Abstract
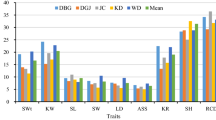
China is one of the countries most severely affected by desertification. Haloxylon ammodendron is an ecologically important component of the desert ecosystem and is one of the main shrub species used for ecological restoration. We compared the genetic variation in seed and seedling traits among six H. ammodendron provenances arrayed from east to west in China. The experiment was carried out in a greenhouse in well-prepared seedling beds (lines 1.5 m apart and seeds with in lines 1.0 m apart, 2.0 cm deep) with five lines (seven seeds per line) per provenance in a randomized block design with six replicates. The seed traits of fruit wing length, kernel weight, germination rate, and survival rate were compared, as were the seedling traits of internode length, branch number, assimilation shoot diameter, height, collar diameter, new shoot length, main root number, main root length, aboveground fresh weight, and underground fresh weight. Moreover, correlations between each seed and seedling trait and climate and geographical factors were assessed. The results show that the seeds from Dengkou County, Inner Mongolia had the best performance. Germination rate and survival rate were significantly positively correlated with longitude; and fruit wing length, kernel weight, seedling height, and new shoot length were significantly negatively correlated with latitude. Fruit wing length was significantly correlated with altitude. Among the climatic factors, the temperature in January had a strong direct effect on fruit wing length, germination rate, seedling height, and new shoot length. The mean annual rainfall had a strong direct effect on collar diameter. Humidity had a strong direct effect on survival rate. Seedling height, aboveground weight, and collar diameter could be important criteria for early provenance selection in the seedling stage. This study provides a reference for the selection of high-quality H. ammodendron seeds for drylands of northwest China.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An SQ, Fang TZ, Liu ZK, Deng XF, Zhang J (1996) Study on seedling growth among five species of shrub and their provenances. J Inn Mong For Coll 18(3):21–28 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Arbuckle JL (1995) Amos 3.5 for Windows. SmallWaters Corporation, Chicago
Bedunah DJ, Schmidt SM (2000) Rangelands of Gobi Gurvan Saikhan national conservation park, Mongolia. Rangelands 22:18–24
Bradshaw AD (1987) The reclamation of derelict land and the ecology of ecosystems. In: Jordan WR, Gilpin ME, Aber JD (eds) Restoration ecology: a synthetic approach to ecological research. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 53–83
Casati P, Andreo CS, Edwards GE (1999) Characterization of NADP-malic enzyme from two species of Chenopodiaceae: Haloxylon persicum (C4) and Chenopodium album (C3). Phytochemistry 52:985–992
CCICCD (Chinese Committee for Implementing UN Convention to Combat Desertification) (1997) China Country Paper to Combat Desertification. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing
Chen P, Pan XL (2001) Change of betaine contents and activity of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase in seedlings of Haloxylon ammodendron under drought and NaCl stress. Plant Physiol Commun 37:520–522 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo QS, Tan DY, Liu YJ, Wang CL (2004) Advance in studies of Haloxylon Bunge’s mechanism of adaptation and resistance to drought. For Res 17:796–803 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo QS, Guo ZH, Yan H, Wang CL, Tan DY, Ma C, He YH (2005a) Study on potential distribution of Haloxylon plants dominated desert vegetation in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 25:848–853 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo QS, Wang CL, Guo ZH, Tan DY, Shi ZM (2005b) Geographic distribution of existing Haloxylon desert vegetation and its patch character in China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 41:2–7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang PX (2002) No-irrigation vegetation and its restoration in arid area. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Huang ZC, Pu JC, Zhao CX (1984) Net photosynthesis and CO2 compensation points of desert plants in Minqin and Shapotou region. J Desert Res 4:23–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang ZY, Zhang XS, Zheng GH, Gutterman Y (2003) Influence of light, temperature, salinity and storage on seed germination of Haloxylon ammodendron. J Arid Environ 55:453–464
Jiang J (1992) The physioecological characters of transpiration of two species of Haloxylon. Arid Zone Res 9:14–17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang XC, Guo XH, Pan XL, Song SQ (2004) Construction and differential screening of a cDNA library specific to osmotic stress of Haloxylon ammodendron Seedlings. J Biochem Mol Biol 37:527–532 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Johnsen KH, Seiler JR (1996) Growth, shoot phenology and physiology of diverse seed sources of black spruce, I: seedling responses to varied atmospheric CO2 concentrations and photoperiods. Tree Physiol 16:367–373
Knapp EE, Rice KJ (1994) Starting from seed: genetic issues in using native grasses for restoration. Restor Manage Notes 12:40–45
Lanzhou Institute of Desert Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1985) Desert flora of China. Science Press, Beijing, pp 342–343 (in Chinese)
Lesica P, Allendorf FW (1999) Ecological genetics and the restoration of plant communities: mix or match? Restor Ecol 7:42–50
Li ZQ, Wang ZT (2000) Inheritance and variation of floral and fruit quantitative traits of Liriodendron interspecific hybrid and its parent species. For Res 13:290–294 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li HS, Zhang XL, Hou CX, Ma J (1995) The study on diversity of adaptation of Haloxylon Ammodendron to drought. Arid Zone Res 12:15–17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J, Zhao CY, Zhu H, Wang F, Wang LJ, Kou SY (2007) Multi-scale heterogeneity of soil moisture following snow thawing in Haloxylon ammodendron shrubland. Sci China Ser D 50:49–55
