Abstract
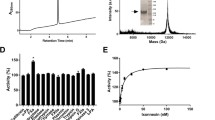
Blood-sucking arthropods have different types of anticoagulants to allow the ingestion of a blood meal from their hosts. In this study, five anticoagulants prolonging the activated partial thromboplastin time were resolved from the salivary gland crude extract of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii by chromatography on diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-cellulose column. They were designated P1, P2, P3, P4 and P5 according to their elution order. P5 was found to be a potent thrombin inhibitor and purified by ultrafiltration through two centrifugal concentrators of 50 and 30 kDa molecular weight cut-off (MWCO), respectively. The camel tick salivary gland thrombin inhibitor was purified 60.6 folds with a specific activity of 564 units/mg protein. It turned out to be homogenous on native-PAGE with molecular weight of 36 kDa as detected on 12% SDS-PAGE. It inhibits bovine thrombin competitively with K i value of 0.55 μM. A task for the future will be the elucidation of this thrombin inhibitor structure to allow its application in thrombosis treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APTT:
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DEAE:
-
Diethylaminoethyl
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid
- FXa:
-
Activated factor X
- MWCO:
-
Molecular weight cut-off
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- SBTI:
-
Soybean trypsin inhibitor
References
Abebe M, Cupp MS, Ramberg FB, Cupp EW (1994) Anticoagulant activity in salivary gland extracts of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). J Med Entomol 31:908–911
Andersen JF, Gudderra NP, Francischetti IM, Valenzuela JG, Ribeiro JM (2004) Recognition of anionic phospholipid membranes by an antihemostatic protein from a blood-feeding insect. Biochemistry 43:6987–6994
Becker U, Jering H, Roschlau P (1984) Coagulation methods. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 5. Academic Press, New York, pp 486–499
Bowman AS, Sauer JR, Zhu K, Dillwith JW (1995) Biosynthesis of salivary prostaglandins in the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:225–233
Bowman AS, Dillwith JW, Sauer JR (1996) Tick salivary prostaglandins: presence, origin and significance. Parasitol Today 12:388–396
Bowman AS, Coons LB, Needham GR, Sauer JR (1997) Tick saliva: Recent advances and implications for vector competence. Med Vet Entomol 3:277–285
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Ciprandi A, Kobe de Oliveira S, Masuda A, Horn F, Termignoni C (2006) Boophilus microplus: its saliva contains microphilin, a small thrombin inhibitor. Exp Parasitol 114:40–46
Ehebauer MT, Mans BJ, Gaspar AR, Neitz AW (2002) Identification of extrinsic blood coagulation pathway inhibitors from the tick Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari: Argasidae). Exp Parasitol 101:138–148
Erlanger BF, Kokowsky N, Cohen W (1961) Preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:271–278
Erlanger BF, Cooper AG, Bendisch AJ (1964) The heterogenity of three times crystallized a-chymotrypsin. Biochemistry 3:1880–1883
Francischetti IM, Valenzuela JG, Andersen JF, Mather TN, Ribeiro JM (2002) Ixolaris, a novel recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) from the salivary gland of the tick, Ixodes scapularis: identification of factor X and factor Xa as scafolds for the inhibition of factor VIIa/tissue factor complex. Blo 99:3602–3612
Friedrich T, Kroger B, Bialojan S, Lemaire HG, Hoffken HW, Reuschenbach P, Otte M, Dodt J (1993) A Kazal-type inhibitor with thrombin specificity from Rhodnius prolixus. J Biol Chem 268:16216–16222
Gaspar ARM, Crause JC, Neitz AWH (1995) Identification of anticoagulant activities in the salivary glands of the soft tick, Ornithodoros savignyi. Exp Appl Acarol 19:117–126
Guglielmone AA, Robbing RG, Apanaskevich DA, Petney TN, Estrada-Peña A, Horak IG, Shao R, Barker SC (2010) The Argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida) of the world: a list of valid species names. Zootaxa 2528:1–28
Hoffmann A, Walsmann P, Riesener G, Paintz M, Markwardt F (1991) Isolation and characterization of a thrombin inhibitor from the tick Ixodes ricinus. Pharm 46:209–212
Horn F, Dos Santos P, Termignoni C (2000) Boophilus microplus anticoagulant protein: an antithrombin inhibitor isolated from the cattle tick saliva. Arch Biochem Bioph 384:68–73
