Abstract
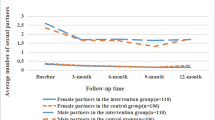
HIV self-testing (HIVST) is an effective method to expand HIV testing coverage worldwide. We analyze the results of HIVST and sexual behaviors of first-time testers among Men who have sex with men (MSM) who participated in a secondary distribution of HIVST kits. A total of 589 participants were recruited, including 173 first-time testers and 416 non-first-time testers. The first-time testers were mainly of Han ethnicity (aOR 1.88, 95% CI 1.10, 3.24), more likely to be HIV positive (aOR 7.18, 95% CI 2.37, 21.72), and had higher income (aOR 2.01, 95% CI 1.10, 3.69). Both groups were less likely to have anal sex with male partners (χ2: 146.24, P < 0.01), (χ2: 582.72, P < 0.01) or have sex with female partners (χ2: 19.01, P < 0.01), (χ2: 35.74, P < 0.01) after HIVST. We should expand HIVST among MSM and other key populations to identify first-time testers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNAIDS. UNAIDS DATA 2021. 2021; https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/JC3032_AIDS_Data_book_2021_En.pdf.
Dong MA-O, Peng B, Liu ZF, et al. The prevalence of HIV among MSM in China: a large-scale systematic analysis. (1471–2334 (Electronic)).
Xu JJ, Han MJ, Jiang YJ, et al. Prevention and control of HIV/AIDS in China: lessons from the past three decades. (2542–5641 (Electronic)).
Chao HJJHW. Incidence of new HIV infection and its influencing factors among men who have sex with men in China: a meta-analysis. Prev Med. 2022;34(01):70–7.
World Health Organziation. Guidelines on HIV self-testing and partner notification: supplement to consolidated guidelines on HIV testing services.
Figueroa C, Johnson C, Verster A, Baggaley R. Attitudes and acceptability on HIV self-testing among key populations: a literature review. AIDS Behav. 2015;19(11):1949–65.
Bao HY, Xiong Y, Marley M, Tang WM. [Current status of HIV self-testing application]. (0254–6450 (Print)).
Wu D, Cheng WB, Xiong Y, Lu Y, Ni YX, Tang WM. [Changing trends of HIV testing and HIV self-testing in men who have sex with men on a gay social networking app]. (0254–6450 (Print)).
Bien CH, Best Jm Fau - Muessig KE, Muessig Ke Fau - Wei C, Wei C Fau - Han L, Han L Fau - Tucker JD, Tucker JD. Gay apps for seeking sex partners in China: implications for MSM sexual health. (1573–3254 (Electronic)).
Sze WN, Kwan TH, Kei LKC, Chui LJY, Shan LS. Delineation of chemsex patterns of men who have sex with men in association with their sexual networks and linkage to HIV prevention. Int J Drug Policy. 2020;75:102591.
Marshall BDL, Goedel WC, King MRF, et al. Potential effectiveness of long-acting injectable pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men: a modelling study. (2352–3018 (Electronic)).
Ngure K, Heffron R, Mugo N, et al. Feasibility and acceptability of HIV self-testing among pre-exposure prophylaxis users in Kenya. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017;20:21234.
Wu DA-O, Zhou Y, Yang N, et al. Social Media-Based Secondary Distribution of Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Syphilis Self-testing Among Chinese Men Who Have Sex with Men. (1537–6591 (Electronic)).
Dailey AF, Hoots BE, Hall HI, et al. Vital Signs: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Testing and Diagnosis Delays - United States. (1545–861X (Electronic)).
Jin X, Xu JJ, Smith MK, et al. An internet-based self-testing model (easy test): cross-sectional survey targeting men who have sex with men who never tested for HIV in 14 Provinces of China. J Med Internet Res. 2019;21(5):e11854.
Zhang J, Gao Y, Li D, Li T, Yang Y. Willingness and influencing factors on HIV testing among college young students in Daxing District, Beijing. Chin J Aids STD. 2021;27(7):763–6.
Yu B, Yang S, Pei R, Huang Y. Ways and willingness of HIV testing of college students and influencing factors in Sichuan province. Chin J Aids STD. 2021;27(2):141–5.
