Abstract
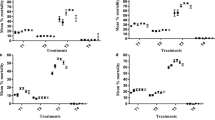
Traditionally estimating pesticide effects by measuring only lethal effect may underestimate the total negative effect on beneficial arthropods and sublethal effects should be assessed to estimate the total effect of their applications. In this study, sublethal effect of the acaricide abamectin (Vermectin® 1.8% EC, Giah, Iran) on the predatory mite Phytoseius plumifer (Canestrini & Fanzago) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) fed on Tetranychus urticae Koch was assessed in laboratory conditions. The adult predators were exposed to the residues of the acaricide on fig leaves and the LC50 value was determined based on a concentration–response analysis. The results showed that sublethal concentrations (LC10, LC20 and LC30) of abamectin severely affected the fecundity and longevity of the treated females of P. plumifer. Furthermore, reproductive and life table parameters of the subsequent generation were affected. The results indicated that adverse effects of abamectin on population growth of P. plumifer were significant, so the results from this study can be used to develop approximate guidelines for the use of abamectin in order to minimize their impact on P. plumifer and related natural enemies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Animal Ecol 17:15–26
Bostanian NJ, Akalach M (2006) The effect of indoxacarb and five other insecticides on Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae), Amblyseius fallacies (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and nymph of Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Pest Manag Sci 62:334–339
Bostanian NJ, Trudeau M, Lasnier J (2003) Management of the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) in eggplant fields. Phytoprotection 84:1–8
Brattsten LB, Holyoke CW, Leeper JR et al (1986) Insecticide resistance: challenge to pest management and basic research. Science 231:1255–1260
Carey JR (1993) Applied demography for biologists. Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford, p 211
Chen T, French JV, Liu T et al (2003) Residual toxicities of pesticides to the predaceous mite Galendromus helveolus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on Texas citrus. Subtrop Plant Sci 55:40–45
Cote KW, Lewis EE, Schultz PB (2002) Compatibility of acaricide residues with Phytoseiulus persimilis and their effects on Tetranychus urticae. Hortsci 37:906–909
Croft BA (1990) Arthropod biological control agents and pesticides. John Wiley, New York
Elzen GW (2001) Lethal and sublethal effects of insecticide residues on Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) and Geocoris punctipes (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae). J Econ Entomol 94:55–59
Frank R, Braun HE, Ripely BD, Clegg BS (1990) Contamination of rural ponds with pesticides, 1971–85, Ontario. Canada Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 44:401–409
Galvan TL, Koch RL, Hutchison WD (2005) Effects of spinosad and indoxacarb on survival, development, and reproduction of the multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 34:108–114
Grafton-Cardwell EE, Hoy MA (1983) Comparative toxicity of avermectin B1 to the predator Metaseiulus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and the spider mites Tetranychus urticae Koch and Panonychus ulmi (Koch) (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Econ Entomol 76:1216–1220
Hamedi N, Fathipour Y, Saber M, Sheikhi Gargan A (2009) Sublethal effects of two common acaricides on the consumption of Tetranychus urticae (Prostigmata: Tetranychidae) by Phytoseius plumifer (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae). Syst Appl Acarol 14:197–205
Hamedi N, Fathipaur Y, Saber M (2010) Sublethal effects of fenpyroximate on life table parameters of the predatory mite Phytoseius plumifer. Biocontrol 55:271–278
Hoy MA, Cunningham GL, Knutson L (1983) Biological control of pests by mites. Univ Calif Div Agric Nat Res Publ, Berkeley, CA
Ibrahim YB, Yee TS (2000) Influence of sublethal exposure to abamectin on the biological performance of Neoseiulus longispinosus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). J Econ Entomol 93:1085–1089
Jeppson LR, Keifer HH, Baker EW (1975) Mites injurious to economic plants. University of California Press, Berkeley CA
Kim DS, Brooks DJ, Riedl R (2006) Lethal and sublethal effects of abamectin, spinosad, methoxyfenozide and acetamiprid on the predaceous plant bug Deraeocoris brevis in the laboratory. Biocontrol 51:465–484
Kreiter S, Sentenac G, Weber M, Valentin G (1993) Les Phytoseiidae des vignobles français. Synthèse de 8 années de recensement. In: Ledent F, Reboulet J-N (eds) Proceedings of the third international conference on pests in agriculture. ANPP pub, Paris, pp 597–609
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Camponhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life-table parameters using Jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Marcic D (2005) Sublethal effects of tebufenpyrad on the eggs and immatures of two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. Exp Appl Acarol 36:177–185
Marcic D (2007) Sublethal efects of spirodiclofen on life history and life-table parameters of two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae). Exp Appl Acarol 42:121–129
Nadimi A, Kamali K, Arbabi M, Abdoli F (2009) Selectivity of three miticides to spider mite predator, Phytoseius plumifer (Acari: Phytoseiidae) under laboratory conditions. Agric Sci China 8:326–331
Pielou EC (1977) Mathematical Ecology. Wiley/Interscience, New York
Roush RT (1989) Designing resistance management programs: how can you choose? Pestic Sci 26:423–441
Sáenz-de-Cabezón Irigaray FJ, Zalom FG, Thompson PB (2007) Residual toxicity of acaricides to Galendromus occidentalis and Phytoseiulus persimilis reproductive potential. Bio Control 40:153–159
Sanderson JP, Zhang ZQ (1995) Dispersion, sampling, and potential for integrated control of two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae) on greenhouse roses. J Econ Entomol 88:343–351
SAS Institute (2002) SAS software version 9.0. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Shipp JL, Wang K, Ferguson G (2000) Residual toxicity of avermectin b1 and pyridaben to eight commercially produced beneficial arthropod species used for control in greenhouse pests. Biol Control 17:125–131
Sim C (2000) Genetics and fitness of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) resistance to abamectin and pyridaben. M. S. thesis, Korea University, Seoul, Korea
Stark JD, Jepson PC, Mayer DF (1995) Limitations to use of topical toxicity data for predictions of pesticide side effects in the fields. J Econ Entomol 88:1081–1088
Strong L, Brown TA (1987) Avermectins in insect control and biology: a review. Bull Entomol Res 77:357–389
Zaher MA, Wafa AK, Shehata KK (1969) Life history of the predatory mite Phytoseius plumifer and the effect of nutrition on its biology (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Entomol Exp Appl 12:383–388
Zhang Z, Sanderson JP (1990) Relative toxicity of abamectin to the predatory mite Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). Annu Rev Entomol 83:1783–1790
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by a grant (No. 84-63) from the Iran National Science Foundation and partly from Tarbiat Modares University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamedi, N., Fathipour, Y. & Saber, M. Sublethal effects of abamectin on the biological performance of the predatory mite, Phytoseius plumifer (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 53, 29–40 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-010-9382-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-010-9382-8