Abstract
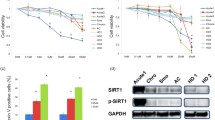
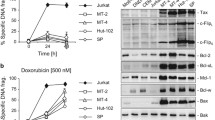
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is an aggressive lymphoproliferative disease of very poor clinical prognosis associated with infection by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I). Treatment of patients with ATLL using conventional chemotherapy has limited benefit because HTLV-I cells are refractory to most apoptosis-inducing agents. In this study, we report that Celecoxib induces cell death via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway in HTLV-I transformed leukemia cells. Treatment with Celecoxib was associated with activation of Bax, decreased expression of Mcl-1, loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase-9-dependent apoptosis. These effects were independent from Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. We also found that Celecoxib inhibited the Akt/GSK3 β survival pathway in HTLV-I cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD, Gallo RC (1980) Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7415–7419
Franchini G, Nicot C, Johnson JM (2003) Seizing of T cells by human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1. Adv Cancer Res 89:69–132
Bellon M, Datta A, Brown M et al (2006) Increased expression of telomere length regulating factors TRF1, TRF2 and TIN2 in patients with adult T-cell leukemia. Int J Cancer 119:2090–2097
Sinha-Datta U, Horikawa I, Michishita E et al (2004) Transcriptional activation of hTERT through the NF-κB pathway in HTLV-I-transformed cells. Blood 104:2523–2531
Grassmann R, Aboud M, Jeang KT (2005) Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 Tax. Oncogene 24:5976–5985
Bazarbachi A, Ghez D, Lepelletier Y et al (2004) New therapeutic approaches for adult T-cell leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 5:664–672
Hermine O, Allard I, Levy V, Arnulf B, Gessain A, Bazarbachi A (2002) A prospective phase II clinical trial with the use of zidovudine and interferon-α in the acute and lymphoma forms of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Hematol J 3:276–282
Datta A, Bellon M, Sinha-Datta U et al (2006) Persistent inhibition of telomerase reprograms adult T-cell leukemia to p53-dependent senescence. Blood 108:1021–1029
Bazarbachi A, Hermine O (2001) Treatment of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma: current strategy and future perspectives. Virus Res 78:79–92
Nicot C, Mahieux R, Takemoto S, Franchini G (2000) Bcl-X(L) is up-regulated by HTLV-I and HTLV-II in vitro and in ex vivo ATLL samples. Blood 96:275–281
Hwang D, Scollard D, Byrne J, Levine E (1998) Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in human breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:455–460
Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D et al (2000) COX-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer 89:2637–2645
Mori N, Inoue H, Yoshida T, Tanabe T, Yamamoto N (2001) Constitutive expression of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene in T-cell lines infected with human T cell leukemia virus type I. Int J Cancer 94:813–819
Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK et al (2000) The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med 342:1946–1952
Elder DJ, Paraskeva C (1999) Induced apoptosis in the prevention of colorectal cancer by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Apoptosis 4:365–372
Elder DJ, Paraskeva C (1998) COX-2 inhibitors for colorectal cancer. Nat Med 4:392–393
Jendrossek V, Handrick R, Belka C (2003) Celecoxib activates a novel mitochondrial apoptosis signaling pathway. FASEB J 17:1547–1549
Brown M, Bellon M, Nicot C (2007) Emodin and DHA potently increase arsenic trioxide interferon-alpha-induced cell death of HTLV-I-transformed cells by generation of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of Akt and AP-1. Blood 109:1653–1659
Jendrossek V, Handrick R, Belka C (2003) Celecoxib activates a novel mitochondrial apoptosis signaling pathway. FASEB J 17:1547–1549
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC et al (2006) Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol 8:1348–1358
Hsu YT, Youle RJ (1998) Bax in murine thymus is a soluble monomeric protein that displays differential detergent-induced conformations. J Biol Chem 273:10777–10783
Hsu YT, Youle RJ (1997) Nonionic detergents induce dimerization among members of the Bcl-2 family. J Biol Chem 272:13829–13834
Toker A, Yoeli-Lerner M (2006) Akt signaling and cancer: surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res 66:3963–3966
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Park HU, Brady JN (2005) Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 24:6719–6728
Liu Y, Wang Y, Yamakuchi M et al (2001) Phosphoinositide-3 kinase-PKB/Akt pathway activation is involved in fibroblast Rat-1 transformation by human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax. Oncogene 20:2514–2526
Tomita M, Kikuchi A, Akiyama T, Tanaka Y, Mori N (2006) Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax dysregulates β-catenin signaling. J Virol 80:10497–10505
Datta A, Sinha-Datta U, Dhillon NK, Buch S, Nicot C (2006) The HTLV-I p30 interferes with TLR4 signaling and modulates the release of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines from human macrophages. J .Biol Chem 281:23414–23424
Han J, Goldstein LA, Gastman BR, Rabinovitz A, Rabinowich H (2005) Disruption of Mcl-1.Bim complex in granzyme B-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280:16383–16392
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G et al (2005) Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 19:1294–1305
Kern MA, Haugg AM, Koch AF et al (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition induces apoptosis signaling via death receptors and mitochondria in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 66:7059–7066
Cuconati A, Mukherjee C, Perez D, White E (2003) DNA damage response and MCL-1 destruction initiate apoptosis in adenovirus-infected cells. Genes Dev 17:2922–2932
Gradilone A, Silvestri I, Scarpa S et al (2007) Failure of apoptosis and activation on NFkappaB by celecoxib and aspirin in lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 17:823–828
Pang RP, Zhou JG, Zeng ZR et al (2007) Celecoxib induces apoptosis in COX-2 deficient human gastric cancer cells through Akt/GSK3β/NAG-1 pathway. Cancer Lett 251:268–277
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute grant CA106258 to C.N.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
U. Sinha-Datta and J. M. Taylor have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha-Datta, U., Taylor, J.M., Brown, M. et al. Celecoxib disrupts the canonical apoptotic network in HTLV-I cells through activation of Bax and inhibition of PKB/Akt. Apoptosis 13, 33–40 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0148-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0148-7