Abstract
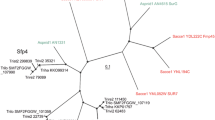
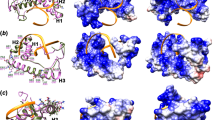
We have previously shown that protein kinase A of the medically important zygomycete Mucor rouxii participates in fungal morphology through cytoskeletal organization. As a first step towards finding the link between protein kinase A and cytoskeletal organization we here demonstrate the cloning of the Rho1 gene and the characterization of its protein product. The RHO1 protein primary sequence shows 70–85% identity with fungal RHO1 or mammalian RhoA. Two protein kinase A phosphorylation sequences in adequate context are predicted, Ser73 and Ser135. The peptide IRRNSQKFV, containing Ser135 proved to be a good substrate for M. rouxii protein kinase A catalytic subunit. The over-expressed Rho1 fully complements a Saccharomyces cerevisiae null mutant. The endogenous protein was identified by western blot against a developed antibody and by ADP-ribosylation. Localization in germlings was visualized by immunofluorescence; the protein was localized in patches in the mother cell surface and excluded from the germ tube. Measurement of Rho1 expression during germination indicates that Rho1, at both the mRNA and protein levels, correlates with differentiation and not with growth. Rho1 has been shown to be the regulatory protein of the β-1,3-glucan synthase complex in fungi in which β-1,3-glucans are major components of the cell wall. Even though glucans have not been detected in zygomycetes, caspofungin, an echinochandin known to be an inhibitor of β-1,3-glucan synthase complex, is shown here to have a negative effect on growth and to produce an alteration on morphology when added to M. rouxii growth culture medium. This result has an important impact on the possible participation of β-1,3-glucans on the regulation of morphology of zygomycetes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Mr:
-
Mucor rouxii
- PKA:
-
protein kinase A
References
Arikan S, Lozano-Chiu M, Paetznick V, Rex JH (2001) In vitro susceptibility testing methods for caspofungin against Aspergillus and Fusarium isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:327–330
Barth G, Gaillardin C (1997) Physiology and genetics of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Microbiol Rev 19:219–237
Bartnicki-Garcia S, Reyes E (1968) Polyuronides in the cell wails of Mucor rouxii. Biochim Biophys Acta 170:54–62
Bartnicki-García S, Nickerson WK (1962) Nutrition, growth and morphogenesis of Mucor rouxii. J Bacteriol 83:841–858
Cabib E, Drgonova J, Drgon T (1998) Role of small G proteins in yeast cell polarization and wall biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem 67:307–333
Corbett KD, Alber T (2001) The many faces of Ras: recognition of small GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 26:710–716
DeMali KA, Wennerberg K, Burridge K (2003) Integrin signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Comparison of morphogenetic networks of filamentous fungi and yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:572–582
Dow JM, Rubery PH (1977) Chemical fractionation of the cell walls of mycelial and yeast-like forms of Mucor rouxii: a comparative study of the polysaccharide and glycoprotein components. J Gen Microbiol 99:29–41
Ellerbroek SM, Wennerberg K, Burridge K (2003) Serine phosphorylation negatively regulates RhoA in vivo. J Biol Chem 278:19023–19031
Forget MA, Desrosiers RR, Gingras D, Beliveau R (2002) Phosphorylation states of Cdc42 and RhoA regulate their interactions with Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor and their extraction from biological membranes. Biochem J 361:243–254
Gancedo JM (2001) Control of pseudohyphae formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:107–23
Guest MG, Lin X, Momany M (2004) Aspergillus nidulans RhoA is involved in polar growth, branching and cell wall synthesis. Fungal Genet Biol 41:13–22
Haidle CW, Storck R (1966) Control of dimorphism in Mucor rouxii. J Bacteriol 92:1236–1244
Hancock JF, Cadwallader K, Paterson H, Marshall CJ (1991) A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J 10:4033–4039
Harris SD, Momany M (2004) Polarity in filamentous fungi: moving beyond the yeast paradigm. Fungal Genet Biol 41:391–400
Harris SD, Read ND, Roberson RW, Shaw B, Seiler S, Plamann M, Momany M (2005) Polarisome meets spitzenkorper: microscopy, genetics, and genomics converge. Eukar Cell 4:225–229
Ibrahim AS, Bowman JC, Avanessian V, Brown K, Spellberg B, Edwards JE Jr, Douglas CM (2005) Caspofungin inhibits Rhizopus oryzae 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase, lowers burden in brain measured by quantitative PCR, and improves survival at a low but not a high dose during murine disseminated zygomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:721–727
Inoue SB, Qadota H, Arisawa M, Anraku Y, Watanabe T, Ohya Y (1996) Signaling toward yeast 1,3-beta-glucan synthesis. Cell Struct Funct 5:395–402
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:247–269
Kurtz MB, Heath IB, Marrinan J, Dreikorn S, Onishi J and Douglas C (1994) Morphological effects of lipopeptides against Aspergillus fumigatus correlate with activities against (1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:1480–1489
