Abstract
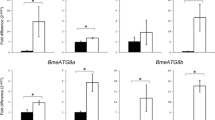
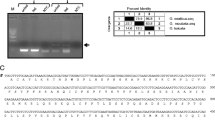
Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus is an obligate haematophagous arthropod and the major problem for cattle industry due to economic losses it causes. The parasite shows a remarkable adaptability to changing environmental conditions as well as an exceptional ability to survive long-term starvation. This ability has been related to a process of intracellular protein degradation called autophagy. This process in ticks is still poorly understood and only few autophagy-related (ATG) genes have been characterized. The aim of the present study was to examine the ESTs database, BmiGI, of R. microplus searching for ATG homologues. We predicted five putative ATG genes, ATG3, ATG4, ATG6 and two ATG8s. Further characterization led to the identification of RmATG8a and RmATG8b, homologues of GABARAP and MAP1LC3, respectively, and both of them belonging to the ATG8 family. PCR analyses showed that the expression level of RmATG8a and RmATG8b was higher in egg and larval stages when compared to ovary and midgut from adult ticks. This up-regulation coincides with the period in which ticks are in a starvation state, suggesting that autophagy is active in R. microplus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
da Silva VIJr, Imamura S, Nakajima C, de Cardoso FC, Ferreira CAS, Renard G, Masuda A, Ohashi K, Onuma M (2005) Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding for Boophilus microplus, Haemaphysalis longicornis and Rhipicephalus appendiculatus actins. Vet Parasitol 127:147–155
Davey RB, Garza J, Thompson GD, Drummond RO (1980) Ovipositional biology of the southern cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae), in the laboratory. J Med Entomol 17:117–121
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker John M (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Humana Press, New York, pp 571–607
Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rousseau ME, Sunkara S, Quackenbush J, Lee Y, Nene V (2005) BmiGI: a database of cDNAs expressed in Boophilus microplus, the tropical/southern cattle tick. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35:585–595
Kawano S, Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Boldbaatar D, Matsuoka K, Tanaka T, Fujisaki K (2011) Cloning and characterization of the autophagy-related gene 6 from the hard tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Parasitol Res 109:1341–1349
Klionsky DJ, Schulman BA (2014) Dynamic regulation of macroautophagy by distinctive ubiquitin-like proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:336–345
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Le Grand JN, Bon K, Fraichard A, Zhang J, Jouvenot M, Risold PY, Boyer-Guittaut M, Delage-Mourroux R (2013) Specific distribution of the autophagic protein GABARAPL1/GEC1 in the developing and adult mouse brain and identification of neuronal populations expressing GABARAPL1/GEC1. PLoS One 8(5):e63133 15
Lilienbaum A (2013) Relationship between the proteasomal system and autophagy. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 4:1–26
Malagoli D, Abdalla FC, Cao Y, Feng Q, Fujisaki K, Gregorc A, Matsuo T, Nezis IP, Papassideri IS, Sass M, Silva-Zacarin ECM, Tettamanti G, Umemiya-Shirafuji R (2010) Autophagy and its physiological relevance in arthropods: current knowledge and perspectives. Autophagy 6:575–588
Nijhof AM, Balk JA, Postigo M, Jongejan F (2009) Selection of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks and determination of the expression profile of Bm86. BMC Mol Biol 10:112
Ribeiro VLS, Toigo E, Bordignon AL, Gonçalves K, von Poser G (2007) Acaricidal properties of extracts from the aerial parts of Hypericum polyanthemum on the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Vet Parasitol 147:199–203
Rosario-Cruz R, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Dominguez-García DI, Cornel AJ, Hernandez-Ortiz R, George JE (2005) Roles played by esterase activity and by a sodium channel mutation involved in pyrethroid resistance in populations of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from Yucatan, Mexico. J Med Entomol 42:1020–1025
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 365–386
Ryter SW, Cloonan SM, Choi AMK (2013) Autophagy: a critical regulator of cellular metabolism and homeostasis. Mol Cells 36:7–16
Shpilka T, Weidberg H, Pietrokovski S, Elazar Z (2011) Atg8: an autophagy-related ubiquitin-like protein family. Genome Biol 12(7):226
Spickler AR (2007) Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/DiseaseInfo/factsheets.php. Accessed 3 Oct 2013
Tsuda A, Mulenga A, Sugimoto C, Nakajima M, Ohashi K, Onuma M (2001) cDNA cloning, characterization and vaccine effect analysis of Haemaphysalis longicornis tick saliva proteins. Vaccine 19:4287–4296
Umemiya R, Matsuo T, Hatta T, Sakakibara S, Boldbaatar D, Fujisaki K (2007) Cloning and characterization of an autophagy-related gene, ATG12, from the three-host tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:975–984
Umemiya R, Matsuo T, Hatta T, Sakakibara S, Boldbaatar D, Fujisaki K (2008) Autophagy-related genes from a tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis. Autophagy 4:79–81
Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Matsuo T, Liao M, Boldbaatar D, Battur B, Suzuki H, Fujisaki K (2010) Increased expression of ATG genes during nonfeeding periods in the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Autophagy 6:473–481
Umemiya-Shirafuji R, Linggatong RG, Maeda H, Kawano S, Tanaka T, Fukumoto S, Suzuki H, Tsuji N, Fujisaki K (2014) Expression analysis of autophagy-related genes in the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Vet Parasitol 201:169–175
Yoshimoto K, Hanaoka H, Sato S, Kato T, Tabata S, Noda T, Ohsumi Y (2004) Processing of ATG8s, ubiquitin-like proteins, and their deconjugation by ATG4 s are essential for plant autophagy. Plant Cell 16:2967–2983
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant SEP-CONACYT-CB-2008-01-104006 from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología México to M.M.V. J.M.F.F. received a scholarship from CONACYT. We thank Tina Coop of Peace Corps México for the critical review of the language of the manuscript. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. All experiments comply with the current laws of Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flores Fernández, J.M., Gutiérrez Ortega, A., Rosario Cruz, R. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of two novel autophagy-related genes belonging to the ATG8 family from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 64, 533–542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-014-9838-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-014-9838-3