Abstract
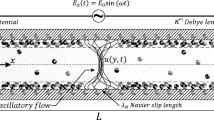
In consideration of the electroosmotic flow in a slit microchannel, the constitutive relationship of the Eyring fluid model is utilized. Navier’s slip condition is used as the boundary condition. The governing equations are solved analytically, yielding the velocity distribution. The approximate expressions of the velocity distribution are also given and discussed. Furthermore, the effects of the dimensionless parameters, the electrokinetic parameter, and the slip length on the flow are studied numerically, and appropriate conclusions are drawn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, D. Q. Encyclopedia of Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, Springer, Heidelberg (2008)
Li, D. Q. Electrokinetics in Microfluidics, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2004)
Masliyah, J. H. and Bhattacharjee, S. Electrokinetic and Colloid Transport Phenomena, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2006)
Kirby, B. J. Micro- and Nano-Scale Fluid Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Hunter, R. J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principle and Applications, Academic Press, London (1981)
Zhao, C. L. and Yang, C. Electrokinetics of non-Newtonian fluids: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 201, 94–108 (2013)
Das, S. and Chakraborty, S. Analytical solutions for velocity, temperature and concentration distribution in electroosmotic microchannel flows of a non-Newtonian bio-fluid. Analytica Chimica Acta, 559, 15–24 (2006)
Chakraborty, S. Electroosmotically driven capillary transport of typical non-Newtonian biofluids in rectangular microchannels. Analytica Chimica Acta, 605, 175–184 (2007)
Zhao, C. L., Zholkovskij, E., Masliyah, J. H., and Yang, C. Analysis of electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 326, 503–510 (2008)
Zhao, C. L. and Yang, C. An exact solution for electroosmosis of non-Newtonian fluids in microchannels. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 166, 1076–1079 (2011)
Tang, G. H., Li, X. F., He, Y. L., and Tao, W. Q. Electroosmotic flow of non-Newtonian fluid in microchannels. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 157, 133–137 (2009)
Park, H. M. and Lee, W. M. Helmholtz-Smoluchowski velocity for viscoelastic electroosmotic flows. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 317, 631–636 (2008)
Berli, C. L. A. and Olivares, M. L. Electrokinetic flow of non-Newtonian fluids in microchannels. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 320, 582–589 (2008)
Afonso, A. M., Alves, M. A., and Pinho, F. T. Analytical solution of mixed electroosmotic/pressure driven flows of viscoelastic fluids in microchannels. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 159, 50–63 (2009)
Sadeghi, A., Saidi, M. H., and Mozafari, A. A. Heat transfer due to electroosmotic flow of viscoelastic fluids in a slit microchannel. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 54, 4069–4077 (2011)
Hayat, T., Afzal, S., and Hendi, A. Exact solutions of electroosmotic flow in generalized Burgers fluid. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 32, 1119–1126 (2011) DOI 10.1007/s10483-011-1486-6
Zhao, M. L., Wang, S. W., and Wei, S. S. Transient electro-osmotic flow of Oldroyd-B fluids in a straight pipe of circular cross section. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 201, 135–139 (2013)
Zhao, C. L. and Yang, C. Exact solutions for electro-osmotic flow of viscoelastic fluids in rectangular micro-channels. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 211, 502–509 (2009)
Yang, F. Q. Flow behavior of an Eyring fluid in a nanotube: the effect of the slip boundary condition. Applied Physics Letters, 90, 133105 (2007)
Thompson, P. A. and Troian, S. M. A general boundary condition for liquid flow at solid surfaces. nature, 389, 360–362 (1997)
Eyring, H. Viscosity, plasticity, and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates. Journal of Chemical Physics, 4, 283–291 (1936)
Bird, R. B., Armstrong, R., and Hassager, O. Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 169–253 (1987)
Philip, J. R. and Wooding, R. A. Solution of the Poisson-Boltzmann equation about a cylindrical particle. Journal of Chemical Physics, 52, 953–959 (1970)
Liu, X. L., Jiang, M., Yang, P., and Kaneta, M. Non-Newtonian thermal analyses of point EHL contacts using the Eyring model. ASME Journal of Tribology, 127, 70–81 (2005)
Bosse, M. A., Araya, H., Troncoso, S. A., and Arce, P. E., Batch electrophoretic cells with Eyring fluids: analysis of the hydrodynamics. Electrophoresis, 23, 2149–2156 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11102102 and 91130017) and the Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (No. 2013ZRYQ002)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Z., Qi, Ht. & Jiang, Xy. Electroosmotic flow of Eyring fluid in slit microchannel with slip boundary condition. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 35, 689–696 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1822-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1822-6