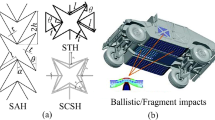
Abstract
Auxetic honeycomb structures are promising metamaterials with outstanding mechanical properties, and can be potentially used in energy absorption applications. In this study, a novel modified re-entrant hybrid auxetic metamaterial inspired by Islamic motif art is designed by integrating four-pointed double re-entrant motifs with symmetric semi-hexagonal unit cells to achieve a high energy absorption capacity (EAC). Theoretical analyses and numerical simulations are performed to examine the dynamic crushing behavior of the four-pointed double re-entrant combined structure (FDRCS). The developed finite element models (FEMs) are validated by the experiments under quasi-static compression. The deformation mode and stress-strain curves are further studied under low, medium, and high crushing velocities. The theoretically predicted plateau stress of the FDRCS under different crushing velocities is consistent with the numerical simulation results. The crushing stress and the EAC of the FDRCS are influenced by the geometric parameters and crushing velocities. The FDRCS exhibits a negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR), owing to the four-point re-entrant structure (RES). Moreover, the specific energy absorption (SEA) of these structures is higher than that of nonauxetic hexagonal and auxetic re-entrant structures, owing to the generation of more plastic hinges that dissipate more energy during dynamic crushing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BIAN, Y. J., LI, P. H., YANG, F., WANG, P., LI, W. W., and FAN, H. L. Deformation mode and energy absorption of polycrystal-inspired square-cell lattice structures. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 41(10), 1561–1582 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2648-8
ZHANG, J. X. and GUO, H. Y. Low-velocity impact of rectangular foam-filled fiber metal laminate tubes. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 42(12), 1733–1742 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2799-7
WANG, T., AN, J. H., HE, H., WEN, X., and XI, X. L. A novel 3D impact energy absorption structure with negative Poisson’s ratio and its application in aircraft crashworthiness. Composite Structures, 262, 113663 (2021)
LU, H., WANG, X. P., and CHEN, T. N. In-plane dynamics crushing of a combined auxetic honeycomb with negative Poisson’s ratio and enhanced energy absorption. Thin-Walled Structures, 160, 107366 (2021)
LINFORTH, S., NGO, T., TRAN, P., RUAN, D., and ODISH, R. Investigation of the auxetic oval structure for energy absorption through quasi-static and dynamic experiments. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 147, 103741 (2021)
DALELA, S., BALAJI, P. S., and JENA, D. P. A review on application of mechanical metamaterials for vibration control. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 29(22), 3237–3262 (2022)
HRISHIKESH, G. M., SHAMMO, D., ARAVIND, K., HARIPRASAD, M. P., and BALAKRISHNAN, S. Proposed auxetic cluster designs for lightweight structural beams with improved load bearing capacity. Engineering Structures, 260, 114241 (2022)
QI, C., JIANG, F., YANG, S., REMENNIKOV, A., CHEN, S., and DING, C. Dynamic crushing response of novel re-entrant circular auxetic honeycombs: numerical simulation and theoretical analysis. Aerospace Science and Technology, 124, 107548 (2022)
HANNA, B., ADAMS, R., TOWNSEND, S., ROBINSON, M., SOE, S., STEWART, M., BUREK, R., and THEOBALD, P. Auxetic metamaterial optimisation for head impact mitigation in American football. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 157, 103991 (2021)
CHOUDHRY, N. K., PANDA, B., and KUMAR, S. In-plane energy absorption characteristics of a modified re-entrant auxetic structure fabricated via 3D printing. Composites Part B: Engineering, 228, 109437 (2022)
AN, M. R., WANG, L., LIU, H. T., and REN, F. G. In-plane crushing response of a novel bidirectional re-entrant honeycomb with two plateau stress regions. Thin-Walled Structures, 170, 108530 (2022)
CHEN, Y. and WANG, Z. W. In-plane elasticity of the re-entrant auxetic hexagonal honeycomb with hollow-circle joint. Aerospace Science and Technology, 123, 107432 (2022)
MATHEUS, B. F., JOÃO, L. J. P., GUILHERME, A. O., LUCAS, R. R. D. S., SEBASTIÃO, S. C. J., and GUILHERME, F. G. A review on the energy absorption response and structural applications of auxetic structures. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 29, 3237–3262 (2022)
FATIH, U., HALIT, S. T., and FABRIZIO, S. High-velocity impact resistance of doubly curved sandwich panels with re-entrant honeycomb and foam core. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 165, 104230 (2022)
WANG, H., LU, Z. X., YANG, Z. Y., and LI, X. A novel re-entrant auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane impact resistance. Composite Structures, 208, 758–770 (2019)
KRISHNA, P. L., VELMURUGAN, R., JAYAGANTHAN, R., ZHANYUAN, G., and RUAN, D. Quasi-static and dynamic compression behaviors of a novel auxetic structure. Composite Structures, 254, 112853 (2020)
JIANG, F., YANG, S., QI, C., and LIU, H. T. Two plateau characteristics of re-entrant auxetic honeycomb along concave direction. Thin-Walled Structures, 179, 109665 (2022)
