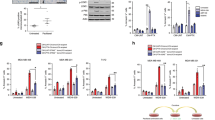
Abstract
The antiapoptotic BCL2 family member MCL1 is rapidly upregulated upon exposure of ML-1 myeloid leukemia cells to either differentiation-inducing phorbol 12′-myristate 13′-acetate (PMA) or chemotherapeutic microtubule disrupting agents (MTDAs). This report examined how signaling for MCL1 upregulation is coupled to these two different phenotypic changes, and tested for upregulation in other hematopoietic cancers. With PMA, ERK stimulated MCL1 mRNA expression and ML-1 cell differentiation, and ERK additionally stabilized expression of the MCL1 protein. However, with MTDAs, transient ERK and ensuing JNK activation contributed to initial MCL1 upregulation and viability-retention, but sustained JNK activation eventually resulted in cell death. MCL1 was upregulated by PMA in THP-1 and U937 myeloid leukemia cells, but by MTDAs only in THP-1 cells. MCL1 expression was constitutively elevated in multiple myeloma cell lines, and was not affected by PMA/ERK or MTDAs. Thus, MCL1 expression level and sensitivity to regulation are important considerations in selecting approaches for targeting this antiapoptotic gene product to kill cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craig RW (2002) Mcl1 provides a window on the role of the bcl2 family in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 16:444–454
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P, Craig RW (1993) Mcl1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to bcl2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:3516–3520
Moulding DA, Giles RV, Spiller DG et al (2000) Apoptosis is rapidly triggered by antisense depletion of Mcl-1 in differentiating u937 cells. Blood 96:1756–1763
Zhou P, Qian L, Bieszczad CK et al (1998) Mcl-1 in transgenic mice promotes survival in a spectrum of hematopoietic cell types and immortalization in the myeloid lineage. Blood 92:3226–3239
Zhou P, Qian L, Kozopas KM, Craig RW (1997) Mcl-1, a bcl-2 family member, delays the death of hematopoietic cells under a variety of apoptosis-inducing conditions. Blood 89:630–643
Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C et al (2003) Development and maintenance of b and t lymphocytes requires antiapoptotic Mcl-1. Nature 426:671–676
Chao JR, Wang JM, Lee SF et al (1998) Mcl-1 is an immediate-early gene activated by the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (gm-csf) signaling pathway and is one component of the gm-csf viability response. Mol Cell Biol 18:4883–4898
Opferman JT, Iwasaki H, Ong CC et al (2005) Obligate role of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 in the survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 307:1101–1104
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E et al (2003) Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev 17:1475–1486
Cuconati A, Mukherjee C, Perez D, White E (2003) DNA damage response and Mcl-1 destruction initiate apoptosis in adenovirus-infected cells. Genes Dev 17:2922–2932
Townsend KJ, Trusty JL, Traupman M, Eastman A, Craig RW (1998) Expression of the antiapoptotic Mcl1 gene product is regulated by a mitogen activated protein kinase-mediated pathway triggered through microtubule disruption and protein kinase c. Oncogene 17:1223–1234
Stadheim TA, Xiao H, Eastman A (2001) Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (erk) mediates cell cycle phase independent apoptosis in vinblastine-treated ml-1 cells. Cancer Res 61:1533–1540
Zhou P, Levy NB, Xie H et al (2001) Mcl1 transgenic mice exhibit a high incidence of b-cell lymphoma manifested as a spectrum of histologic subtypes. Blood 97:3902–3909
Kitada S, Reed JC (2004) Mcl-1 promoter insertions dial-up aggressiveness of chronic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 642–643
Kaufmann SH, Karp JE, Svingen PA et al (1998) Elevated expression of the apoptotic regulator Mcl-1 at the time of leukemic relapse. Blood 91:991–1000
Wuilleme-Toumi S, Robillard N, Gomez P et al (2005) Mcl-1 is overexpressed in multiple myeloma and associated with relapse and shorter survival. Leukemia 19:1248–1252
Wang J-M, Lai M-Z, Yang-Yen H-F (2003) Interleukin-3 stimulation of Mcl-1 gene transcription involves activation of the pu.1 transcription factor through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. Mol Cell Biol 23:1896–1909
