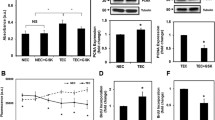
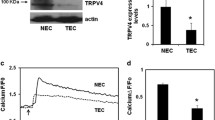
Abstract
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) is a ubiquitously expressed polymodally activated ion channel. TRPV4 has been implicated in tumor progression; however, the cell-specific role of TRPV4 in tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis is unknown. Here, we generated endothelial-specific TRPV4 knockout (TRPV4ECKO) mice by crossing TRPV4lox/lox mice with Tie2-Cre mice. Tumor growth and metastasis were significantly increased in a syngeneic Lewis lung carcinoma tumor model of TRPV4ECKO mice compared to TRPV4lox/lox mice. Multiphoton microscopy, dextran leakage, and immunohistochemical analysis revealed increased tumor angiogenesis and metastasis that were correlated with aberrant leaky vessels (increased width and reduced pericyte and VE-cadherin coverage). Mechanistically, increases in VEGFR2, p-ERK, and MMP-9 expression and DQ gelatinase activity were observed in the TRPV4ECKO mouse tumors. Our results demonstrated that endothelial TRPV4 is a critical modulator of vascular integrity and tumor angiogenesis and that deletion of TRPV4 promotes tumor angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data to support the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Adapala RK, Thoppil RJ, Ghosh K, Cappelli HC, Dudley AC, Paruchuri S, Keshamouni V, Klagsbrun M, Meszaros JG, Chilian WM, Ingber DE, Thodeti CK (2016) Activation of mechanosensitive ion channel TRPV4 normalizes tumor vasculature and improves cancer therapy. Oncogene 35(3):314–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.83
Adapala RK, Thoppil RJ, Luther DJ, Paruchuri S, Meszaros JG, Chilian WM, Thodeti CK (2013) TRPV4 channels mediate cardiac fibroblast differentiation by integrating mechanical and soluble signals. J Mol Cell Cardiol 54:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.10.016
Cappelli HC, Kanugula AK, Adapala RK, Amin V, Sharma P, Midha P, Paruchuri S, Thodeti CK (2019) Mechanosensitive TRPV4 channels stabilize VE-cadherin junctions to regulate tumor vascular integrity and metastasis. Cancer Lett 442:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.042
Hartmannsgruber V, Heyken WT, Kacik M, Kaistha A, Grgic I, Harteneck C, Liedtke W, Hoyer J, Kohler R (2007) Arterial response to shear stress critically depends on endothelial TRPV4 expression. PLoS One 2(9):e827
Liedtke W (2005) TRPV4 plays an evolutionary conserved role in the transduction of osmotic and mechanical stimuli in live animals. J Physiol 567(Pt 1):53–58
Matthews BD, Thodeti CK, Tytell JD, Mammoto A, Overby DR, Ingber DE (2010) Ultra-rapid activation of TRPV4 ion channels by mechanical forces applied to cell surface beta1 integrins. Integr Biol (Camb) 2(9):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ib00034e
Mendoza SA, Fang J, Gutterman DD, Wilcox DA, Bubolz AH, Li R, Suzuki M, Zhang DX (2010) TRPV4-mediated endothelial Ca2+ influx and vasodilation in response to shear stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298(2):H466-476
O’Neil RG, Heller S (2005) The mechanosensitive nature of TRPV channels. Pflugers Archiv : Eur J Physiol 451(1):193–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1424-4
Thodeti CK, Matthews B, Ravi A, Mammoto A, Ghosh K, Bracha AL, Ingber DE (2009) TRPV4 channels mediate cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell reorientation through integrin-to-integrin signaling. Circ Res 104(9):1123–1130
Fang Y, Liu G, Xie C, Qian K, Lei X, Liu Q, Liu G, Cao Z, Fu J, Du H, Liu S, Huang S, Hu J, Xu X (2018) Pharmacological inhibition of TRPV4 channel suppresses malignant biological behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma via modulation of ERK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 101:910–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.014
Lee WH, Choong LY, Jin TH, Mon NN, Chong S, Liew CS, Putti T, Lu SY, Harteneck C, Lim YP (2017) TRPV4 plays a role in breast cancer cell migration via Ca(2+)-dependent activation of AKT and downregulation of E-cadherin cell cortex protein. Oncogenesis 6(5):e338. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2017.39
Lee WH, Choong LY, Mon NN, Lu S, Lin Q, Pang B, Yan B, Krishna VS, Singh H, Tan TZ, Thiery JP, Lim CT, Tan PB, Johansson M, Harteneck C, Lim YP (2016) TRPV4 Regulates breast cancer cell extravasation, stiffness and actin cortex. Sci Rep 6:27903. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27903
Liu X, Zhang P, Xie C, Sham KWY, Ng SSM, Chen Y, Cheng CHK (2019) Activation of PTEN by inhibition of TRPV4 suppresses colon cancer development. Cell Death Dis 10(6):460. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1700-4
Olivan-Viguera A, Garcia-Otin AL, Lozano-Gerona J, Abarca-Lachen E, Garcia-Malinis AJ, Hamilton KL, Gilaberte Y, Pueyo E, Kohler R (2018) Pharmacological activation of TRPV4 produces immediate cell damage and induction of apoptosis in human melanoma cells and HaCaT keratinocytes. PLoS One 13(1):e0190307. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190307
Tang B, Wu J, Zhu MX, Sun X, Liu J, Xie R, Dong TX, Xiao Y, Carethers JM, Yang S, Dong H (2019) VPAC1 couples with TRPV4 channel to promote calcium-dependent gastric cancer progression via a novel autocrine mechanism. Oncogene 38(20):3946–3961. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0709-6
