Abstract
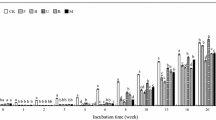
Trees in farming systems can improve fertility of soils through mineralization of N in their litter. This study was to determine the quality parameters (i.e., chemical composition) of organic residues that are associated with N mineralization in soils under submerged and aerobic conditions, and to demonstrate that aeration conditions should be taken into account in categorization of organic residues as N sources in farming systems. Incubation experiments were conducted in Aeric Paleaquult soil under submerged and Oxic Paleustult soil under aerobic conditions. Treatments included litter and some fresh materials from trees as well as rice straw available in farming systems of Northeast Thailand. S. grandiflora and L. leucocephala (32 g kg−1 N) had the highest net N mineralization in both conditions. Some lower-quality (< 20 g kg−1 N) residues did exhibit low net N mineralization during the 16-week period under submerged conditions, but displayed almost no net N mineralization in aerobic conditions. Under submerged conditions, their net N mineralization was higher and more rapid. The nitrogen content of the residues was the most important factor controlling N mineralization under both conditions. Polyphenols exerted the highest negative influence on N mineralization in aerobic conditions, but exhibited no negative effect in submerged conditions. In categorizing organic residues for their effective use in soil fertility management, soil aeration conditions, as well as other environmental factors, should be taken into consideration in addition to residue quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Adulprasertsuk P. Vityakon B. Prachaiyo (1997) Leaf litter of some native trees in Northeast Thailand: Their decomposition and derived soil organic matter characteristics Proceedings of the International Conference on Tropical Forestry in the 21st Century. Vol. 2. Global changes in the tropical contexts Faculty of Forestry, Kasetsart University Bangkok, Thailand 25–28
J.M. Anderson J.S.I. Ingram (1993) Tropical soil biology and fertility: A handbook of methods EditionNumber2nd edition CAB International Wallingford, UK
F. Azam F.W. Simmons R.L. Mulvaney (1993) ArticleTitleMineralization of N from plant residues and its interaction with native soil N Soil Biol. Biochem. 25 1787–1792 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(93)90184-D
A.K.M. Azmal K Marumoto H. Shindo M. Nishiyama (1996) ArticleTitleMineralization and change in microbial biomass in water-saturated soil amended with some tropical plant residues Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 42 IssueID3 483–492
M. Becker J.K. Ladha J.C.G. Ottow (1994) ArticleTitleParameters affecting residue nitrogen mineralization in flooded soils Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 58 1666–1671 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitlCjsrk%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800060013x
F.E. Broadbent (1979) Mineralization of organic nitrogen in paddy soils Nitrogen and rice IRRI Los Banos, Philippines 105–118
M. Constantinides J.S. Fownes (1994) ArticleTitleNitrogen mineralization from leaves and litter of tropical plants: Relationship to nitrogen, lignin and soluble polyphenol concentrations Soil Biol. Biochem. 26 49–55 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(94)90194-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhvFSnsL4%3D
C. Ehaliotis G. Cadisch K.E. Giller (1998) ArticleTitleSubstrate amendments can alter microbial dynamics and N availability from maize residues to subsequent crops Soil. Biol. Biochem. 30 1281–1292 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00035-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkslCms7c%3D
P.M. Gale J.T. Gilmour (1988) ArticleTitleNet mineralization of carbon and nitrogen under aerobic and anaerobic conditions Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52 1006–1010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXmt12ntbo%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200040019x
E. Handayanto G. Cadisch K.E. Giller (1994) ArticleTitleNitrogen release from prunings of legume hedgerow trees in relations to quality of prunings and incubation method Plant and Soil 160 237–248 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXktlCisbs%3D
E. Handayanto G Cadisch K.E. Giller (1995) ArticleTitleManipulation of quality and mineralization of tropical legume tree prunings by varying N supply Plant and Soil 176 149–160 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00017685 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXot1Olu78%3D
E. Handayanto K.E. Giller G. Cadisch (1997) ArticleTitleRegulating N release from legume tree prunings by mixing residues of different quality Soil Biol. Biochem. 29 1417–1426 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00047-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtVCnsL4%3D
N.Z. Lupwayi I. Haque (1998) ArticleTitleMineralization of N, P, K, Ca and Mg from sesbania and leucaena leaves varying in chemical composition Soil Biol. Biochem. 33 IssueID3 337–343
Myers R.J.K., Palm C.A., Cuevas E., Gunatilleki I.U.N. and Brossard M. 1994. The synchronisation of nutrient mineralisation and plant nutrient demand. In: Woomer P.L. and Swift M.J. (eds), The biological management of tropical soil fertility, Wiley, pp. 81-116.
K. Oglesby J.H. Fownes (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of chemical composition on nitrogen mineralization from green manures of seven tropical leguminous trees Plant and Soil 143 127–132 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00009137 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XkvV2ntrY%3D
S. Ono (1989) ArticleTitleNitrogen mineralization from paddy and upland soils under flooded and nonflooded incubation Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 35 417–426
C.A. Palm P.A. Sanchez (1991) ArticleTitleNitrogen release from the leaves of some tropical legumes as affected by their lignin and polyphenolic contents Soil Biol. Biochem. 23 83–88 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(91)90166-H Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXht1SktLY%3D
C.A. Palm C.N. Gachengo R.J. Delve G. Cadisch K.E. Giller (2001) ArticleTitleOrganic inputs for soil fertility management in tropical agroecosystems: application of an organic resource database Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 83 27–42
S. Ruaysoongnern V. Trelo-ges T. Chuasavatee (1998) Nutrient cycling of leguminous tree species through litter fall. I. Nitrogen fixation of leguminous tree species in the Northeast of Thailand Faculty of Agriculture, Khon Kaen University Khon Kaen, Thailand
S. Sae-Lee P. Vityakon B. Prachaiyo (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of trees on paddy bunds on soil fertility and rice growth in Northeast Thailand Agroforestry Systems 18 213–223 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00123318
Tawinteung N., Murali N.S., Poovarodom S. and Upasena S.H. 1996. Availability of nitrogen from seven leguminous tree leaves under lowland rice cultivation on an acid sulfate soil. In: Attanandana T. et al. (eds), Proceedings of the International Symposium on ‘Maximizing sustainable rice yields through improved soil and environment management’. International Society of Soil Science, Soil and Fertilizer Society of Thailand, pp. 249-255.
B. Toomsan G. Cadisch M. Srichantawong C. Tongsodsaeng K.E. Giller V. Limpinuntana (2000) ArticleTitleBiological N2 fixation and residual N benefit of pre-rice leguminous crops and green manures Netherlands Journal of Agricultural Science 48 19–29
Vityakon P. 1995. Decomposition of and nutrient release from leaf litter of 5 multipurpose tree species in paddy rice agroecosystem of Northeast Thailand. In: Abstract of the Conference on Driven By Nature: Plant litter quality and decomposition. Wye College, University of London, p. 36.
P. Vityakon (2001) ArticleTitleThe role of trees in countering land degradation in cultivated fields in Northeast Thailand Southeast Asian Studies 39 398–416
P. Vityakon S. Meepetch G. Cadisch B. Toomsan (2000) ArticleTitleSoil organic matter and nitrogen transformation mediated by plant residues of different qualities in sandy acid upland and paddy soils Netherlands Journal of Agriculture Science 48 75–90 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosl2kurs%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vityakon, P., Dangthaisong, N. Environmental influences on nitrogen transformation of different quality tree litter under submerged and aerobic conditions. Agroforest Syst 63, 225–236 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-005-4161-y
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-005-4161-y