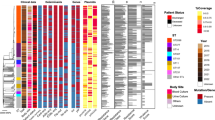
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus has become a major source of hospital infections and the risk of colonisation and infection by community-acquired methicillin-resistant S. aureus (CA-MRSA) is increasingly higher. Because of the importance of S. aureus to public health, many molecular typing methods have been developed to determine its transmission routes and source of infection during epidemiological investigations. In this study we evaluated the usefulness of multiplex PCR based Multi-Locus VNTR Fingerprinting (MLVF) as the first step method for rapid differentiation of Croatian and Polish S. aureus isolates in hospital and community settings. This is a first report of the usefulness of MLVF in typing of hospital-acquired methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (HA-MSSA) and four CA-MRSA isolates. A total of 47 isolates of S. aureus recovered in Croatia in 2004 and in Poland in 2006 and 2007 were tested. The MLVF results were compared to those produced by other typing methods, such as Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE), Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) and spa typing. The MLVF analysis showed almost the same clonality results as the remaining typing methods although some differences were found. Epidemiological data about the relation among S. aureus isolates and the results produced by typing methods applied in the present study indicate that because of the advantages in ease and speed of Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR) procedure over PFGE, spa typing and MLST, MLVF can be used as a first screening method followed by additional typing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung M, de Lencastre H, Matthews P et al (2000) Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: comparison of results obtained in a multilaboratory effort using identical protocols and MRSA strains. Microb Drug Resist 6:189–198
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2005) Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests approved standard—eighth edition & performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing fifteenth informational supplement M100-S15; for Disk (M2-A-8); for MIC (M7-A6) CLSI, Vayne, PA
Comite de l’Antibiogramme de la Societe Francaise de Microbiologie (2006) Communiqué (Edition de Janvier 2006 Mise à jour en novembre 2006). Societe Francaise de Microbiologie
Cookson BD, Robinson A, Monk AB, Murchan S, Deplano A, de Ryck R et al (2007) Evaluation of molecular typing methods in characterizing a European collection of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains: the harmony collection. J Clin Microbiol 45:1830–1837. doi:10.1128/JCM.02402-06
Crisostomo MI, Westh H, Tomasz A, Chung M, Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2001) The evolution of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: similarity of genetic backgrounds in historically early methicillin-susceptible and -resistant isolates and contemporary epidemic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9865–9870. doi:10.1073/pnas.161272898
Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG (2000) Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 38:1008–1015
Grundmann H, Hori S, Tanner G (2001) Determining confidence intervals when measuring genetic diversity and the discriminatory abilities of typing methods for microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol 39:4190–4192. doi:10.1128/JCM.39.11.4190-4192.2001
Grundmann H, Hori S, Enright MC, Webster C, Tami A, Feil EJ et al (2002) Determining the genetic structure of the natural population of Staphylococcus aureus: a comparison of multilocus sequence typing with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis, and phage typing. J Clin Microbiol 40:4544–4546. doi:10.1128/JCM.40.12.4544-4546.2002
Harmsen D, Claus H, Witte W, Rothganger J, Claus H, Turnwald D et al (2003) Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J Clin Microbiol 41:5442–5448. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.12.5442-5448.2003
Hryniewicz W (1999) Epidemiology of MRSA. Infection 27(Suppl 2):13–16. doi:10.1007/BF02561663
Koreen L, Ramaswamy SV, Graviss EA, Naidich S, Musser JM, Kreiswirth BN (2004) spa typing method for discriminating among Staphylococcus aureus isolates: implications for use of a single marker to detect genetic micro- and macrovariation. J Clin Microbiol 42:792–799. doi:10.1128/JCM.42.2.792-799.2004
Krzyszton-Russjan J, Empel J, Leski T, Gniadkowski M, Hryniewicz W (2005) Clonal structure of the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) population in Poland: revision and update. Microb Drug Resist 11:127–136. doi:10.1089/mdr.2005.11.127
Krzyszton-Russjan J, Tambic-Andrasevic A, Bukovski S, Sabat A, Hryniewicz W (2006) First community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains in Croatia. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:697–698. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01493.x
Kuroda M, Ohta T, Uchiyama I et al (2001) Whole genome sequencing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 357:1225–1240. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04403-2
Lina G, Piemont Y, Godail-Gamot F, Bes M, Peter MO, Gauduchon V et al (1999) Involvement of Panton–Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 29:1128–1132. doi:10.1086/313461
Lina G, Boutite F, Tristan A, Bes M, Etienne J, Vandenesch F (2003) Bacterial competition for human nasal cavity colonization: role of Staphylococcal agr alleles. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:18–23. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.1.18-23.2003
