Abstract
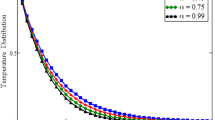
The wavelet approach is introduced to study the influence of the natural convection stagnation point flow of the Williamson fluid in the presence of thermophysical and Brownian motion effects. The thermal radiation effects are considered along a permeable stretching surface. The nonlinear problem is simulated numerically by using a novel algorithm based upon the Chebyshev wavelets. It is noticed that the velocity of the Williamson fluid increases for assisting flow cases while decreases for opposing flow cases when the unsteadiness and suction parameters increase, and the magnetic effect on the velocity increases for opposing flow cases while decreases for assisting flow cases. When the thermal radiation parameter, the Dufour number, and Williamson’s fluid parameter increase, the temperature increases for both assisting and opposing flow cases. Meanwhile, the temperature decreases when the Prandtl number increases. The concentration decreases when the Soret parameter increases, while increases when the Schmidt number increases. It is perceived that the assisting force decreases more than the opposing force. The findings endorse the credibility of the proposed algorithm, and could be extended to other nonlinear problems with complex nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- λ:
-
Buoyancy effect due to the temperature difference
- λ*:
-
Buoyancy effect due to the concentration difference
- k*:
-
coefficient of the mean absorption
- β C :
-
coefficient of the concentration expansion
- ρ :
-
density of the fluid
- σ :
-
electrical conductivity
- M :
-
Hartmann number
- B :
-
magnetic field strength
- T m :
-
mean fluid temperature
- c s :
-
ratio of the thermal diffusion
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- r :
-
stagnation point parameter
- Sr :
-
Soret number
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- A :
-
unsteadiness parameter
- σ*:
-
Boltzmann constant
- k T :
-
concentration susceptibility
- Γ:
-
coefficient of the Williamson fluid
- β T :
-
coefficient of thermal expansion
- Du :
-
Dufour number
- g :
-
gravitational acceleration
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity
- D B :
-
mass diffusivity coefficient
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- R :
-
ratio of λ* to λ
- c p :
-
specific heat
- S :
-
suction parameter
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number
- Rd :
-
thermal radiation
- Λ:
-
Williamson fluid parameter
References
HIEMENZ, K. Die grenzschicht an einem in den gleichförmigen Flüssigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder. Dingler’s Polytechnic Journal, 326, 321–324 (1911)
HOMANN, F. and ANGEW, Z. Der einfluss grosser Zähigkeit bei der Strömung um den zylinder und um die Kugel. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 16, 153–164 (1936)
MAKINDE, O. D., KHAN, W. A., and KHAN, Z. H. Buoyancy effects on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a convectively heated stretching/shrinking sheet. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 62, 526–533 (2013)
HAQ, R. U., NADEEM, S., KHAN, Z. H., and AKBAR, N. S. Thermal radiation and slip effects on MHD stagnation point flow of nanofluid over a stretching sheet. Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 65, 17–23 (2015)
HAYAT, T., KHAN, M. I., WAQAS, M., ALSAEDI, A., and FAROOQ, M. Numerical simulation for melting heat transfer and radiation effects in stagnation point flow of carbon-water nanofluid. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 315, 1011–1024 (2017)
TARAKARAMU, N. and NARAYANA, P. V. Nonlinear thermal radiation and Joule heating effects on MHD stagnation point flow of a nanofluid over a convectively heated stretching surface. Journal of Nanofluids, 8, 1066–1075 (2019)
PAL, D. Heat and mass transfer in stagnation-point flow towards a stretching surface in the presence of buoyancy force and thermal radiation. Meccanica, 44, 145–158 (2009)
USMAN, M., ZUBAIR, T., HAMID, M., HAQ, R. U., and WANG, W. Wavelets solution of MHD 3-D fluid flow in the presence of slip and thermal radiation effects. Physics of Fluids, 30, 023104 (2018)
MOHYUD-DIN, S. T., USMAN, M., AFAQ, K., HAMID, M., and WANG, W. Examination of carbon-water nanofluid flow with thermal radiation under the effect of Marangoni convection. Engineering Computations, 34, 2330–2343 (2017)
HAYAT, T., QASIM, M., SHEHZAD, S. A., and ALSAEDI, A. Unsteady stagnation point flow of second grade fluid with variable free stream. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 53, 455–461 (2014)
BOULAHIA, Z., WAKIF, A., and SEHAQUI, R. Heat transfer and cu-water nanofluid flow in a ventilated cavity having central cooling cylinder and heated from the below considering three different outlet port locations. Frontiers in Heat and Mass Transfer, 11, 11 (2018)
SAIDUR, R., LEONG, K. Y., and MOHAMMAD, H. A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 1646–1668 (2011)
CHOI, S. U. S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows, Springer, New York (1995)
BUONGIORNO, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. Journal of Heat Transfer, 128, 240–250 (2006)
TIWARI, R. K. and DAS, M. K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 50, 2002–2018 (2007)
HAYAT, T., ABBASI, F. M., AL-YAMI, M., and MONAQUEL, S. Slip and Joule heating effects in mixed convection peristaltic transport of nanofluid with Soret and Dufour effects. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 194, 93–99 (2014)
