Abstract
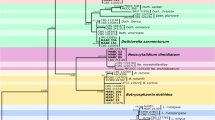
A necrotrophic member of the Sclerotiniaceae family (herewith named strain C10) isolated from withered rotten-grapes, is described. Interestingly, the fungus has no defined taxonomic position since it has been impossible to attribute it to an existing genus. Phylogenetic analysis of partial sequences of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (G3PDH), heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) and DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit (RPB2), revealed that strain C10 is distantly related to Amphobotrys and Botrytis. This evidence clearly distinguishes this new Sclerotiniaceae member from other taxa of the family. Moreover, its morphological characteristics did not match those of Amphobotrys and Botrytis. Infectivity assays demonstrated that strain C10 could be a potential postharvest pathogen of withered grapes. This study revealed the taxonomic importance of this strain suggesting the existence of a possible new genus, a theory that requires further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abawi GS, Grogan RG (1979) Epidemiology of diseases caused by Sclerotinia species. Phytopathology 69:899–904
Andrew M, Barua R, Short SM, Kohn LM (2012) Evidence for a common toolbox based on necrotrophy in a fungal lineage spanning necrotrophs, biotrophs, endophytes, host generalists and specialists. PlosOne 7:1–14
Azzolini M, Tosi E, Faccio S, Lorenzini M, Torriani S, Zapparoli G (2013) Selection of Botrytis cinerea and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for the improvement and valorization of Italian passito style wines. FEMS Yeast Res 13:540–552
Bolton MD, Thomma BP, Nelson DB (2006) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary: biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol Plant Pathol 7:1–16
Bullock S, Willetts HJ (1996) Ultrastructural and histochemical studies on mycelial germination of sclerotia of Sclerotinia minor. Mycol Res 100:561–570
Hall BH, McMahon RL, Wicks TJ (2002) First report of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on grape (Vitis vinifera) in South Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 31:417–418
Hennebert GL (1973) Botrytis and Botrytis-like genera. Persoonia 7:183–204
Holst-Jensen A, Kohn LM, Schumacher T (1997) Nuclear rDNA phylogeny of the Sclerotiniaceae. Mycologia 89:885–899
Holst-Jensen A, Vrålstad T, Schumacher T (2004) Kohninia linnaeicola, a new genus and species of the Sclerotiniaceae pathogenic to Linnaea borealis. Mycologia 96:135–142
Latorre BA, Guerrero MJ (2001) First report of shoot blight of grapevine caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Chile. Plant Dis 85:1122
Li X, Kerrigan J, Chai W, Schnabel G (2012) Botrytis caroliniana, a new species isolated from blackberry in South Carolina. Mycologia 104:650–658
Lorenzini M, Zapparoli G (2014) An isolate morphologically and phylogenetically distinct from Botrytis cinerea obtained from withered grapes possibly represents a new species of Botrytis. Plant Pathol 63:1326–1335
Lorenzini M, Azzolini M, Tosi E, Zapparoli G (2013) Post-harvest grape infection of Botrytis cinerea and its interactions with other moulds under withering conditions to produce noble-rotten grapes. J Appl Microbiol 114:762–770
Masuya H, Kusunoki M, Kosaka H, Aikawa T (2009) Haradamyces foliicola anam. gen. et sp. nov., a cause of zonate leaf blight disease in Cornus florida in Japan. Mycol Res 113:173–181
Ordóñez-Valencia C, Ferrera-Cerrato R, Quintanar-Zúñiga RE, Flores-Ortiz CM, Márquez Guzmán GJ, Alarcón A, Larsen J, García-Barradas O (2015) Morphological development of sclerotia by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: a view from light and scanning electron microscopy. Ann Microbiol 65:765–770
Pitt JI, Hocking AD (1997) Fungi and Food Spoilage, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Saharan GS, Mehta N (2008) Sclerotinia disease of crop plants: biology, ecology and disease management, 1st edn. Springer, The Netherlands
Smith EA, Boland GJ (1989) A reliable method for production of apothecia of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Can J Plant Pathol 11:45–48
Staats M, van Baarlen P, van Kan JAL (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the plant pathogenic genus Botrytis and the evolution of host specificity. Mol Biol Evol 22:333–346
Staats M, van Baarlen P, Schouten A, van Kan JAL, Bakker FT (2007) Positive selection in phytotoxic protein-encoding genes of Botrytis species. Fungal Genet Biol 44:52–63
Takahashi Y, Ichihashi Y, Sano T, Harada Y (2005) Monilinia jezoensis sp. nov. in the Sclerotiniaceae, causing leaf blight and mummy fruit disease of Rhododendron kaempferi in Hokkaido, northern Japan. Mycoscience 46:106–109
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Willetts HJ (1997) Morphology, development and evolution of stromata/sclerotia and macroconidia of the Sclerotiniaceae. Mycol Res 101:939–952
Williamson B, Tudzynski B, Tudzynski P, van Kan JAL (2007) Pathogen profile Botrytis cinerea: the cause of grey mould disease. Mol Plant Pathol 8:561–580
Zhou YJ, Zhang J, Wang XD, Yang L, Jiang DH, Li GQ, Hsiang T, Zhuang WY (2014) Morphological and phylogenetic identification of Botrytis sinoviticola, a novel cryptic species causing gray mold disease of table grapes (Vitis vinifera) in China. Mycologia 106:43–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorenzini, M., Zapparoli, G. Description of a taxonomically undefined Sclerotiniaceae strain from withered rotten-grapes. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109, 197–205 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0621-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0621-1