Abstract
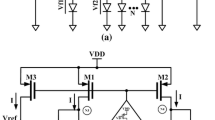
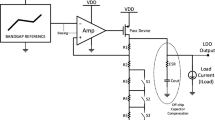
This paper reports a high-temperature integrated linear voltage regulator implemented in a 0.8-μm BCD (bipolar, CMOS and DMOS)-on-silicon-on-insulator process. This step-down voltage regulator converts an unregulated high input DC voltage to a regulated nominal CMOS voltage (i.e. 5 V) for the low-side buffer (pre-driver) and other digital and analog building blocks of a high-temperature integrated gate driver circuit. An error amplifier inside the regulator has been designed using inversion coefficient methodology, and a temperature stable current reference has been used to bias the error amplifier. The linear regulator provides an output voltage of 5.3 V at room temperature and can supply a maximum load current of 200 mA. The linear voltage regulator integrated circuit has been tested at ambient temperatures from 25 to 200 °C with the input voltage varying from 10 to 30 V. A compensation method (pole swap) that extends the range of the system stability has been implemented and analyzed in detail. The simulated unity gain bandwidth can reach approximately 4 MHz when the load current is 200 mA and the measured transient response time is less than 150 nS when the load current is 50 mA and the ambient temperature is 200 °C.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieberding, W. C., & Powell, J. A. (1982). High-temperature electronic requirements in aeropropulsion systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 29(2), 103–106.
Werner, M. R., & Fahrner, W. R. (2001). Review on materials, microsensors, systems and devices for high-temperature and harsh-environment applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 48(2), 249–257.
Tolbert, L. M., Peng, F. Z., Cunnyngham, T., & Chiasson, J. N. (2002). Charge balance control schemes for cascade multilevel converter in hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 49(5), 1058–1064.
M. A. Huque, S. K. Islam, B. J. Blalock, C. Su, R. Vijayaraghavan & L. M. Tolbert. (2008). Silicon-on-Insulator Based High-Temperature for automotive applications (pp. 2538–2543). Cambridge: IEEE International Symposium Industrial Electronics (ISIE08), June 30–July 2, 2008.
Huque, M. A., Tolbert, L. M., Blalock, B. J., & Islam, S. K. (2010). SOI-based high-voltage, high-temperature integrated circuit gate driver for SiC-based power FETs. IET Power Electronics, 3(6), 1001–1009.
Rincon-Mora, G. A., & Allen, P. E. (1998). A low-voltage, low quiescent current, low drop-out regulator. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(1), 36–44.
Bontempo, G., Signorelli, T., & Pulvirenti, F. (2001). Low supply voltage, low quiescent current, ULDO linear regulator. The 8th IEEE International Conference Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 1, 409–412.
B. W. Ohme, & M. R. Larson. (1998). Control circuit design for high temperature linear regulators (pp. 45–50). Albuquerque, NM: The Fourth International High Temperature Electronics Conference (HITEC), June 14–18, 1998.
B. Holter, & T. Fallet. (1997). High temperature integrated voltage regulator system design (pp. 1465–1468), vol. 2. Sacramento, CA: Proceedings of the 40th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, August 3–6, 1997.
T. Romanko. (2008). Extreme design: developing integrated circuit for −55 degC to +250 degC. Honeywell, High Temperature Electronics, Technical Article, 2008.
Shoucair, F. (1986). Design consideration in high temperature analog CMOS integrated circuits. IEEE Transactions on Components, Hybrids, and Manufacturing Technology, 9(3), 242–251.
J. P. Coling. (2004). SOI for hostile environment applications (pp. 1–4). Charleston: IEEE International SOI Conference, October 4–7, 2004.
Demeus, L., Dessard, V., Viviani, A., Adriaensen, S., & Flandre, D. (2001). Integrated sensor and electronic circuits in fully depleted SOI technology for high-temperature applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 48(2), 272–280.
G. A. Rincon-Mora. (2009). Analog IC design with low-dropout regulators. McGraw-Hill Companies, ISBN 978-0-07-1608930.
D. A. Badillo. (2002). 1.5 V CMOS current reference with extended temperature operating range (pp. 197–200, vol. 3). Phoenix, AZ: IEEE International Symposium Circuits and Systems, May 26–29, 2002.
D. M Binkley. (2007). Tradeoffs and optimization in analog CMOS design (pp. 47–60). Ciechocinek: 14th International Conference on Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and System, June 21–23, 2007.
Binkley, D. M. (2008). Tradeoffs and optimization in analog CMOS design. Chichester: Wiley-Interscience.
S. C. Terry, J. M. Rochelle, D. M Binkley, B. J. Blalock, D. P. Foty, & M. Bucher. (2003). Comparison of a BSIM3V3 and EKV MOSFET model for a 0.5 μm CMOS process and implications for analog circuit design. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 50(4 Pt 1), 915–920.
Allen, P. E., & Holberg, D. R. (2002). CMOS analog circuit design (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Cissoid. CHT-LDOP family: Versatile low dropout linear voltage regulator. www.cissoid.com.
P. Crepaldi, T. Pimenta, & R. Moreno. (2010). A CMOS low drop out voltage regulator. Cairo: 22nd IEEE International Conference on Microelectronics, 2010.
Z. Liu, Xi. Jin, N. Jin, Y. He, & Y. Cheng. (2010). Design of wide power supply, high performance voltage regulator with BCD process. Shanghai: 2010 Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics and Electronics, 2010.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Oak Ridge National Laboratory through the U.S. Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Program and the II-VI Inc. Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, C., Islam, S.K., Zhu, K. et al. A high-temperature, high-voltage, fast response linear voltage regulator. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 72, 405–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-012-9877-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-012-9877-9