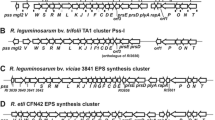
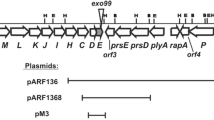
Abstract
Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii exopolysaccharide (EPS) plays an important role in determining symbiotic competence. The pssA gene encoding the first glucosyl-IP-transferase and rosR encoding a positive transcriptional regulator are key genes involved in the biosynthesis and regulation of EPS production. Mutation in pssA resulted in deficiency in EPS production and rosR mutation substantially decreased the amount of EPS. Both mutants induced nodules but the bacteria were unable to fix nitrogen. Defective functions of pssA and rosR mutants were fully restored by wild type copies of the respective genes. Introduction of multiple rosR and pssA gene copies on the plasmid vector pBBR1MCS-2 into five R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii nodule isolates resulted in significantly increased growth rates, EPS production and the number of nodules on clover roots. Increase in fresh and dry shoot mass of clovers and nodule occupation was also statistically significant. Interestingly, additional copies of pssA but particularly rosR gene, increased strains’ competitiveness in relation to the wild type parental strains nearly twofold. Overall, experimental evidence is provided that increased amount of EPS beneficially affects R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii competitiveness and symbiosis with clover.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage P, Berry G (1987) Statistical methods in medical research. Blackwell, Oxford
Becker A, Pühler A (1998) Production of exopolysaccharides. In: Spaink HP, Kondorosi A, Hooykaas PJJ (eds) Rhizobiaceae: molecular biology of plant-associated bacteria. Kluwer, Boston, pp 97–118
Bittinger MA, Handelsman J (2000) Identification of genes in the RosR regulon of Rhizobium etli. J Bacteriol 182:1706–1713
Bittinger MA, Milner JL, Saville BJ, Handelsman J (1997) rosR, a determinant of nodulation competitveness in Rhizobium etli. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10:180–186
Borthakur D, Barker CE, Lamb JW, Daniels MJ, Downie JA, Johnston AWB (1986) A mutation that blocks exopolysaccharide synthesis prevents nodulation of peas by Rhizobium leguminosarum but not of beans by R. phaseolii and is corrected by cloned DNA from Rhizobium or the phytopathogen Xanthomonas. Mol Gen Genet 203:320–323
Brewin NJ (1998) Tissue and cell invasion by Rhizobium: the structure and development of infection threads and symbiosomes. In: Spaink HP, Kondorosi A, Hooykaas PJJ (eds) The Rhizobiaceae: molecular biology of plant-associated bacteria. Kluwer, Boston, pp 417–429
Cooper JE (2007) Early interactions between legumes and rhizobia: disclosing complexity in a molecular dialogue. J Appl Microbiol 103:1355–1365
Daniels R, Reynaert S, Hoekstra H, Verreth C, Janssens J, Braeken K, Fauvart M, Beullens S, Heusdens C, Lambrichts I, De Vos DE, Vanderleyden J, Vermant J, Michiels J (2006) Quorum signal molecules as biosurfactants affecting swarming in Rhizobium etli. PNAS 103:14965–14970
Davies BW, Walker GC (2007) Identification of novel Sinorhizobium meliloti mutants compromised for oxidative stress protection and symbiosis. J Bacteriol 189:2110–2113
D’Haeze W, Holsters M (2004) Surface polysaccharides enable bacteria to evade plant immunity. Trends Microbiol 12:555–561
Djordjevic MA, Chen HC, Natera S, Van Noorden G, Menzel C, Taylor S, Renard C, Geiger O, Weiller GF, The Sinorhizobium DNA sequencing consortium (2003) A global analysis of protein expression profiles in Sinorhizobium meliloti: discovery of new genes for nodule occupancy and stress adaptation. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:508–524
Eckhardt T (1978) A rapid method for the identification of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid 13:99–105
Fraysse N, Couderc F, Poinsot V (2003) Surface polysaccharide involvement in establishing the rhizobium—legume symbiosis. Eur J Biochem 270:1365–1380
Gage DJ (2004) Infection and invasion of roots by symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing rhizobia during nodulation of temperate legumes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:280–300
Garg B, Dogra RC, Shama PK (1999) High-efficiency transformation of R. leguminosarum by electroporation. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2802–2804