Leuenroth SJ, Grutkoski PS, Ayala A, Simms HH (2000) The loss of Mcl-1 expression in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes promotes apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol 68:158–166
Huang HM, Huang CJ, Yen JJ (2000) Mcl-1 is a common target of stem cell factor and interleukin-5 for apoptosis prevention activity via mek/mapk and pi-3k/akt pathways. Blood 96:1764–1771
Kuo ML, Chuang SE, Lin MT, Yang SY (2001) The involvement of pi 3-k/akt-dependent up-regulation of Mcl-1 in the prevention of apoptosis of hep3b cells by interleukin-6. Oncogene 20:677–685
Liu H, Perlman H, Pagliari LJ, Pope RM (2001) Constitutively activated akt-1 is vital for the survival of human monocyte-differentiated macrophages. Role of Mcl-1, independent of nuclear factor (nf)-kappab, bad, or caspase activation. J Exp Med 194:113–126
Wang JM, Chao JR, Chen W et al (1999) The antiapoptotic gene Mcl-1 is up-regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt signaling pathway through a transcription factor complex containing creb. Mol Cell Biol 19:6195–6206
Puthier D, Bataille R, Amiot M (1999) Il-6 up-regulates Mcl-1 in human myeloma cells through jak/stat rather than ras/map kinase pathway. Eur J Immunol 29:3945–3950
Epling-Burnette PK, Liu JH, Catlett-Falcone R et al (2001) Inhibition of stat3 signaling leads to apoptosis of leukemic large granular lymphocytes and decreased Mcl-1 expression. J Clin Invest 107:351–362
Liu H, Ma Y, Cole SM et al (2003) Serine phosphorylation of stat3 is essential for Mcl-1 expression and macrophage survival. Blood 102:344–352
Zhang B, Potyagaylo V, Fenton RG (2003) Il-6-independent expression of Mcl-1 in human multiple myeloma. Oncogene 22:1848–1859
Bingle CD, Craig RW, Swales BM et al (2000) Exon skipping in Mcl-1 results in a bcl-2 homology domain 3 only gene product that promotes cell death. J Biol Chem 275:22136–22146
Yang T, Buchan HL, Townsend KJ, Craig RW (1996) Mcl-1, a member of the bcl-2 family, is induced rapidly in response to signals for cell differentiation or death, but not to signals for cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol 166:523–536
Yang T, Kozopas KM, Craig RW (1995) The intracellular distribution and pattern of expression of Mcl-1 overlap with, but are not identical to, those of bcl-2. J Cell Biol 128:1173–1184
Domina AM, Smith JH, Craig RW (2000) Myeloid cell leukemia 1 is phosphorylated through two distinct pathways, one associated with extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and the other with g2/m accumulation or protein phosphatase 1/2a inhibition. J Biol Chem 275:21688–21694
Domina AM, Vrana JA, Gregory MA, Hann SR, Craig RW (2004) Mcl1 is phosphorylated in the pest region and stabilized upon erk activation in viable cells, and at additional sites with cytotoxic okadaic acid or taxol. Oncogene 23:5301–5315
Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki J, Sandberg A (1986) Cytogenetic characterization of putative human myeloblastic leukemia cell lines (ml-1, -2, and -3): Origin of the cells. Cancer Res 46:3642–3647
Sundstrom C, Nilsson K (1976) Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (u-937). Int J Cancer 17:565–577
Tsuchiya S, Yamabe M, Yamaguchi Y et al. (1980) Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (thp-1). Int J Cancer 26:171–176
Namba M, Ohtsuki T, Mori M et al (1989) Establishment of five human myeloma cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 25:723–729
Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Canessa C, Cleaveland ES, Aldrich G, G F-T (1999) Sgk is an aldosterone-induced kinase in the renal cortical collecting duct. Effects on epithelial na+ channels. J Biol Chem 274:16973–16978
Vrana JA, Bieszczad CK, Cleaveland ES et al (2002) An Mcl1-overexpressing burkitt lymphoma subline exhibits enhanced survival on exposure to serum deprivation, topoisomerase inhibitors, or staurosporine but remains sensitive to 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Cancer Res 62:892–900
