Abstract
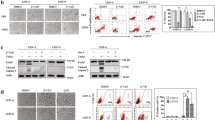
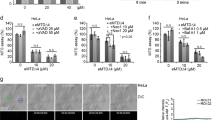
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) initiate pathways of cell death in which caspase activation is mediated either directly (without mitochondrial amplification), or indirectly via the release of apoptogenic factors from mitochondria. Phospholipid scramblases (PLS) are enzymes that play a key role in cellular function by inducing bidirectional movement of membrane lipids. Changes in mitochondrial membrane lipids, cardiolipin, are critical for mediating apoptotic response in many cell-types. PLS3 is a phospholipid scramblase that is localized to mitochondria and is thought to be involved in the regulation of apoptotic signals. Here we report that exogenous-expression of PLS3 enhances apoptotic death induced by TRAIL. This is acheived by potentiating the mitochondrial arm of the death pathway. Thereby, PLS3 expression facilitates changes in mitochondrial membrane lipids that promote the release of apoptogenic factors and consequent full activation and processing of the caspase-9 and effector caspase-3. Moreover, we show that knock-down of endogenous PLS3 suppresses TRAIL-induced changes in cardiolipin. Finally, we demonstrate that TRAIL-induced activation of PKC-delta mediates regulation of the PLS3-induced changes in cardiolipin.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Kurakin A, Mohseni-Maybodi M, Kay B, Khosravi-Far R (2000) The complexity of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Ann NY Acad Sci 926:52–63
LeBlanc HN, Ashkenazi A (2003) Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ 10:66–75
MacFarlane M (2003) TRAIL-induced signalling and apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 139:89–97
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2004) Apoptosis, autophagy, and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2405–2419
Khosravi-Far R, Esposti MD (2004) Death receptor signals to mitochondria. Cancer Biol Ther 3:1051–1057
Wang X (2001) The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 15:2922–2933
Peter ME, Krammer PH (2003) The CD95(APO-1/Fas) DISC and beyond. Cell Death Differ 10:26–35
Golstein P (1997) Cell death: TRAIL and its receptors. Curr Biol 7: R750–R753
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2007) Cell death in health and disease. J Cell Mol Med 11:1214–1224
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S et al (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104:155–162
French LE, Tschopp J (1999) The TRAIL to selective tumor death. Nat Med 5:146–147
Ozoren N, El-Deiry WS (2003) Cell surface Death Receptor signaling in normal and cancer cells. Semin Cancer Biol 13:135–147
Thorburn A (2004) Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 16:139–144
Song K, Benhaga N, Anderson RL, Khosravi-Far R (2006) Transduction of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand into hematopoietic cells leads to inhibition of syngeneic tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 66:6304–6311
Kayagaki N, Yamaguchi N, Nakayama M, Eto H, Okumura K, Yagita H (1999) Type I interferons (IFNs) regulate tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression on human T cells: a novel mechanism for the antitumor effects of type I IFNs. J Exp Med 189:1451–1460
Mackay F, Kalled SL (2002) TNF ligands and receptors in autoimmunity: an update. Curr Opin Immunol 14:783–790
Mariani SM, Krammer PH (1998) Surface expression of TRAIL/Apo-2 ligand in activated mouse T and B cells. Eur J Immunol 28:1492–1498
Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Alava MA, Gamen S et al (1998) Involvement of APO2 ligand/TRAIL in activation-induced death of Jurkat and human peripheral blood T cells. Eur J Immunol 28:2714–2725
Wang S, El-Deiry WS (2003) TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene 22:8628–8633
Zamai L, Ahmad M, Bennett IM, Azzoni L, Alnemri ES, Perussia B (1998) Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity: differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature and mature primary human NK cells. J Exp Med 188:2375–2380
Ozoren N, El-Deiry WS (2002) Defining characteristics of Types I and II apoptotic cells in response to TRAIL. Neoplasia 4:551–557
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A et al (1998) Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. Embo J 17:1675–1687
Muzio M, Stockwell BR, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1998) An induced proximity model for caspase-8 activation. J Biol Chem 273:2926–2930
Yang X, Chang HY, Baltimore D (1998) Autoproteolytic activation of pro-caspase by oligomerization. Mol Cell 2:319
Boatright KM, Renatus M, Scott FL et al (2003) A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol Cell 11:529–541
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656
Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL, Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV, Boldin MP (1999) Tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Immunol 17:331–367
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):1–16
