin JL, Zheng J, Bird IM (2004) Functional characterization of HUVEC-CS: Ca2+ signaling, ERK 1/2 activation, mitogenesis and vasodilator production. J Endocrinol 182(3):485–499. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1820485
Faehling M, Kroll J, Fohr KJ et al (2002) Essential role of calcium in vascular endothelial growth factor A-induced signaling: mechanism of the antiangiogenic effect of carboxyamidotriazole. FASEB J 16(13):1805–1807
McLaughlin AP, De Vries GW (2001) Role of PLC gamma and Ca2+ in VEGF- and FGF-induced choroidal endothelial cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281(5):C1448–C1456
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China, Grant Number: 30370313, 30570372, 30600724, 30700120; CMB(China Medical Board of New York, Inc.); Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, Grant Number: NCET-040792; Program for Doctoral Station in University, Grant Number: 20070558209,20070558215; Team Project of Nature Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China, Grant Number: 06201946; Key Sci-tech Research Project of Guangdong Province, China, Grant Number: 2005A10902003, 2006B35502001; Nature Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China, Grant Number: 06021260; Key Sci-tech Research Project of Guangzhou Municipality, Guangdong Province, China, Grant Number: 2006Z3-E4111, 2007Z3-E5041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhonghan Yang, Xuehua Mo, and Qing Gong have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Mo, X., Gong, Q. et al. Critical effect of VEGF in the process of endothelial cell apoptosis induced by high glucose. Apoptosis 13, 1331–1343 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0257-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0257-y