Peters AA, Jamaludin SYN, Yapa K, Chalmers S, Wiegmans AP, Lim HF, Milevskiy MJG, Azimi I, Davis FM, Northwood KS, Pera E, Marcial DL, Dray E, Waterhouse NJ, Cabot PJ, Gonda TJ, Kenny PA, Brown MA, Khanna KK, Roberts-Thomson SJ, Monteith GR (2017) Oncosis and apoptosis induction by activation of an overexpressed ion channel in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 36(46):6490–6500. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.234
Fiorio Pla A, Ong HL, Cheng KT, Brossa A, Bussolati B, Lockwich T, Paria B, Munaron L, Ambudkar IS (2012) TRPV4 mediates tumor-derived endothelial cell migration via arachidonic acid-activated actin remodeling. Oncogene 31(2):200–212
Moore C, Cevikbas F, Pasolli HA, Chen Y, Kong W, Kempkes C, Parekh P, Lee SH, Kontchou NA, Yeh I, Jokerst NM, Fuchs E, Steinhoff M, Liedtke WB (2013) UVB radiation generates sunburn pain and affects skin by activating epidermal TRPV4 ion channels and triggering endothelin-1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(34):E3225-3234. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1312933110
Adapala RK, Talasila PK, Bratz IN, Zhang DX, Suzuki M, Meszaros JG, Thodeti CK (2011) PKCalpha mediates acetylcholine-induced activation of TRPV4-dependent calcium influx in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(3):H757-765
Thoppil RJ, Adapala RK, Cappelli HC, Kondeti V, Dudley AC, Gary Meszaros J, Paruchuri S, Thodeti CK (2015) TRPV4 channel activation selectively inhibits tumor endothelial cell proliferation. Sci Rep 5:14257. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14257
Thoppil RJ, Cappelli HC, Adapala RK, Kanugula AK, Paruchuri S, Thodeti CK (2016) TRPV4 channels regulate tumor angiogenesis via modulation of Rho/Rho kinase pathway. Oncotarget 7(18):25849–25861. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8405
Wang J, Niu N, Xu S, Jin ZG (2019) A simple protocol for isolating mouse lung endothelial cells. Sci Rep 9(1):1458. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37130-4
Kanugula AK, Adapala RK, Midha P, Cappelli HC, Meszaros JG, Paruchuri S, Chilian WM, Thodeti CK (2019) Novel noncanonical regulation of soluble VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling by mechanosensitive ion channel TRPV4. FASEB J: Off Publ Feder Am Soc Exp Biol 33(1):195–203. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800509R
Tang Y, Harrington A, Yang X, Friesel RE, Liaw L (2010) The contribution of the Tie2+ lineage to primitive and definitive hematopoietic cells. Genesis 48(9):563–567. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvg.20654
Bentley K, Franco CA, Philippides A, Blanco R, Dierkes M, Gebala V, Stanchi F, Jones M, Aspalter IM, Cagna G, Westrom S, Claesson-Welsh L, Vestweber D, Gerhardt H (2014) The role of differential VE-cadherin dynamics in cell rearrangement during angiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 16(4):309–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2926
Le Guelte A, Dwyer J, Gavard J (2011) Jumping the barrier: VE-cadherin, VEGF and other angiogenic modifiers in cancer. Biol Cell 103(12):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1042/BC20110069
Agrawal V, Maharjan S, Kim K, Kim NJ, Son J, Lee K, Choi HJ, Rho SS, Ahn S, Won MH, Ha SJ, Koh GY, Kim YM, Suh YG, Kwon YG (2014) Direct endothelial junction restoration results in significant tumor vascular normalization and metastasis inhibition in mice. Oncotarget 5(9):2761–2777. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1942
Duda DG, Batchelor TT, Willett CG, Jain RK (2007) VEGF-targeted cancer therapy strategies: current progress, hurdles and future prospects. Trends Mol Med 13(6):223–230
Mammoto A, Connor KM, Mammoto T, Yung CW, Huh D, Aderman CM, Mostoslavsky G, Smith LE, Ingber DE (2009) A mechanosensitive transcriptional mechanism that controls angiogenesis. Nature 457(7233):1103–1108
Caporarello N, Lupo G, Olivieri M, Cristaldi M, Cambria MT, Salmeri M, Anfuso CD (2017) Classical VEGF, Notch and Ang signalling in cancer angiogenesis, alternative approaches and future directions (Review). Mol Med Rep 16(4):4393–4402. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7179
Casanovas O, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Hanahan D (2005) Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 8(4):299–309
Cuevas I, Boudreau N (2009) Managing tumor angiogenesis: lessons from VEGF-resistant tumors and wounds. Adv Cancer Res 103:25–42
Shibuya M (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-Receptor2: its biological functions, major signaling pathway, and specific ligand VEGF-E. Endothel: J Endothel Cell Res 13(2):63–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/10623320600697955
di Tomaso E, London N, Fuja D, Logie J, Tyrrell JA, Kamoun W, Munn LL, Jain RK (2009) PDGF-C induces maturation of blood vessels in a model of glioblastoma and attenuates the response to anti-VEGF treatment. PLoS One 4(4):e5123
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [NIH-(R15CA202847; R01HL119705 and R01HL148585 to CKT; R01 AI144115 and R15HL133918 to SP].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK, RA, AJ, NL and BG performed the research, analyzed the data, and edited the manuscript. WL provided the TRPV4lox/lox mice and edited the manuscript. LY and SP edited the manuscript. CKT designed, interpreted, and analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanugula, A.K., Adapala, R.K., Jamaiyar, A. et al. Endothelial TRPV4 channels prevent tumor growth and metastasis via modulation of tumor angiogenesis and vascular integrity. Angiogenesis 24, 647–656 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-021-09775-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-021-09775-9