Cao Y, Meng XY, Weng H, Peng MJ, Yan H, Li SY. Prevalence of AIDS-related sexual behaviors and HIV infection status in young men who have sex with men in China: a meta-analysis. Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi = Zhonghua liuxingbingxue zazhi. 2016;37(7):1021–7.
Zhou Y, Lin K, Dai W, et al. Analysis of HIV testing and associated factors among college students in Zhuhai. Chin J Aids STD. 2020;26(11):1193–6.
Khawcharoenporn T, Mongkolkaewsub S, Naijitra C, Khonphiern W, Apisarnthanarak A, Phanuphak N. HIV risk, risk perception and uptake of HIV testing and counseling among youth men who have sex with men attending a gay sauna. AIDS Res Therapy. 2019;16:1–11.
Gao M, Xiao C, Cao Y, Yu B, Li S, Yan H. Associations between sexual sensation seeking and AIDS-related knowledge, attitudes and behaviors among young men who have sex with men in China. Psychol Health Med. 2017;22(5):596–603.
Yawei ZYYYDW. Willingness and demands for AIDS-related health education among college students in Zhuhai. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(05):902–6.
Ijadunola KT, Abiona TC, Odu OO, Ijadunola MY. College students in Nigeria underestimate their risk of contracting HIVAIDS infection. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2007;12(2):131–7.
Ye R, Liu C, Tan S, et al. Factors associated with past HIV testing among men who have sex with men attending university in China: a cross-sectional study. (1449–8987 (Electronic)).
Cheng WB, Egan JE, Liu Q, Xu HF, Stall R, Friedman MR. Psychosocial correlates of HIV testing frequency among men who have sex with men in Guangzhou, China. AIDS Behav. 2020;24(2):363–72.
Jin W, Cheng W, Zhong F, et al. Willingness and correlated factors of HIV self-testing used for sexual partners among HIV-infected MSM in Guangzhou. Chin J Aids STD. 2019;25(5):472–5.
Jiang J, Pan XH, Yang JZ, et al. Willingness for HIV test and associated factors among 535 college students who had sex in Zhejiang province. Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi = Zhonghua liuxingbingxue zazhi. 2016;37(10):1356–60.
Leblanc NM, Andes KL. An exploration of men’s knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of HIV, HIV Risk, and willingness to test for HIV in Yendi District, Northern Ghana. JANAC J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2015;26(3):281–95.
Xiao D, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Factors associated with the willingness to HIV test in men who have sex with men in Fengtai district of Beijing. China Prev Med. 2021;22(7):513–6.
Jiao KD, Wei R, Li HC, et al. HIV testing frequency and associated factors among five key populations in ten cities of China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):1–12.
Tang W, Huang W, Lu H, et al. What happens after HIV self-testing? Results from a longitudinal cohort of Chinese men who have sex with men. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):1–7.
Choi KWY, Choi EPH, Chow EPF, et al. The experience of using dating applications for sexual hook-ups: a qualitative exploration among HIV-negative men who have sex with men in Hong Kong. (1559–8519 (Electronic)).
Stevens DR, Vrana CJ, Dlin RE, Korte JE. A global review of HIV self-testing: themes and implications. AIDS Behav. 2018;22(2):497–512.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to all the participants who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Medical Science and Technology Foundation of Guangdong Province [Grant Number 20201110143347920].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, YF and HL; Methodology, ZG and MC; Software, YW and HT; Validation, MD and SH; Formal analysis, JL and YF; Data curation, YZ and MD; Writing—original draft preparation, YF and HL; Writing—review and editing, YF and HL; Visualization, SZ and HL; upervision, YZ; Project administration, WM and WT; Funding acquisition, WM and WT; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Prior to launching the study, ethical approval was obtained from the institutional review board of the Zhuhai Municipal Center for Diseases Prevention and Control in China (ZHCDC2018014).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, H., Feng, Y., Zhou, Y. et al. Factors Associated with First-Time HIV Testing Among MSM via Secondary Distribution of HIV Self-test Kits in Zhuhai, China. AIDS Behav 27, 1942–1949 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-022-03927-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-022-03927-8