Ibrahim MA, Ghazy AM, Maharem T, Khalil M (2001) Isolation and properties of two forms of thrombin inhibitor from the nymphs of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 25:675–698
Iwanaga S, Okada M, Isawa H, Morita A, Yuda M, Chinzei Y (2003) Identification and characterization of novel salivary thrombin inhibitors from the ixodidae tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Eur J Biochem 270:1926–1934
Joubert AM, Crause JC, Gaspar AR, Clarke FC, Spickett AM, Neitz AW (1995) Isolation and characterization of an anticoagulant present in the salivary glands of the bont-legged tick, Hyalomma truncatum. Exp Appl Acarol 19:79–92
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of Bacteriophage T4. Nat 227:680–685
Lai R, Takeuchi H, Jonczy J, Rees HH, Turner PC (2004) A thrombin inhibitor from the ixodid tick, Amblyomma hebraeum. Gene 342:243–249
Mans BJ, Neitz AW (2004) Adaptation of ticks to a blood-feeding environment: evolution from a functional perspective. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 34:1–17
Mans BJ, Gaspar AR, Louw AI, Neitz AW (1998) Apyrase activity and platelet aggregation inhibitors in the tick Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari: Argasidae). Exp Appl Acarol 22:353–366
Maritz-Olivier C, Stutzer C, Jongejan F, Neitz AWH, Gaspar ARM (2007) Tick anti-hemostatics: targets for future vaccines and therapeutics. Trends Parasitol 23(9):397–407
Nienaber J, Gaspar AR, Neitz AW (1999) Savignin, a potent thrombin inhibitor isolated from the salivary glands of the tick Ornithodoros savignyi (Acari: Argasidae). Exp Parasitol 93:82–91
Rabilloud T, Carpenter G, Tarroux P (1988) Improvement and simplification of low-background silver staining of proteins by using sodium dithionite. Electroph 9:288–291
Ribeiro JM (1987) Ixodes dammini: salivary anti-complement activity. Exp Parasitol 64:347–353
Ribeiro JM, Francischetti IM (2003) Role of arthropod saliva in blood feeding: sialome and post-sialome perspectives. Ann Rev Entomol 48:73–88
Ribeiro JMC, Evans PM, Mc Swain JL, Sauer JR (1992) Amblyomma americanum: characterization of salivary prostaglandins E2 and F2α by RP-HPLC/bioassay and gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Exp Parasitol 74:112–116
Ricci CG, Pinto AFM, Berger M, Termignoni C (2007) A thrombin inhibitor from the gut of Boophilus microplus ticks. Exp Appl Acarol 42:291–300
Ryle AP (1970) The porcine pepsins and pepsinogens. Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York, pp 316–336
Sauer JRRC, Essenberg RC, Bowman AS (2000) Salivary glands in ixodid ticks: control and mechanism of secretion. J Ins Physiol 46:1069–1078
Smith I (1969) Acrylamide gel disc electrophoresis. In: Smith I (ed) Electrophoretic techniques. Academic Press, New York, pp 365–515
Sonenshine DE (1991) Biology of ticks. Oxford University Press, New York
Stark KR, James AA (1995) A factor Xa-directed anticoagulant from the salivary glands of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. Exp Parasitol 81:321–331
Strube KH, Kroger B, Bialojan S, Otte M, Dodt J (1993) Isolation, sequence analysis, and cloning of haemadin. An anticoagulant peptide from the Indian leech. J Biol Chem 268:8590–8595
Weber K, Osborn M (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem 244:4406–4412
Wikel SK, Ramachandra RN, Bergman DK, Burkot TR, Piesman J (1997) Infestation with pathogen-free nymphs of the tick Ixodes scapularis induces host resistance to transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi by ticks. Infect Immun 65:335–338
Williams TJ, Peck MJ (1977) Role of prostaglandin mediated vasodilation in inflammation. Nat 270:530–532
Zhu K, Bowman AS, Brigham DL, Essenberg RC, Dillwith JW, Sauer JR (1997) Isolation and characterization of americanin, a specific inhibitor of thrombin, from the salivary glands of the lone star tick Amblyomma americanum (L.). Exp Parasitol 87:30–38
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Research Centre, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim, M.A., Masoud, H.M.M. Thrombin inhibitor from the salivary gland of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii . Exp Appl Acarol 74, 85–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-017-0196-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-017-0196-9