Abstract
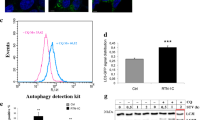
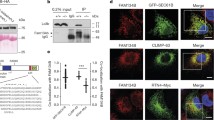
Reticulon3 (RTN3), firstly isolated from the retina and widely expressed in human tissues with the highest expression in the brain, is presumed to play an important role in the developing axons through the transport of liquids and proteins. We have identified and characterized RTN3 as a RTN4B/ASY interaction protein. Here we demonstrated that ER-stress activated RTN3 expression. CHOP and ATF6 were sufficient to up-regulate the expression of RTN3. The down-regulation of RTN3 would induce apoptosis and attenuate the anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-2, indicating RTN3 was required for the cellular survival and optimal anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-2. Our present studies also indicated ER-stress induced RTN3 up-regulation could trigger Bcl-2 translocation from ER to mitochondria. Moreover, the previous studies showed that RTN4B was also a Bcl-2-interacted protein. We found that RTN3 and RTN4B could block the access of Bcl-2 to each other and thereafter determined the Bcl-2 subcellular distribution. Taken together, our findings indicate that RTN3 is directly involved in the ER-constituents trafficking events through dually acting as an essential and important ER-stress sensor, and a trigger for the Bcl-2 translocation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufman R (1999) Stress signaling from the lumen of the ER: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes & Development 13:1211–1233
Pahl H, Baeuerle P (1997) The ER-overload response: activation of NF-κB. Trends in Biochem Sci 22:63–67
Okada T, Yoshida H, Akazawa R, Negishi M, Mori K (2002) Distinct roles of activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) and double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) in transcription during the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biochem J 366:585–594
Travers KJ, Patil CK, Wodicka L, Lockhart DJ, Weissman JS, Walter P (2000) Functional and genomic analyses reveal an essential coordination between the unfolded protein response and ER-associated degradation. Cell 101:249–258
Szczesna-Skorupa E, Chen C, Liu H, Kemper B (2004) Gene expression changes associated with the endoplasmic reticulum stress response induced by microsomal cytochrome p450 overexpression. J Biol Chem 279:13953–13961
Oertle T, Schwab W (2003) Nogo and its paRTNers. Trends in Cell Biol 13:187–194
Oertle T, Klinger M, Stuermer CA, Schwab ME (2003) A reticular rhapsody: phylogenic evolution and nomenclature of the RTN/Nogo gene family. FASEB J 17:1238–1247
Moreira E, Jaworski C, Rodriguez I (1999) Cloning of a novel member of the reticulon gene family (RTN3): gene structure and chromosomal localization to 11q13. Genomics 58:73–81
Qi B, Qi Y, Watari A et al (2003) Pro-apoptotic ASY/Nogo-B protein associates with ASYIP. J Cell Physiol 196:312–318
Kuang E, Wan Q, Li X, Xu H, Liu Q, Qi YER (2005) Ca2+ depletion triggers apoptotic signals for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) overload response induced by overexpressed reticulon 3 (RTN3/HAP). J Cell Physiol 204:549–559
Qu X, Qi Y, Lan P, Liu Q (2002) The novel endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-targeted protein HAP induces cell apoptosis by the depletion of the ER Ca2+ stores. FEBS Lett 529:325–331
Di Sano F, Fazi B, Citro G, Lovat PE, Cesareni G, Piacentini M (2003) Glucosylceramide synthase and its functional interaction with RTN-1C regulate chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis in neuroepithelioma cells. Cancer Res 63:3860–3865
Oertle T, Merkler D, Schwab M (2003) Do cancer cells die because of Nogo-B? Oncogene 22:1390–1399
Kumamaru E, Kuo C, Fujimoto T et al (2004) Reticulon 3 expression in rat optic and olfactory systems. Neurosci Lett 356:17–20
He W, Lu Y, Qahwash I, Hu XY, Chang A, Yan R (2004) Reticulon family members modulate BACE1 activity and amyloid-beta peptide generation. Nat Med 10:959–965
Tagami S, Eguchi Y, Kinoshita M, Takeda M, Tsujimoto Y (2000) A novel protein, RTN-XS, interacts with both Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 on endoplasmic reticulum and reduces their anti-apoptotic activity. Oncogene 19:5736–5746
McCullough K, Martindale J, Klotz L, Aw T, Holbrook N (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21:1249–1259
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K et al (2000) ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 20:6755–6767
Wattenberg B, Lithgow T (2001) Targeting of C-terminal (tail)-anchored proteins: understanding how cytoplasmic activities are anchored to intracellular membranes. Traffic 2:66–71
Snapp EL, Hegde RS, Francolini M et al (2003) Formation of stacked ER cisternae by low affinity protein interactions. J Cell Biol 163:257–269
Xiang R, Liu Q, Zhu L et al (2006) Adaptor FADD is recruited by RTN3/HAP in ER-bound signaling complexes. Apoptosis In Press
Oyadomari S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Apoptosis 7:335–345
Di Scala F, Dupuis L, Gaiddon C et al (2004) Tissue specificity and regulation of the amino-terminal diversity of reticulon 3. Biochem J 385:125–134
Di Scala F, Dupuis L, Rene F, De Tapia M, Pradat P-Fmeininger V, Loeffler J (2003) Loss of spinal reticulon 3 contributes to neuronal death in ALS. ALS and other motor neuron disorders 4:66–70
Ho Y (2002) Systematic identification of protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry. Nature 415:180–183
Iwahashi J, Hamada N (2003) Human reticulon 1-A and 1-B interact with a medium chain of the AP-2 adaptor complex. Cell Mol Biol 49:467–471
Iwahashi J, Kawasaki I, Kohara Y et al (2002) Caenorhabditis elegans reticulon interacts with RME-1 during embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:698–704
Steiner P, Kulangara K, Sarria JC, Glauser L, Regazzi R, Hirling H (2004) Reticulon 1-C/neuroendocrine-specific protein-C interacts with SNARE proteins. J Neurochem 89:569–580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Q. Wan and E. Kuang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Q., Kuang, E., Dong, W. et al. Reticulon 3 mediates Bcl-2 accumulation in mitochondria in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis 12, 319–328 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0574-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0574-y