Abstract
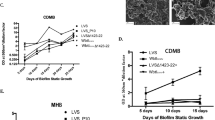
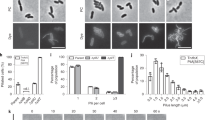
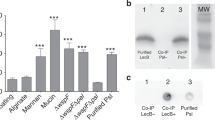
Extracellular DNA can play a structural role in the microbial environment. Here evidence is presented that an environmental isolate of Acidovorax temperans utilises extracellular DNA for intercellular and cell-surface attachment and that Type IV pili and electrostatic interactions play a role in this interaction. Preliminary attempts to isolate and purify extracellular polysaccharides from A. temperans strain CB2 yielded significant amounts of DNA raising the question of whether this molecule was present as a structural component in the extracellular matrix. The role of DNA in attachment was indicated by experiments in which the addition of DNase to liquid medium inhibited the attachment of Acidovorax to glass wool. A Tn5 insertional mutant, lacking Type IV pili, was unable to initiate attachment. Addition of DNase caused rapid detachment of bound cells, but no detachment occurred when proteinase, RNase or inactivated DNase were used. Addition of MgCl2 also caused significant detachment, supporting the possible mechanistic role of electrostatic interactions in the attachment process. Although attachment was apparent in early to mid-log phase growth, surprisingly DNA was not detected in the culture supernatant until late stationary phase and coincided with an appreciable loss of cell viability. This suggests that during log-phase growth attachment is mediated by eDNA that is released in low quantities and/or is highly localised within the extracellular matrix and also that stationary phase DNA release through widespread cell lysis may be a separate and unrelated event.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas FE, Lovold C, Koomey M (2002) An inhibitor of DNA binding and uptake events dictates the proficiency of genetic transformation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: mechanism of action and links to Type IV pilus expression. Mol Microbiol 46:1441–1450. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03265.x
Allesen-Holm M, Barken KB, Yang L, Klausen M, Webb JS, Kjelleberg S, Molin S, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2006) A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 59:1114–1128. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.05008.x
Bockelmann U, Janke A, Kuhn R, Neu TR, Wecke J, Lawrence JR, Szewzyk U (2006) Bacterial extracellular DNA forming a defined network-like structure. FEMS Microbiol Lett 262:31–38. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00361.x
Bockelmann U, Lunsdorf H, Szewzyk U (2007) Ultrastructural and electron energy-loss spectroscopic analysis of an extracellular filamentous matrix of an environmental bacterial isolate. Environ Microbiol 9:2137–2144. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01325.x
Chen I, Dubnau D (2004) DNA uptake during bacterial transformation. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:241–249. doi:10.1038/nrmicro844
Costerton JW, Lewandowski Z, Caldwell DE, Korber DR, Lappin-Scott HM (1995) Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:711–745. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003431
Dreiseikelmann B (1994) Translocation of DNA across bacterial membranes. Microbiol Rev 58:293–316
Dubnau D (1999) DNA uptake in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:217–244. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.53.1.217
Finkel SE, Kolter R (2001) DNA as a nutrient: novel role for bacterial competence gene homologs. J Bacteriol 183:6288–6293. doi:10.1128/JB.183.21.6288-6293.2001
Izano EA, Amarante MA, Kher WB, Kaplan JB (2008) Differential roles of poly-N-acetylglucosamine surface polysaccharide and extracellular DNA in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:470–476. doi:10.1128/AEM.02073-07
Jurcisek JA, Bakaletz LO (2007) Biofilms formed by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in vivo contain both double-stranded DNA and type IV pilin protein. J Bacteriol 189:3868–3875. doi:10.1128/JB.01935-06
Kjaergaard K, Schembri MA, Ramos C, Molin S, Klemm P (2000) Antigen 43 facilitates formation of multispecies biofilms. Environ Microbiol 2:695–702. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00152.x
Lorenz MG, Gerjets D, Wackernagel W (1991) Release of transforming plasmid and chromosomal DNA from two cultured soil bacteria. Arch Microbiol 156:319–326. doi:10.1007/BF00263005
O’Toole G, Kaplan HB, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:49–79. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.49
Palmgren R, Nielsen PH (1996) Accumulation of DNA in the exopolymeric matrix of activated sludge and bacterial cultures. Water Sci Technol 34:233–240. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(96)00650-6
Pelicic V (2008) Type IV pili: e pluribus unum? Mol Microbiol 68:827–837. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06197.x
Petersen FC, Tao L, Scheie AA (2005) DNA binding-uptake system: a link between cell-to-cell communication and biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 187:4392–4400. doi:10.1128/JB.187.13.4392-4400.2005
Qin Z, Ou Y, Yang L, Zhu Y, Tolker-Nielsen T, Molin S, Qu D (2007) Role of autolysin-mediated DNA release in biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiology 153:2083–2092. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2007/006031-0
Sutherland IW (2001) The biofilm matrix - an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol 9:222–227. doi:10.1016/S0966-842X(01)02012-1
van Schaik EJ, Giltner CL, Audette GF, Keizer DW, Bautista DL, Slupsky CM, Sykes BD, Irvin RT (2005) DNA binding: a novel function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type IV pili. J Bacteriol 187:1455–1464. doi:10.1128/JB.187.4.1455-1464.2005
Watanabe M, Suzuki Y, Sasaki K, Nakashimada Y, Nishio N (1999) Flocculating property of extracellular polymeric substance derived from a marine photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodovulum sp. J Biosci Bioeng 87:625–629. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(99)80125-X
Whitchurch CB, Tolker-Nielsen T, Ragas PC, Mattick JS (2002) Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 295:1487. doi:10.1126/science.295.5559.1487
Willems A, Gillis M (2005) Genus II. Acidovorax. In: Garrity G (ed) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol II, 2nd edn. Springer, US, pp 696–703
Acknowledgments
This project has been funded from the New Economy Research Fund administered by the New Zealand Foundation for Research Science & Technology. B. Heijstra is the recipient of a University of Auckland Doctoral Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heijstra, B.D., Pichler, F.B., Liang, Q. et al. Extracellular DNA and Type IV pili mediate surface attachment by Acidovorax temperans . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 95, 343–349 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9320-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-009-9320-0