Abstract
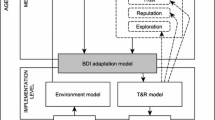
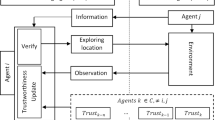
Computational trust and reputation models have been recognized as one of the key technologies required to design and implement agent systems. These models manage and aggregate the information needed by agents to efficiently perform partner selection in uncertain situations. For simple applications, a game theoretical approach similar to that used in most models can suffice. However, if we want to undertake problems found in socially complex virtual societies, we need more sophisticated trust and reputation systems. In this context, reputation-based decisions that agents make take on special relevance and can be as important as the reputation model itself. In this paper, we propose a possible integration of a cognitive reputation model, Repage, into a cognitive BDI agent. First, we specify a belief logic capable to capture the semantics of Repage information, which encodes probabilities. This logic is defined by means of a two first-order languages hierarchy, allowing the specification of axioms as first-order theories. The belief logic integrates the information coming from Repage in terms if image and reputation, and combines them, defining a typology of agents depending of such combination. We use this logic to build a complete graded BDI model specified as a multi-context system where beliefs, desires, intentions and plans interact among each other to perform a BDI reasoning. We conclude the paper with an example and a related work section that compares our approach with current state-of-the-art models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Rahman, A., & Hailes, S. (2000). Supporting trust in virtual communities. In Proceedings of the Hawaii’s international conference on systems sciences, Maui, Hawaii.
Bordini R. H., Hnbner J. F., Wooldridge M. (2007) Programming multi-agent systems in AgentSpeak using Jason. Wiley, Chichester
Carbo, J., Molina, J., & Davila, J. (2002). Comparing predictions of sporas vs. a fuzzy reputation agent system. In 3rd International conference on fuzzy sets and fuzzy systems, Interlaken (pp. 147–153).
Carbo J., Molina J., Davila J. (2002) Trust management through fuzzy reputation. International Journal in Cooperative Information Systems 12(1): 135–155
Casali, A. (2008). On intentional and social agents with graded attitudes. PhD thesis, Universitat de Girona.
Casali, A., Godo, L., & Sierra, C. (2004). Graded models for BDI agents. In J. Leite & P. Torroni (Eds.), CLIMA V, Lisboa, Portugal (pp. 18–33).
Casali, A., Godo, L., & Sierra, C. (2008). A logical framework to represent and reason about graded preferences and intentions. In Proceedings of KR’08, Sydney, Australia.
Castelfranchi, C., & Falcone, R. (1998). Social trust. In Proceedings of the first workshop on deception, fraud and trust in agent societies, Minneapolis, USA (pp. 35–49).
Conte R., Paolucci M. (2002) Reputation in artificial societies: Social beliefs for social order. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Demolombe, R., & Liau, C. (2001). A logic of graded trust and belief fusion. In Proceedings of the 4th workshop on deception, fraud and trust in agent societies (pp. 13–25).
eBay. (2002). eBay. http://www.eBay.com.
Enderton H. B. (1972) A mathematical introduction to logic. Academic Press, New York
Fagin R., Halpern J. (1994) Reasoning about knowledge and probability. Journal of the ACM 41(2): 340–367
Flaminio T., Pinna G. M., Tiezzi E. B. P. (2008) A complete fuzzy logical system to deal with trust management systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 159(10): 1191–1207
ForTrust. (2009). ForTrust: Social trust analysis and formalization. http://www.irit.fr/ForTrust/.
Gaertner, D., Noriega, P., & Sierra, C. (2006). Extending the BDI architecture with commitments. In Proceedings of the CCIA’06 (pp. 247–257).
Giunchiglia F., Serafini L. (1994) Multilanguage hierarchical logic (or: How we can do without modal logics). Journal of AI 65: 29–70
Grabisch, M., Orlovski, S. A., & Yager, R. R. (1998). Fuzzy aggregation of numerical preferences. In Fuzzy sets in decision analysis, operations research and statistics (pp. 31–68).
Grant J., Kraus S., Perlis D. (2000) A logic for characterizing multiple bounded agents. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 3(4): 351–387
Hájek, P., Godo, L., & Esteva, F. (1995). Fuzzy logic and probability. In Uncertainty in artificial intelligence conference (pp. 237–244).
Herzig A., Lorini E., Hubner J. F., Vercouter L. (2010) A logic of trust and reputation. Logic Journal of the IGPL 18(1): 214–244
Huynh T., Jennings N., Shadbolt N. (2006) An integrated trust and reputation model for open multi-agent systems. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems 13(2): 119–154
Joseph, S., Dellunde, P., Schorlemmer, M., & Sierra, C. (2008). Formalizing deductive coherence: An application to norm evaluation. In NORMAS (pp. 158–172).
