Abstract
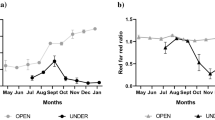
Most of Pinus brutia (Ten.) Holmboe forests are grazed, as silvopastoralism is well adapted in the Mediterranean environment. However, little attention has been paid to the demographic dynamic of the understorey vegetation even though it is strongly affected by the absorbed radiation. The purpose of this study was to examine the adaptation of herbaceous plant species under a Pinus brutia canopy, in Northern Greece. Monocultures of four plant groups (annual and perennial grasses, annual and perennial legumes) were sown in experimental areas of 50%, 70% and 100% light intensity. The density of annual and perennial grasses and perennial legumes were decreased by the shade cast by the Pinus brutia canopy. Population density of the annual legumes was little affected by light intensity: the annual grasses Bromus mollis L. and Lolium rigidum Gaudin; the perennial grasses Dactylis glomerata L. var. palestine, Festuca arundinacea and Agropyron cristatum (L.) Gaertn; the perennial legume Medicago sativa L. var. romana; the annual legumes Medicago lupulina L. and all the tested varieties of Trifolium subterraneum adapted well to the 50% light intensity habitat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chazdon RL, Pearcy RW, Lee DW, Fetcher N (1996) Photosynthetic responses of tropical forests plant to contrasting light environments. In: Mulkey S, Chazdon RL, Smith AP (eds) Tropical plant ecophysiology. Chapman and Hall, New York
Crawford RMM (1989) Studies in plant survival. Blackwell, Oxford
Grime JP (1973) Competitive exclusion in herbaceous vegetation. Nature 242:344–347
Harper JL (1977) Population biology of plants. Academic Press, London
Joffre R, Rambal S, Ratte JP (1999) The dehesa system of southern Spain and Portugal as a natural ecosystem mimic. Agroforest Syst 45:57–79
Joffre R, Vacher J, De Los Llanos C, Long G (1988) The dehesa: an agrosilvopastoral system of the Mediterranean region with special reference to the Sierra Morena area of Spain. Agroforest Syst 6:71–96
Koukoura Z, Nastis AS (1989) Effect of shade on production and herbage quality of herbaceous species. Geotech Sci Iss 1:17–25 (In Greek, English summary)
Koukoura Z, Ispikoudis I, Nastis A (1998) Effects of animal husbandry on plant diversity in various habitats. In: Waterhouse A, McEwan E (eds) Landscapes, livestock and livelihoods in European less favoured areas. SAC, Auchincruive, Ayr
Koukoura Z, Noitsakis B (2001) Demographic changes in mixed herbaceous plant stands undertorey of P. brutia. In: Radoglou K (eds) Forest research: a challenge for an integrated European approach. NAGREF, Thessaloniki
Koukoura Z, Papanastasis V (1996) Establishment and growth of seeded grasses and legumes in pine silvopastoral systems. In: Etienne M (eds) Western European silvopastoral systems. INRA, Paris
Kyriazopoulos AP, Koukoura Z, Nastis AS (1999) Effects of wild cherry (Prunus avium) and grazing on the herbaceous understorey and its crude protein content. Grassld Sci Europe 4:187–190
Lamaire G, Chapman DE (1996) Tissue flows in grazed communities. In: Hodgon J, Illius AW (eds) The ecology and management of grazing systems. CAB International, Wallingford
Lamaire G, Agnusdei M, (2000) Leaf tissue turnover and efficiency of herbage utilization. In: Lamaire G, Hodgson J, de Moraes A, de Carvalho PC, Nabinger C (eds) Grassland ecophysiology and grazing ecology. CAB International, Wallingford
Larcher W (1980) Physiological plant ecology. Springer-Verlag, New York
Mantzanas KT, Papanastasis VP (2003) Effects of thinning, N fertilization and legume seeding on the uderstorey production of a Pinus brutia plantation in northern Greece. In: Platis P, Papachristou T (eds) Range science and development of mountainous regions. Proceedings of the 3rd Panhellenic Rangeland Congress. HPRS, Athens (In Greek, English summary)
Ministry of Agriculture (1992) Results of the First Forest Survey. General secretariat of forests and natural environment, GSFNE. Athens (In Greek)
Mosquera-Losada MR, Pinto-Tobalina M, Rigueiro-Rodriguez A (2005b) The herbaceous component in temperate silvopastoral systems. In: Mosquera-Losada MR, McAdam J, Rigueiro-Rodriguez A (eds) Silvopastoralism and sustainable land management. CAB International, Oxfordshire
Mosquera-Losada MR, Rigueiro-Rodriguez A, Rois-Dias M, Schuck A, Van Brusselen J (2005a) Assessing biodiversity on silvopastoral systems across Europe. Grassld Sci Europe 10:44–51
Nichols JT, Sanson DW, Myran DD (1993) Effect of grazing strategies and pasture species on irrigated pasture beef production. J Rang Manag 46:65–69
Olea L, Lopez-Bellido RJ Poblaciones MJ (2005) European types of silvopastoral systems in the Mediterranean area: dehesa. In: Mosquera-Losada MR, McAdam J, Rigueiro-Rodriguez A (eds) Silvopastoralism and sustainable land management. CAB International, Oxfordshire
Ovalle C, Avendano J (1988) Interaction de la strate ligneuse avec la strate herbacee dans les formations d’Acacia carven au Chili: I. Influence de l’arbre sur la composition floristique, la production et la phenologie de la strate herbacee. Ecol Plant 22(4):385–404
Papanastasis V (1996) Silvopastoral systems and range management in the Mediterranean region. In: Etienne M (eds) Western European silvopastoral systems. INRA, Paris
Peri PL, McNeil DL, Moot DJ, Varella AC, Lucas RJ (2002) Net photosynthetic rate of cocksfoot leaves under continuous and fluctuating shade conditions in the field. Grass Forage Sci 57(2):157–170
Pieper RD (1990) Overstory—understorey relation in pinyon—juniper woodlands in New Mexico. J Rang Manag 43:413–415
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koukoura, Z., Kyriazopoulos, A. Adaptation of herbaceous plant species in the understorey of Pinus brutia . Agroforest Syst 70, 11–16 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-007-9031-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-007-9031-3