Abstract
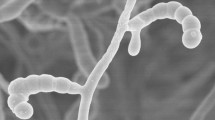
During the course of screening for industrially important microorganisms, an alkalitolerant and thermotolerant actinomycete, strain DAS 131T, was isolated from a soil sample collected from the Gulbarga region, Karnataka province, India. The strain was characterized by a polyphasic approach that showed that it belonged to the genus Streptomyces. Growth was observed over a wide pH range (pH 6–12) and at 45°C. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain DAS 131T was deposited in the GenBank database under the accession number DQ317411. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain DAS 131Twas most closely related to Streptomyces venezuelae ISP 5230T (AY999739) with a sequence similarity of 99.5% (8 nucleotide differences out of 1,477). Despite this very high sequence similarity, strain DAS 131T was phenetically distinct from S. venezuelae. The DNA relatedness between these strains was 54%, indicating that strain DAS 131T is a distinct genomic species. On the basis of phenetic and genetic analyses, strain DAS 131T is classified as a new species in the genus Streptomyces, for which we propose the name Streptomyces gulbargensis sp. nov.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker B, Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1965) Chemical composition of cell-wall preparations from strains of various form-genera of aerobic actinomycetes. Appl Microbiol 13:236–243
Brosius J, Palmer ML, Kennedy JP, Noller HP (1978) Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coil. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4801–4805
Chun J, Youn HD, Yim Y-I, Lee H, Kim MY, Hath YC, Kang S-O (1997) Streptomyces seoulensis sp.nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:492–498
Collins MD (1985) Isoprenoid quinone analysis in classification and identification. In: Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (eds) Chemical methods in bacterial systematics. Acdemic Press, London, pp 267–287
Cui XL, Mao PH, Tseng M, Li WJ, Zhang LP, Xu LH, Jiang CL (2001) Streptomonospora gen. Nov., a new member of the family Nocardiopsaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:357–363
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenesis: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Goodfellow M, Simpson KE (1987) Ecology of Streptomyces, frontiers. Appl Microbiol 2:97–125
Goodfellow M, Willaims ST (1983) Ecology of actinomycetes. Annu Rev Microbiol 37:189–216
Hoopwood DA, Bill MJ, Charter KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM, Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation of Streptomycetes: a laboratory manual. John Innes Foundation. Norwich, United Kingdom
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Iwai H, Takahashi Y (1992) Selection of microbial sources of bioactive compounds. In: Omura S (ed) The search for bioactive compounds from microorganisms. Springer-Ver-Lag, New York, pp 281–302
Jahnke KD (1992) Basic computer program for evolution spectroscopic DNA renaturation data from Gilford system 2600 spectrophotometer on a PC/XT/AT type personal computer. J Microbiol Methods 15:61–73
Kazav Komagata, Ken-Ichiro Suzuki (1987) Lipid and cell wall analysis in bacterial systematics. In methods in microbiology, vol 19. Academic press, London, pp 161–207
Kelly KL (1964) Inter society color council-National Bureau of standard color name charts illustrated with centroid colors. Published in US
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequence. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Korn-Wendisch F, Kutzner HJ (1992) The family Streptomycetaceae. In: Balows A, Trueper HG, Doworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The Prokaryotes; a handbook on the biology of Bacteria; Ecophysiology, isolation, identification, application 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, pp 921–995
Kumar S, Tamura K, Kakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA 2; molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Kuster K, Williams ST (1964) Selection of media for isolation of Streptomycetes 202:928–929
Labeda DP, Lechevalier MP, Testa RT (1997) Streptomyces stramineus sp.nov., a new species of the verticillate streptomyces. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:747–753
Lechevalier HA, Lechevalier MPA (1967) Biology of actinomycetes. Annu Rev Microbiol 21:71–100
Lechevalier HA, Lechevalier MPA (1970a) Critical evaluation of genera of aerobic actinomycetes. In: Prauser H (ed) The actinomycetes, Glustal Fischer. Verlag, Jena, pp 393–405
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1970b) Chemical composition as acriterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Bacteriol 20:435–443
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier HA (1980) The chemotaxonomy of actinomycetes. In: Dietz, Thayer (eds) Actinomycete taxonomy. society for industrail microbiology. Arlington, VA, pp 22–291
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Nolan RD, Cross T (1988) Isolation and screening of actinomycetes. In Goodfellow M, Williams ST, Mardarski M (eds) Actinomycetes in biotechnology. Academic Press, London, pp 2–8
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comp Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pridham TG, Gottilieb D (1948) The utilization of carbon compounds by some actinomycetales as an aid for species determination. J Bacteriol 56:107–114
Pridham TG, Anderson P, Foley C, Lindenfelser LA, Hesseltine CW, Benedict RG (1957) A selection of media for maintenance and taxonomic study of Streptomyces. Antibiot Ann 947–953
Pridham TG, Hesseltine CW, Benedict RG (1958) A guide for the classification of Streptomycetes according to selected groups placement of strains in morphological sections. Appl Microbiol 6:52–79
Saadoun I, Gharaibeh R (2002) The Streptomyces flora of Jordan and its potential as a source of antibiotics active against antibiotic resistant gram-negative bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:465–470
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour joining method; a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1968a) Cooperative description of type cultures of Streptomyces.II. Species description from first study. Int J Syst Bacteriol 18:69–189
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1968b) Cooperative description of type cultures of Streptomyces.III. Additional description from first and second studies. Int J Syst Bacteriol 18:279–392
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1969) Cooperative description of type cultures of Streptomyces.IV. Species descriptions from the second, third and fourth studies. Int J Syst Bacteriol 19:391–512
Takeuchi M, Hatano K (1998) Union of the genera Microbacteriam Orla-Jensen and Aureobacterium Collins et al. in a redefined genus Microbacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:739–849
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4888
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore WIC, Murry RGE, Stackerbrandt E, Starr MP, Truper HG (1987) Report of the adhoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington EMH, Sneath PHA, Sackin MJ (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
G. Dastager, S., Li, WJ., Agasar, D. et al. Streptomyces gulbargensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in Karnataka, India. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 91, 99–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9099-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9099-1