Linhart YB (1995) Restoration, revegetation, and the importance of genetic and evolutionary perspectives. In: Roundy BA, McArthur ED, Haley JS, Mann DK (eds) Proceedings: wildland shrub and arid land restoration symposium, October 19–21, 1993, Las Vegas, Nevada. General Technical Report INT-GTR-315. US Forest Service, Ogden, UT, USA, pp 271–287
Liu GZ, Liu YH (1982) Influence of moisture on seed germination of Haloxylon ammodendron. J Xinjiang For Sci Technol 1:40–42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma L, Kong DS (2002) Primary study on selecting and breeding of improved seed quality in desertifed area. J Arid Land Resour Environ 16:107–111 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ma HB, Bao GX, Ma WD, Rong ZJ, Wang XY, Li B (2000) The resource, protection and utilization of Haloxylon ammodendron deserted grassland in Inner Mongolia. Pratacult Sci 17:1–5 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mantovan NG (2002) Early growth differentiation among Prosopis flexuosa D.C. provenances from the Monte phytogeographic province, Argentina. New For 23:19–30
Nichols-Orians CM, Fritz RS, Clausen TP (1993) The genetic basis for variation in the concentration of phenolic glycosides in Salix sericea clonal variation and sex-based differences. Biochem Syst Ecol 21:535–542
Raddad EAY (2007) Ecophysiological and genetic variation in seedling traits and in first-year field performance of eight Acacia senegal provenances in the Blue Nile, Sudan. New For 34:207–222
Rehfeldt GE (1993) Genetic variation in the Ponderosae of the Southwest. Am J Bot 80:330–343
Sheng JH, Liu HY, Pan DZ, Yang XJ, Zhai ZX, Guo YH (2003) Study on phonological phases of Haloxylon Ammodendron (C.A.Mey.)Bunge. Rev China Agric Sci Technol 5:60–63 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song J, Feng G, Tian CY, Zhang F (2005) Strategies for adaptation of Suaeda physophora, Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum to a saline environment during seed germination stage. Ann Bot 96:399–405
Song J, Feng G, Tian CY, Zhang FS (2006) Osmotic adjustment traits of Suaeda physophora, Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum in field or controlled conditions. Plant Sci 170:113–119
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Su PX, Liu XM, Zhang LX, Zhao AF, Li WR, Chen HS (2004) Comparison of d 13C values and gas exchange of assimilating shoots of desert plants Haloxylon ammodendron and Calligonum mongolicum with other plants. Isr J Plant Sci 52:87–97
Su PX, Cheng GD, Yan QD, Liu XM (2007) Photosynthetic regulation of C4 desert plant Haloxylon ammodendron under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul 51:139–147
Sun XF, Sun RC, Lu Q, Xu F, Lin L (2002) Fractional isolation and physico-chemical characterization of hemicelluloses by two-stage treatment from Haloxylon ammodendron and Elaeagnus angustifolia. J Agric Food Chem 50:6400–6407
Tobe K, Li XM, Omasa K (2000) Effects of Sodium chloride on seed germination and growth of two Chinese desert shrubs, Haloxylon ammodendron and H. persicum (Chenopodiaceae). Aust J Bot 48:455–460
Tobe K, Li XM, Omasa K (2005) Effects of irrigation on seedling emergence and seedling survival of a desert shrub Haloxylon ammodendron (Chenopodiaceae). Aust J Bot 53:529–534
Ungar IA (1991) Ecophysiology of vascular halophytes. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wang Y, Yin LK (1989) Preliminary evaluation of Haloxylon seeds quality from different provenances. Arid Zone Res 1:45–49 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang W, Liang CZ, Zhu ZY (2001) Studies on the measuring method of growth rings of Haloxylon Ammodendron and its growing dynamics. J Arid Land Resour Environ 15:67–74 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang CL, Guo QS, Tan DY, Shi ZM, Ma C (2005) Haloxylon ammodendron community patterns in different habitats along southeastern edge of Zhunger Basin. Chin J Appl Ecol 16:1224–1229 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei J, Zhang XM, Shan LS, Yan HL, Liang SM (2007) Seedling growth dynamic of Haloxylon ammodendron and its adaptation strategy to habitat condition in hinterland of desert. Sci China Ser D 50:107–114
West NE (ed) (1983) Temperate deserts and semi-deserts. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Wu ZY (1995) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing
Xu LH, Liu HY, Chu XZ, Su K (2006) Desert vegetation patterns at the northern foot of Tianshan Mountains: the role of soil conditions. Flora 201:44–50
Yang ZW, Zheng RH, Hou BX, Zeng ZG (2003) A study on the biomass variance and comprehensive evaluation at the seedling stage of Fokienia hodginsii provenances. For Res 16:39–44 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao MF, Ge C, Zhai ZH (1997) Study on the determination of salt-tolerance index of main afforestation tree species and their ordination in arid areas with secondary salinization. For Res 10:194–198 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou ZB, Xu XW (2002) Absorption characteristics of ions in three species of shrubs of the artificially-planted greenbelts in the hinterland of Taklamakan Desert. Arid Zone Res 19:49–52 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu GL, Mosyakin SL, Clemants SE (2003) Chenopodiaceae. In: Flora of China Editorial Committee (ed) Flora of China, vol 5. Science Press, Beijing, pp 351–414
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by State Sci. & Tech. Supporting Project (2006BAD26B05). We thank Prof. Longjun Ci for her comments on this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J.L., Wang, Y.G., Yang, X.H. et al. Genetic variation in seed and seedling traits of six Haloxylon ammodendron shrub provenances in desert areas of China. Agroforest Syst 81, 135–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-010-9361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-010-9361-4