Matarrese P, Gambardella L, Cassone A, Vella S, Cauda R, Malorni W (2003) Mitochondrial membrane hyperpolarization hijacks activated T lymphocytes toward the apoptotic-prone phenotype: homeostatic mechanisms of HIV protease inhibitors. J Immunol 170:6006–6015
Ouasti S, Matarrese P, Paddon R et al (2007) Death receptor ligation triggers membrane scrambling between golgi and mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 14:453–461
Sahu SK, Gummadi SN, Manoj N, Aradhyam GK (2007) Phospholipid scramblases: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 462:103–114
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Rose DM, Pearson A, Ezekewitz RA, Henson PM (2000) A receptor for phosphatidylserine-specific clearance of apoptotic cells. Nature 405:85–90
Liu J, Chen J, Dai Q, Lee RM (2003) Phospholipid scramblase 3 is the mitochondrial target of protein kinase C delta-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 63:1153–1156
Liu J, Dai Q, Chen J et al (2003) Phospholipid scramblase 3 controls mitochondrial structure, function, and apoptotic response. Mol Cancer Res 1:892–902
Sandra F, Degli Esposti M, Ndebele K et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand alters mitochondrial membrane lipids. Cancer Res 65:8286–8297
Esposti MD (2002) The roles of Bid. Apoptosis 7:433–440
Goonesinghe A, Mundy ES, Smith M, Khosravi-Far R, Martinou JC, Esposti MD (2005) Pro-apoptotic Bid induces membrane perturbation by inserting selected lysolipids into the bilayer. Biochem J 387:109–118
Kuwana T, Mackey MR, Perkins G et al (2002) Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cell 111:331–342
Newmeyer DD, Ferguson-Miller S (2003) Mitochondria: releasing power for life and unleashing the machineries of death. Cell 112:481–490
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH et al (2001) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292:727–730
Cifone MG, Roncaioli P, De Maria R et al (1995) Multiple pathways originate at the Fas/APO-1 (CD95) receptor: sequential involvement of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and acidic sphingomyelinase in the propagation of the apoptotic signal. EMBO J 14:5859–5868
Exton JH (1997) Cell signalling through guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) and phospholipases. Eur J Biochem 243:10–20
Han JS, Hyun BC, Kim JH, Shin I (1999) Fas-mediated activation of phospholipase D is coupled to the stimulation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C in A20 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 367:233–239
Boneau C (1960) The effects of violations of assumptions underlying the test. Psychol Bull 57:49–64
Haldane J (1956) The Wilcoxon and related tests of significance. Experientia 205
Westfall PH, Krishen A, Young SS (1998) Using prior information to allocate significance levels for multiple endpoints. Statistics Med 17:2107–2119
Kimberley FC, Screaton GR (2004) Following a TRAIL: update on a ligand and its five receptors. Cell Res 14:359–372
Liu J, Epand RF, Durrant D et al (2008) Role of phospholipid Scramblase 3 in the regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis. Biochemistry 47:4518–4529
Esposti MD, Cristea IM, Gaskell SJ, Nakao Y, Dive C (2003) Proapoptotic Bid binds to monolysocardiolipin, a new molecular connection between mitochondrial membranes and cell death. Cell Death Differ 10:1300–1309
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1997) Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell 91:443–446
Slee EA, Adrain C, Martin SJ (1999) Serial killers: ordering caspase activation events in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:1067–1074
Jin TG, Kurakin A, Benhaga N et al (2004) Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD)-independent recruitment of c-FLIPL to death receptor 5. J Biol Chem 279:55594–55601
Kikkawa U, Matsuzaki H, Yamamoto T (2002) Protein kinase C delta (PKC delta): activation mechanisms and functions. J Biochem (Tokyo) 132:831–839
Brodie C, Blumberg PM (2003) Regulation of cell apoptosis by protein kinase C delta. Apoptosis 8:19–27
Sumitomo M, Ohba M, Asakuma J et al (2002) Protein kinase c delta amplifies ceramide formation via mitochondrial signaling in prostate cancer cells. J Clin Invest 109:827–836
Zhao J, Zhou Q, Stout JG, Luhm RA, Wiedmer T, Sims PJ (1997) Molecular cloning of human plasma membrane phospholipid scrambalase. J Biol Chem 272:18240
He Y, Liu J, Grossman D et al (2007) Phosphorylation of mitochondrial phospholipid scramblase 3 by protein kinase C-delta induces its activation and facilitates mitochondrial targeting of tBid. J Cell Biochem 101:1210–1221
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Wiedmer and Ohno for scramblase and PKCδ constructs, respectively. This work was supported by NIH grants CA105306 and HL080192 to RKF. RKF is an American Cancer Society Scholar. KN was supported by NIH 5 T32 HL07893 and UNCF/MERCK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ndebele, K., Gona, P., Jin, TG. et al. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induced mitochondrial pathway to apoptosis and caspase activation is potentiated by phospholipid scramblase-3. Apoptosis 13, 845–856 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0219-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0219-4