Malachowa N, Sabat A, Gniadkowski M, Krzyszton-Russjan J, Empel J, Miedzobrodzki J et al (2005) Comparison of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, spa typing, and multilocus sequence typing for clonal characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol 43:3095–3100. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.7.3095-3100.2005
Mato R, Campanile F, Stefani S, Crisostomo MI, Santagati M, Sanches SI et al (2004) Clonal types and multidrug resistance patterns of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) recovered in Italy during the 1990s. Microb Drug Resist 10:106–113. doi:10.1089/1076629041310109
McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC (2003) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol 41:5113–5120. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.11.5113-5120.2003
Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2002) Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:2155–2161. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.7.2155-2161.2002
Oliveira DC, Tomasz A, de Lencastre H (2001) The evolution of pandemic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: identification of two ancestral genetic backgrounds and the associated mec elements. Microb Drug Resist 7:349–361. doi:10.1089/10766290152773365
Oliveira DC, Tomasz A, de Lencastre H (2002) Secrets of success of a human pathogen: molecular evolution of pandemic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet Infect Dis 2:180–189. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(02)00227-X
Quelle LS, Corso A, Galas M, Sordelli DO (2003) STAR gene restriction profile analysis in epidemiological typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: description of the new method and comparison with other polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 47:455–464. doi:10.1016/S0732-8893(03)00137-8
Robinson A, Enright MC (2003) Evolutionary models of the emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3926–3934
Robinson A, Hollingshead SK, Musser JM, Parkinson AJ, Briles DE, Crain MJ (1998) The IS1167 insertion sequence is a phylogenetically informative marker among isolates of serotype 6B Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Mol Evol 47:222–229. doi:10.1007/PL00006379
Rybak MJ, La Plante KL (2005) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a review. Pharmacotherapy 25:74–85
Sabat A, Krzyszton-Russjan J, Strzalka W, Filipek Kosowska K, Hryniewicz W, Travis J et al (2003) New method for typing Staphylococcus aureus strains: multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis of polymorphism and genetic relationships of clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol 41:1801–1804
Sabat A, Malachowa N, Miedzobrodzki J, Hryniewicz W (2006) Comparison of PCR-based methods for the typing of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol 40:3804–3807
Saravolatz LD, Pohlod DJ, Arking LM (1982) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a new source for nosocomial outbreaks. Ann Intern 97:325–329
Shopsin B, Gomez M, Montgomery SO, Smith DH, Waddington M, Dodge DE et al (1999) Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol 37:3556–3563
Stranden A, Frei R, Widmar AF (2003) Molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: can PCR replace pulsed-field gel electrophoresis? J Clin Microbiol 41:3181–3186
Struelens MJ (1996) Consensus guidelines for appropriate use and evaluation of microbial epidemiologic typing systems. Clin Microbiol Infect 2:2–11
Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH et al (1995) Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol 33:2233–2239
van Belkum A (2000) Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains: state of affairs and tomorrow’s possibilities. Microb Drug Resist 6:173–188
Wenzel RP, Nettleman MD, Jones RN, Pfaller MA (1991) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: implications for the 1990s and effective control measures. Am J Med 91:221S–227S
Wichelhaus TA, Hunfeld KP, Boddingshaus B, Kraiczy P, Schafer V, Brade V (2001) Rapid molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by PCR-RFLP. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 22:294–298
Acknowledgements
These studies were supported by grant 2 P05A 052 30 (to A. S. and W. H.). We are grateful to Herminia de Lencastre and Alexander Tomasz for kindly providing representatives of the MRSA international clones. We would like to thank Aleksandra Kozinska and Katarzyna Malinowska for excellent technical assistance. We acknowledge the use of the S. aureus MLST database which is located at Imperial College, London, and is founded by the WellcomeTrust. This publication made use of the spa typing website (http://www.spaserver.ridom.de/) and Ridom Staph Type software that is developed by Ridom GmbH and curated by SeqNet.org (http://www.SeqNet.org/). This study was presented in part as a poster at the Twelfth International Symposium on Staphylococci and Staphylococcal Infections, Maastricht, the Netherlands 3–6 September 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luczak-Kadlubowska, A., Sabat, A., Tambic-Andrasevic, A. et al. Usefulness of Multiple-Locus VNTR Fingerprinting in detection of clonality of community- and hospital-acquired Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 94, 543–553 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-008-9271-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-008-9271-x