Gibson KE, Kobayashi H, Walker GC (2008) Molecular determinants of a symbiotic chronic infection. Annu Rev Genet 42:4–44
Guerreiro N, Ksenzenko VN, Djordjevic MA, Ivashina TV, Rolfe BG (2000) Elevated levels of synthesis of over 20 proteins results after mutation of the Rhizobium leguminosarum exopolysaccharide synthesis gene pssA. J Bacteriol 182:4521–4532
Herridge DF, Peoples MB, Boddey RM (2008) Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311:1–18
Ivashina TV, Khmelnitsky MI, Shlyapnikov MG, Kanapin AA, Ksenzenko VN (1994) The pss4 gene from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae VF39: cloning, sequence and the possible role in polysaccharide production and nodule formation. Gene 50:111–116
Janczarek M, Skorupska A (2004) Regulation of pssA and pssB gene expression in R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii in response to environmental factors. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 85:217–227
Janczarek M, Skorupska A (2007) The Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii RosR: transcriptional regulator involved in exopolysaccharide production. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:867–881
Janczarek M, Król J, Kutkowska J, Mazur A, Wielbo J, Borucki W, Kopcińska J, Łotocka B, Urbanik-Sypniewska T, Skorupska A (2001) Mutation in the pssB-pssA intergenic region of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii affects the surface polysaccharide synthesis and nitrogen fixation ability. J Plant Physiol 158:1565–1574
Janczarek M, Kalita M, Skorupska A (2009) New taxonomic markers for identification of Rhizobium leguminosarum and discrimination between closely related species. Arch Microbiol 191:207–219
Jones KM, Kobayashi H, Davies BW, Taga ME, Walker GC (2007) How rhizobial symbionts invade plants: the Sinorhizobium—Medicago model. Nat Rev 5:619–633
Katzen F, Becker A, Ielmini MV, Oddo CG, Ielpi L (1999) New mobilizable vectors suitable for gene replacement in gram-negative bacteria and their use in mapping of the 3’ end of the Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris gum operon. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:278–282
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Laguerre G, Mavingui P, Allard MR, Charnay MP, Louvrier P, Mazurier SI, Rigottier-Gois L, Amarger N (1996) Typing of Rhizobia by PCR DNA fingerprinting and PCR-restriction Fragment length polymorphism analysis of chromosomal and symbiotic gene regions: application to Rhizobium leguminosarum and its different biovars. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2029–2036
Laguerre G, Louvrier P, Allard MR, Amarger N (2003) Compatibility of rhizobial genotypes within natural populations of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae for nodulation of host legumes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2276–2283
Latchford JW, Borthakur D, Johnston AWB (1991) The products of Rhizobium genes, psi and pss, which affect exopolysaccharide production, are associated with the bacterial cell surface. Mol Microbiol 5:2107–2114
Laus MC, van Brussel AAN, Kijne JW (2005) Role of cellulose fibrils and exopolysaccharides of Rhizobium leguminosarum in attachment to and infection of Vicia sativa root hairs. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:533–538
Mathis R, Van Gijsegem F, De Rycke R, D’Haeze W, Van Maelsaeke E, Anthonio E, Van Montagu M, Holsters M, Vereecke D (2005) Lipopolysaccharides as a communication signal for progression of legume endosymbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2655–2660
Navarro E, Somonet P, Normand P, Bardin R (1992) Characterization of natural populations of Nitrobacter sp. using PCR/RFLP analysis of the ribosomal intergenic spacer. Arch Microbiol 157:107–115
Oldroyd GED, Downie JA (2008) Coordinating nodule morphogenesis with rhizobial infection in legumes. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:519–546
Perret X, Staehelin C, Broughton W (2000) Molecular basis of symbiotic promiscuity. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:180–201
Ponsonnet C, Nesme X (1994) Identification of Agrobacterium strains by PCR-RFLP analysis of pTi and chromosomal regions. Arch Microbiol 161:300–309