Townsend KJ, Zhou P, Qian L et al (1999) Regulation of Mcl1 through a serum response factor/elk-1-mediated mechanism links expression of a viability-promoting member of the bcl2 family to the induction of hematopoietic cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 274:1801–1813
Kozopas KM, Buchan HL, Craig RW (1990) Improved coupling between proliferation-arrest and differentiation-induction in ml-1 human myeloblastic leukemia cells. J Cell Physiol 145:575–586
Grant S, Turner AJ, Freemerman AJ et al (1996) Modulation of protein kinase c activity and calcium-sensitive isoform expression in human myeloid leukemia cells by bryostatin 1: Relationship to differentiation and ara-c-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 228:65–75
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ et al (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem 273:18623–18632
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR (1995) Pd098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 270:27489–27494
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW et al (2001) Sp600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of jun n-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13681–13686
Frantz B, Klatt T, Pang M et al (1998) The activation state of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase determines the efficiency of atp competition for pyridinylimidazole inhibitor binding. Biochemistry 37:13846–13853
Craig R, Frankfurt O, Sakagami H, Takeda K, Bloch A (1984) Macromolecular and cell cycle effects of different classes of agents inducing the differentiation of human myeloblastic leukemia (ml-1) cells. Cancer Res 44:2421– 2429
Epling-Burnette PK, Zhong B, Bai F et al (2001) Cooperative regulation of Mcl-1 by janus kinase/stat and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase contribute to granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-delayed apoptosis in human neutrophils. J Immunol 166:7486–7495
Edwards SW, Moulding DA, Derouet M, Moots RJ (2003) Regulation of neutrophil apoptosis. Chem Immunol Allergy 83:204–224
Leuenroth SJ, Grutkoski PS, Ayala A, Simms HH (2000) Suppression of pmn apoptosis by hypoxia is dependent on Mcl-1 and mapk activity. Surgery 128:171–177
Moulding DA, Quayle JA, Hart CA, Edwards SW (1998) Mcl-1 expression in human neutrophils: Regulation by cytokines and correlation with cell survival. Blood 92:2495–2502
Krajewski S, Bodrug S, Krajewska M et al (1995) Immunohistochemical analysis of Mcl-1 protein in human tissues. Differential regulation of Mcl-1 and bcl-2 protein production suggests a unique role for Mcl-1 in control of programmed cell death in vivo. Am J Pathol 146:1309–1319
Krajewski S, Bodrug S, Gascoyne R et al (1994) Immunohistochemical analysis of Mcl-1 and bcl-2 proteins in normal and neoplastic lymph nodes. Am J Pathol 145:515–525
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM et al (2002) Antisense strategy shows that Mcl-1 rather than bcl-2 or bcl-x(l) is an essential survival protein of human myeloma cells. Blood 100:194–199
Jourdan M, Veyrune JL, Vos JD et al (2003) A major role for Mcl-1 antiapoptotic protein in the il-6-induced survival of human myeloma cells. Oncogene 22:2950–2959
Janknecht R, Hunter T (1997) Convergence of map kinase pathways on the ternary complex factor sap-1a. EMBO J 16:1620–1627
Le Gouill S, Podar K, Harousseau JL, Anderson KC (2004) Mcl-1 regulation and its role in multiple myeloma. Cell Cycle 3:1259–1262
Chen G, Goeddel DV (2002) Tnf-r1 signaling: A beautiful pathway. Science 296:1634–1635
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM et al (2002) Antisense strategy shows that Mcl-1 rather than bcl-2 or bcl-x(l) is an essential survival protein of human myeloma cells. Blood 100:194–199
Zhang B, Gojo I, Fenton RG (2002) Myeloid cell factor-1 is a critical survival factor for multiple myeloma. Blood 99:1885–1893
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vrana, J.A., Cleaveland, E.S., Eastman, A. et al. Inducer-and cell type-specific regulation of antiapoptotic MCL1 in myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma cells exposed to differentiation-inducing or microtubule-disrupting agents. Apoptosis 11, 1275–1288 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-7787-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-7787-y