Kooi B. P. (2003) Probabilistic dynamic epistemic logic. Journal of Logic, Language and Information 12(4): 381–408
Kozen, D. (1983). A probabilistic PDL. In STOC ’83: Proceedings of the fifteenth annual ACM symposium on theory of computing, New York, NY, USA (pp. 291–297). ACM.
Liau C. J. (2003) Belief, information acquisition, and trust in multi-agent systems: A modal logic formulation. Artificial Intelligence 149(1): 31–60
Lorini E., Demolombe R. (2008) From binary trust to graded trust in information sources: A logical perspective. In: Barber S., Falcone R., Sabater-Mir J., Singh M. (eds) Trust in agent societies, volume 5396 of LNAI. Springer, New York, pp 205–225
Luck, M., McBurney, P., Shehory, O., & Willmott, S. (2005). Agent technology: Computing as interaction (A roadmap for agent based computing). AgentLink.
Marsh, S. (1994). Formalising trust as a computational concept. PhD thesis, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Stirling.
Miceli, M., & Castelfranchi, C. (2000). The role of evaluation in cognition and social interaction. In Human cognition and social agent technology (pp. 225–259). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Muller, G., & Vercouter, L. (2005). Decentralized monitoring of agent communications with a reputation model. In R. Falcone, K. S. Barber, J. Sabater-Mir, & M. P. Singh (Eds.), Trusting agents for trusting electronic societies, theory and applications in HCI and E-commerce, volume 3577 of Lecture notes in computer science. New York: Springer.
Parsons S., Sierra C., Jennings N. (1998) Agents that reason and negotiate by arguing. Journal of Logic and Computation 8(3): 261–292
Pinyol, I., and Sabater-Mir, J. (2009). Pragmatic–strategic reputation-based decisions in BDI agents. In Proceedings of the AAMAS’09, Budapest, Hungary (pp. 1001–1008).
Pinyol, I., & Sabater-Mir, J. (2010). Metareasoning and social evaluations in cognitive agents. In Autonomic computing and communications systems, volume 23 of LNISCT (pp. 220–235). Berlin: Springer.
Pinyol, I., Sabater-Mir, J., & Cuni, G. (2007). How to talk about reputation using a common ontology: From definition to implementation. In Proceedings of the ninth workshop on trust in agent societies, Hawaii, USA (pp. 90–101).
Pinyol, I., Sabater-Mir, J., & Dellunde, P. (2008). Probabilistic dynamic belief logic for image and reputation. In Proceedings of the CCIA’08, Empuries, Spain.
Rao A.S., Georgeff M.P. (1991) Modeling rational agents within a BDI-architecture. In: Allen J., Fikes R., Sandewall E. (eds) Proceedings of KR’91. San Mateo, CA, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, pp 473–484
Sabater-Mir, J. (2003). Trust and reputation for agent societies. PhD thesis, IIIA-CSIC, Barcelona, Spain.
Sabater-Mir J., Paolucci M. (2007) On representation and aggregation of social evaluations in computational trust and reputation models. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 46(3): 458–483
Sabater-Mir, J., Paolucci, M., & Conte, R. (2006). Repage: Reputation and image among limited autonomous partners. JASSS, 9(2).
Sabater, J., & Sierra, C. (2001). Regret: A reputation model for gregarious societies. In Proceedings of the fourth workshop on deception, fraud and trust in agent societies, Montreal, Canada (pp. 61–69).
Sabater, J., & Sierra, C. (2002). Reputation and social network analysis in multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of AAMAS-02, Bologna, Italy (pp. 475–482).
Sabater J., Sierra C. (2005) Review on computational trust and reputation models. Artificial Intelligence Review 24(1): 33–60
Sabater-Mir J., Sierra C., Parsons S., Jennings N. R. (2002) Engineering executable agents using multi-context systems. Journal of Logic and Computation 12(3): 413–442
Schillo, M., Funk, P., & Rovatsos, M. (2000). Using trust for detecting deceitful agents in artificial societies. Applied Artificial Intelligence (Special issue on trust, deception and fraud in agent societies).
Sen, S., & Sajja, N. (2002). Robustness of reputation-based trust: Boolean case. In Proceedings of the first international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (AAMAS-02), Bologna, Italy (pp. 288–293).
Yu, B., & Singh, M. P. (2001). Towards a probabilistic model of distributed reputation management. In Proceedings of the fourth workshop on deception, fraud and trust in agent societies, Montreal, Canada (pp. 125–137).
Yu, B., & Singh, M. P. (2003). Detecting deception in reputation management. In AAMAS ’03: Proceedings of the second international joint conference on autonomous agents and multiagent systems (pp. 73–80). New York: ACM Press.
Zacharia, G. (1999, September). Collaborative reputation mechanisms for online communities. Master’s thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinyol, I., Sabater-Mir, J., Dellunde, P. et al. Reputation-based decisions for logic-based cognitive agents. Auton Agent Multi-Agent Syst 24, 175–216 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10458-010-9149-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10458-010-9149-y