LIM, T. C. Metacomposite structure with sign-changing coefficients of hygrothermal expansions inspired by Islamic motif. Composite Structures, 251, 12660 (2020)
LIM, T. C. Composite metamaterial square grids with sign-flipping expansion coefficients leading to a type of Islamic design. SN Applied Sciences, 2(5), 918 (2020)
JIANG, H. Y., REN, Y. R., JIN, Q. D., ZHU, G. H., HU, Y. S., and CHENG, F. Crashworthiness of novel concentric auxetic reentrant honeycomb with negative Poisson’s ratio biologically inspired by coconut palm. Thin-Walled Structures, 154, 106911 (2020)
DENG, T. C., WEN, G. L., DING, H., LU, Z. Q., and CHEN, L. Q. A bio-inspired isolator based on characteristics of quasi-zero stiffness and bird multi-layer neck. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 145, 106967 (2020)
PARK, Y. J., GIANMARCO, V., and KENNETH, J. L. Bio-inspired active skins for surface morphing. Scitific Reports, 9(1), 18609 (2019)
MA, Q., CHENG, H. Y., JANG, K. I., LUAN, H. W., HWANG, K. C., ROGERS, J. A., HUANG, Y. G., and ZHANG, Y. H. A nonlinear mechanics model of bio-inspired hierarchical lattice materials consisting of horseshoe microstructures. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 90, 179–202 (2016)
LIM, T. C. Metacomposite with auxetic and in situ sign reversible thermal expansivity upon temperature fluctuation. Composites Communications, 19, 30–36 (2020)
ZHANG, Z. W., TIAN, R. L., ZHANG, X. L., WEI, F. Y., and YANG, X. W. A novel butterfly-shaped auxetic structure with negative Poisson’s ratio and enhanced stiffness. Journal of Materials Science, 56(25), 14139–14156 (2021)
HA, N. S. and LU, G. X. A review of recent research on bio-inspired structures and materials for energy absorption applications. Composites Part B: Engineering, 181, 107496 (2020)
RAFSANJANI, A. and PASINI, D. Bistable auxetic mechanical metamaterials inspired by ancient geometric motifs. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 9, 291–296 (2016)
LIM, T. C. An auxetic system based on interconnected y-elements inspired by Islamic geometric patterns. Symmetry, 13(5), 865 (2021)
ZHANG, X. L., TIAN, R. L., ZHANG, Z. W., LI, G. J., and FENG, W. J. In-plane elasticity of a novel vertical strut combined re-entrant honeycomb structure with negative Poisson’s ratio. Thin-Walled Structures, 163, 107634 (2021)
ZHANG, X. L., HAO, H. N., TIAN, R. L., XUE, Q., GUAN, H. T., and YANG, X. W. Quasi-static compression and dynamic crushing behaviors of novel hybrid re-entrant auxetic metamaterials with enhanced energy-absorption. Composite Structures, 288, 115399 (2022)
ALOMARAH, A., MASOOD, S. H., SBARSKI, I., FAISAL, B., GAO, Z., and RUAN, D. Compressive properties of 3D printed auxetic structures: experimental and numerical studies. Virtual and Physical Prototyping, 15(1), 1–21 (2019)
ZOU, Z., REID, S. R., TAN, P. J., LI, S., and HARRIGAN, J. J. Dynamic crushing of honeycombs and features of shock fronts. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 36(1), 165–176 (2009)
XIAO, D. B., KANG, X., LI, Y., WU, W. W., LU, J. R., ZHAO, G. P., and FANG, D. N. Insight into the negative Poisson’s ratio effect of metallic auxetic reentrant honeycomb under dynamic compression. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 763, 138151 (2019)
LIU, W. Y., WANG, N. L., LUO, T., and LIN, Z. Q. In-plane dynamic crushing of re-entrant auxetic cellular structure. Materials & Design, 100, 84–91 (2016)
LI, X., GAO, L. B., ZHOU, W. Z., WANG, Y. J., and LU, Y. Novel 2D metamaterials with negative Poisson’s ratio and negative thermal expansion. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 30, 100498 (2019)
RAD, M. S., HATAMI, H., ALIPOURI, R., NEJAD, A. F., and OMIDINASAB, F. Determination of energy absorption in different cellular auxetic structures. Mechanics & Industry, 20(302), 1–11 (2019)
QI, C., JIANG, F., and YANG, S. Advanced honeycomb designs for improving mechanical properties: a review. Composites Part B: Engineering, 227, 09393 (2021)
ZHANG, J. J., LU, G. X., and YOU, Z. Large deformation and energy absorption of additively manufactured auxetic materials and structures: a review. Composites Part B: Engineering, 201, 108340 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: TIAN, R. L., GUAN, H. T., LU, X. H., ZHANG, X. L., HAO, H. N., FENG, W. J., and ZHANG, G. L. Dynamic crushing behavior and energy absorption of hybrid auxetic metamaterial inspired by Islamic motif art. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 44(3), 345–362 (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-023-2962-9
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12102274, 12072203, and 11872253), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (No. A2022210005), and the Central Guidance on Local Science and Technology Development Fund of Hebei Province of China (No. 226Z4901G)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, R., Guan, H., Lu, X. et al. Dynamic crushing behavior and energy absorption of hybrid auxetic metamaterial inspired by Islamic motif art. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 44, 345–362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-023-2962-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-023-2962-9