Robleto EA, Scupham AJ, Triplett EW (1997) Trifolitoxin production in Rhizobium etli strain CE3 increases competitiveness for rhizosphere growth and root nodulation of Phaseolus vulgaris in soil. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10:228–233
Robleto EA, Kmiecik K, Oplinger ES, Nienhaus J, Triplett EW (1998) Trifolitoxin production increases nodulation competitiveness of Rhizobium etli strain CE3 under agricultural conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2630–2633
Rolfe BG, Carlson RW, Ridge RW, Dazzo RW, Mateos FB, Pankhurst CE (1996) Defective infection and nodulation of clovers by exopolysaccharide mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii. Aust J Plant Physiol 23:285–303
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Santos R, Herouart D, Sigaud S, Touati D, Puppo A (2001) Oxidative burst in alfalfa—Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiotic interaction. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:86–89
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791
Skorupska A, Białek U, Urbanik-Sypniewska T, van Lammeren A (1995) Two types of nodules induced on Trifolium pratense by mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii deficient in exopolysaccharide production. J Plant Physiol 147:93–100
Skorupska A, Janczarek M, Marczak M, Mazur A, Król J (2006) Rhizobial exopolysaccharides: genetic control and symbiotic functions. Microb Cell Fact 16:7
Stanley J, Dowling DN, Stucker M, Broughton WJ (1987) Screening costramid libraries for chromosomal genes: alternative interspecific hybridization methods. FEMS Microbiol Lett 48:25–30
Toro N (1996) Nodulation competitiveness in the Rhizobium—legume symbiosis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:157–162
Triplett EW (1990a) Construction of a symbiotically effective strain Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii with increased nodulation competitiveness. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4260–4262
Triplett EW (1990b) The molecular genetics of nodulation competitiveness in Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 3:199–206
van Dillewijn P, Soto MJ, Villadas PJ, Toro N (2001) Construction and environmental release of a Sinorhizobium meliloti strain genetically modified to be more competitive for alfalfa nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3860–3865
van Workum WAT, Canter Cremers HCJ, Wijfjes AHM, van der Kolk C, Wijffelman CA, Kijne JW (1997) Cloning and characterization of four genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii involved in exopolysaccharide production and nodulation. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10:290–301
van Workum WAT, van Slageren S, van Brussel AAN, Kijne JW (1998) Role of exopolysaccharides of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae as host plant-specific molecules required for infection thread formation during nodulation of Vicia sativa. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 11:1233–1241
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. International biological program handbook no 15. Blackwell, Oxford
Vlassak KM, Vanderleyden J (1997) Factors influencing nodule occupancy by inoculants rhizobia. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:163–229
Wielbo J, Marek-Kozaczuk M, Kubik-Komar A, Skorupska A (2007) Increased metabolic potential of Rhizobium spp. is associated with bacterial competitiveness. Can J Microbiol 53:957–967
Wilson KJ, Sessitsch A, Corbo JC, Giller KE, Akkermans AD, Jefferson RA (1995) β-Glucuronidase (GUS) transposons for ecological and genetic studies of rhizobia and other gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 141:1691–1705
Acknowledgments
We thank Maria Małek for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the grant from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education no. N N303 092234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janczarek, M., Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J. & Skorupska, A. Multiple copies of rosR and pssA genes enhance exopolysaccharide production, symbiotic competitiveness and clover nodulation in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 96, 471–486 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9362-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9362-3