REDDY, P. S. and CHAMKHA, A. J. Soret and Dufour effects on MHD convective flow of Al2O3-water and TiO2-water nanofluids past a stretching sheet in porous media with heat generation/absorption. Advanced Powder Technology, 27, 1207–1218 (2016)
HAYAT, T., FAROOQ, S., ALSAEDI, A., and AHMAD, B. Numerical study for Soret and Dufour effects on mixed convective peristalsis of Oldroyd 8-constants fluid. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 112, 68–81 (2017)
HAMID, M., USMAN, M., ZUBAIR, T., HAQ, R. U., and WANG, W. Shape effects of MoS2 nanoparticles on rotating flow of nanofluid along a stretching surface with variable thermal conductivity: a Galerkin approach. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 124, 706–714 (2018)
USMAN, M., HAMID, M., MOHYUD-DIN, S. T., WAHEED, A., and WANG, W. Exploration of uniform heat flux on the flow and heat transportation of ferrofluids along a smooth plate: comparative investigation. International Journal of Biomathematics, 11, 1850048 (2018)
SHEIKHOLESLAMI, M. and ROKNI, H. B. Numerical simulation for impact of Coulomb force on nanofluid heat transfer in a porous enclosure in presence of thermal radiation. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 118, 823–831 (2018)
WILLIAMSON, R. V. The flow of pseudoplastic materials. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 21, 1108–1111 (1929)
AMANULLA, C. H., NAGENDRA, N., RAO, A. S., BEG, O. A., and KADIR, A. Numerical exploration of thermal radiation and Biot number effects on the flow of a non-Newtonian MHD Williamson fluid over a vertical convective surface. Heat Transfer-Asian Research, 47, 286–304 (2018)
JAIN, S. and PARMAR, A. Radiation effect on MHD Williamson fluid flow over stretching cylinder through porous medium with heat source. Applications of Fluid Dynamics, Springer, Singapore (2018)
HAMID, M., USMAN, M., KHAN, Z. H., HAQ, R. U., and WANG, W. Numerical study of unsteady MHD flow of Williamson nanofluid in a permeable channel with heat source/sink and thermal radiation. The European Physical Journal Plus, 133, 527 (2018)
MUSTAFA, M., KHAN, J. A., HAYAT, T., and ALSAEDI, A. Buoyancy effects on the MHD nanofluid flow past a vertical surface with chemical reaction and activation energy. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 108, 1340–1346 (2017)
NOOR, N. F., HAQ, R. U., NADEEM, S., and HASHIM, I. Mixed convection stagnation flow of a micropolar nanofluid along a vertically stretching surface with slip effects. Meccanica, 50, 2007–2022 (2015)
HAQ, R. U., NADEEM, S., AKBAR, N. S., and KHAN, Z. H. Buoyancy and radiation effect on stagnation point flow of micropolar nanofluid along a vertically convective stretching surface. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 14, 42–50 (2015)
AKBAR, N. S., TRIPATHI, D., KHAN, Z. H., and BEG, O. A. A numerical study of magnetohydrodynamic transport of nanofluids over a vertical stretching sheet with exponential temperature-dependent viscosity and buoyancy effects. Chemical Physics Letters, 661, 20–30 (2016)
DOHA, E. H., ABD-ELHAMEED, W. M., and ALSUYUTI, M. M. On using third and fourth kinds Chebyshev polynomials for solving the integrated forms of high odd-order linear boundary value problems. Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society, 23, 397–405 (2015)
ZHOU, F. and XU, X. The third kind Chebyshev wavelets collocation method for solving the time-fractional convection diffusion equations with variable coefficients. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 280, 11–29 (2016)
ABD-ELHAMEED, W. M., DOHA, E. H., and YOUSSRI, Y. H. New wavelets collocation method for solving second-order multipoint boundary value problems using Chebyshev polynomials of third and fourth kinds. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2013, 542839 (2013)
MUKHOPADHYAY, S. Effect of thermal radiation on unsteady mixed convection flow and heat transfer over a porous stretching surface in a porous medium. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52, 3261–3265 (2009)
GRUBKA, L. J. and BOBBA, K. M. Heat transfer characteristics of a continuous stretching surface with variable temperature. Journal of Heat Transfer, 107, 248–250 (1985)
CHEN, C. H. Laminar mixed convection adjacent to vertical, continuously stretching sheets. Heat and Mass Transfer, 33, 471–476 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers and editor for suggesting suitable changes in the original manuscript. The first author is also grateful to the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: HAMID, M., USMAN, M., HAQ, R. U., KHAN, Z. H., and WANG, W. Wavelet analysis of stagnation point flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) 40(8), 1211–1226 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2508-6
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51709191, 51706149, and 51606130), the Key Laboratory of Advanced Reactor Engineering and Safety, Ministry of Education of China (No.ARES-2018-10), and the State Key Laboratory of Hydraulics and Mountain River Engineering of Sichuan University of China (No. Skhl1803)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Haq, R.U. et al. Wavelet analysis of stagnation point flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 40, 1211–1226 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2508-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2508-6
Key words
- Williamson nanofluid
- heat and mass transfer
- stagnation point flow
- assisting and opposing flow
- Chebyshev wavelet method