Lang P, Gesbert F, Delespine-Carmagnat M, Stancou R, Pouchelet M, Bertoglio J (1996) Protein kinase A phosphorylation of RhoA mediates the morphological and functional effects of cyclic AMP in cytotoxic lymphocytes. EMBO J 15:510–519
Lee N, D’Souza CA, Kronstad JW (2003) Of smuts, blasts, mildews, and blights: cAMP signaling in phytopathogenic fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 41:399–427
Lengeler KB, Davidson RC, D’Souza CA, Harashima T, Shen WC, Wang P, Pan X, Waugh M, Heitman J (2000) Signal transduction cascades regulating fungal development and virulence. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:746–785
Letscher-Bru V, Herbrecht R (2003) Caspofungin: the first representative of a new antifungal class. J Antimicrob Chemother 51:513–521
Levin DE (2005) Cell wall integrity signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:262–291
Linz JE, Katayama C, Sypherd PS (1986) Three genes for the elongation factor EF-1α in Mucor racemosus. Mol Cell Biol 6:593–600
Madaule P, Axel R, Myers AM (1987) Characterization of two members of the rho gene family from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:779–783
Madhani HD, Fink GD (1998) The control of filamentous differentiation and virulence in fungi. Trends Cell Biol 8:348–335
Odds FC, Brown AJ, Gow NA (2003) Antifungal agents: mechanisms of action. Trends Microbiol 11:272–279
Paduch M, Jeleń F, Otlewski J (2001) Structure of small G proteins and their regulators. Acta Biochim Pol 48:829–850
Peitsch MC (1995) Protein modeling by E-mail. Bio/Technology 13:658–660
Peitsch MC (1996) ProMod and Swiss-Model: Internet-based tools for automated comparative protein modelling. Biochem Soc Trans 24:274–279
Pereyra E, Mizyrycki C, Moreno S (2000) Threshold level of protein kinase A activity and polarized growth in Mucor rouxii. Microbiology 146:1949–1958
Pereyra E, Argimón S, Jackson SL, Moreno S (2003) RGD-containing peptides and cAMP have antagonistic roles in the morphology of Mucor rouxii. Protoplasma 222:23–30
Pereyra E, Zaremberg V, Moreno S (1992) The effect of dibutyryl-cAMP on growth and morphology of germinating Mucor rouxii sporangiospores. Exp Mycol 16:93–101
Pereyra E, Ingerfeld M, Neal A, Jackson SL, Moreno S (2006) Mucor rouxii ultrastructure: cAMP and actin cytoskeleton. Protoplasma in press
Qadota H, Anraku Y, Botstein D, Ohya Y (1994) Conditional lethality of a yeast strain expressing human RHOA in place of RHO1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9317–9321
Ramirez-Ramirez N, Garcia-Soto J, Gonzalez-Hernandez A, Martinez-Cadena G (1999) The small GTP-binding protein Rho is expressed differentially during spore germination of Phycomyces blakesleeanus. Microbiology 145:1097–1104
Rolli-Derkinderen M, Sauzeau V, Boyer L, Lemichez E, Baron C, Henrion D, Loirand G, Pacaud P (2005) Phosphorylation of serine 188 protects RhoA from ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated degradation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 96:1152–1160
Rose TM, Henikoff JG, Henikoff S (2003) CODEHOP (COnsensus-DEgenerate Hybrid Oligonucleotide Primer) PCR primer design. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3763–3766
Roskoski R (1983) Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol 99:3–6
Roze LV, Mahanti N, Mehigh R, McConnell DG, Linz JE (1999) Evidence that MRas1 and MRas3 proteins are associated with distinct cellular functions during growth and morphogenesis in the fungus Mucor racemosus. Fungal Genet Biol 28:171–189
Rua D, Tobe BT, Kron SJ (2001) Cell cycle control of yeast filamentous growth. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:720–727
Ruge E, Korting HC, Borelli C (2005) Current state of three-dimensional characterisation of antifungal targets and its use for molecular modelling in drug design. Int J Antimicrob Agents 26:427–441
Seiler S, Plamann M (2003) The genetic basis of cellular morphogenesis in the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. Mol Biol Cell 14:4352–4364
Wendland J (2001) Comparison of morphogenetic networks of filamentous fungi and yeast. Fungal Genet Biol 34:63–82
Wendland J, Walther A (2005) Ashbya gossypii: a model for fungal developmental biology. Nature Rev Microbiol 3:421–429
Zaremberg V, Donella-Deana A, Moreno S (2000) Mechanism of activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase: in Mucor rouxii the apparent specific activity of the cAMP-activated holoenzyme is different than that of its free catalytic subunit. Arch Biochem Biophys 381:74–82
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the University of Buenos Aires, grant X-270, from CONICET (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas) grant PIP 5239 and from ANPCYT (Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica) grant PICT 01-08793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Argimón, S., Galello, F., Pereyra, E. et al. Mucor rouxii Rho1 protein; characterization and possible role in polarized growth. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 91, 237–251 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9113-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9113-7