Abstract
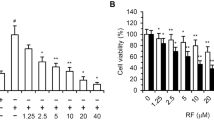
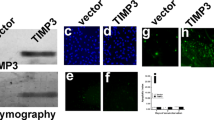
Solid tumors supply oxygen and nutrients required for angiogenesis by producing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Thus, inhibitors of VEGF signaling abrogate tumor angiogenesis, resulting in the suppression of tumor growth and metastasis. We here investigated the effects of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) on VEGF-induced angiogenesis. TRAIL inhibited VEGF-induced in vitro angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and in vivo neovascularization in chicken embryos and mice. TRAIL blocked VEGF-induced angiogenic signaling by inhibiting ERK, Src, FAK, paxillin, Akt, and eNOS. Further, TRAIL blocked intracellular Ca2+ elevation and actin reorganization in HUVECs stimulated with VEGF, without inhibiting VEGF receptor-2 tyrosine phosphorylation. TRAIL increased caspase-8 activity, without inducing caspase-9/-3 activation and apoptosis. Moreover, TRAIL resulted in cleavage of FAK into FAK-related non-kinase-like fragments in VEGF-stimulated HUVECs, which was blocked by a caspase-8 inhibitor and cellular caspase-8-like inhibitory protein. Biochemical and pharmacological inhibition of caspase-8 and FAK blocked the inhibitory effects of TRAIL on VEGF-stimulated anti-angiogenic signaling and events. In addition, caspase-8 knockdown also suppressed VEGF-mediated signaling and angiogenesis, suggesting that procaspase-8 plays a role of a non-apoptotic modulator in VEGF-induced angiogenic signaling. These results suggest that TRAIL inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by increasing caspase-8 activity and subsequently decreasing non-apoptotic signaling functions of procaspase-8, without inducing caspase-3 activation and endothelial cell cytotoxicity. These data indicate that caspase-8 may be used as an anti-angiogenic drug for solid tumors resistant to TRAIL and anti-tumor drugs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TRAIL:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- FRNK:
-
FAK-related non-kinase
- cFLIP:
-
Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein
- DEVDase:
-
Caspase-3-like protease
- IETDase:
-
Caspase-8-like protease
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- CAM:
-
Chick chorioallantoic membrane
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- DAF-FM:
-
3-Amino-4-(N-methylamino)-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- DED:
-
Death effector domain
References
Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, Dixit VM (1997) The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 276:111–113
Mahalingam D, Szegezdi E, Keane M, de Jong S, Samali A (2009) TRAIL receptor signalling and modulation: are we on the right TRAIL? Cancer Treat Rev 35:280–288
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Godowski P, Ashkenazi A (1997) Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 277:818–821
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R, Dixit VM (1997) An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 277:815–818
Di Pietro R, Zauli G (2004) Emerging non-apoptotic functions of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/Apo2L. J Cell Physiol 201:331–340
Thorburn A, Behbakht K, Ford H (2008) TRAIL receptor-targeted therapeutics: resistance mechanisms and strategies to avoid them. Drug Resist Updat 11:17–24
Yoshida T, Zhang Y, Rivera Rosado LA, Zhang B (2009) Repeated treatment with subtoxic doses of TRAIL induces resistance to apoptosis through its death receptors in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 7:1835–1844
Ebos JM, Kerbel RS (2011) Antiangiogenic therapy: impact on invasion, disease progression, and metastasis. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:210–2121
Folkman J (2001) Angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Semin Oncol 28:536–542
Rapisarda A, Melillo G (2012) Role of the VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv Cancer Res 114:237–267
Prokopiou EM, Ryder SA, Walsh JJ (2013) Tumour vasculature targeting agents in hybrid/conjugate drugs. Angiogenesis 16:503–524
Nitzsche B, Gloesenkamp C, Schrader M, Hoffmann B, Zengerling F, Balabanov S, Honecker F, Höpfner M (2012) Anti-tumour activity of two novel compounds in cisplatin-resistant testicular germ cell cancer. Br J Cancer 107:1853–1863
Idbaih A, Ducray F, Sierra Del Rio M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2008) Therapeutic application of noncytotoxic molecular targeted therapy in gliomas: growth factor receptors and angiogenesis inhibitors. Oncologist 13:978–992
Zhang XD, Nguyen T, Thomas WD, Sanders JE, Hersey P (2000) Mechanisms of resistance of normal cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis vary between different cell types. FEBS Lett 482:193–199
Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Carnevale E, Milani D, Pandolfi A, Zella D, Zauli G (2003) TRAIL promotes the survival and proliferation of primary human vascular endothelial cells by activating the Akt and ERK pathways. Circulation 107:2250–2256
Zauli G, Pandolfi A, Gonelli A, Di Pietro R, Guarnieri S, Ciabattoni G, Rana R, Vitale M, Secchiero P (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) sequentially upregulates nitric oxide and prostanoid production in primary human endothelial cells. Circ Res 92:732–740
Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Carnevale E, Corallini F, Rizzardi C, Zacchigna S, Melato M, Zauli G (2004) Evidence for a proangiogenic activity of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Neoplasia 6:364–373
Chen PL, Easton AS (2010) Evidence that tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) inhibits angiogenesis by inducing vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:936–941
Cantarella G, Risuglia N, Dell’eva R, Lempereur L, Albini A, Pennisi G, Scoto GM, Noonan DN, Bernardini R (2006) TRAIL inhibits angiogenesis stimulated by VEGF expression in human glioblastoma cells. Br J Cancer 94:1428–1435
Giacomini A, Righi M, Cleris L, Locatelli SL, Mitola S, Daidone MG, Gianni AM, Carlo-Stella C (2013) Induction of death receptor 5 expression in tumor vasculature by perifosine restores the vascular disruption activity of TRAIL-expressing CD34+ cells. Angiogenesis 16:707–722
Lee SJ, Namkoong S, Kim YM, Kim CK, Lee H, Ha KS, Chung HT, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2006) Fractalkine stimulates angiogenesis by activating the Raf-1/MEK/ERK- and PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent signal pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H2836–H2846
Kim I, Moon SO, Koh KN, Kim H, Uhm CS, Kwak HJ, Kim NG, Koh GY (1999) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of angiopoietin-related protein. angiopoietin-related protein induces endothelial cell sprouting. J Biol Chem 274:26523–26528
Namkoong S, Chung BH, Ha KS, Lee H, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2008) Microscopic technique for the detection of nitric oxide-dependent angiogenesis in an animal model. Methods Enzymol 441:393–402
Lee SJ, Kim KM, Namkoong S, Kim CK, Kang YC, Lee H, Ha KS, Han JA, Chung HT, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2005) Nitric oxide inhibition of homocysteine-induced human endothelial cell apoptosis by down-regulation of p53-dependent Noxa expression through the formation of S-nitrosohomocysteine. J Biol Chem 280:5781–5788
Junn E, Lee KN, Ju HR, Han SH, Im JY, Kang HS, Lee TH, Bae YS, Ha KS, Lee ZW, Rhee SG, Choi I (2000) Requirement of hydrogen peroxide generation in TGF-β1 signal transduction in human lung fibroblast cells: involvement of hydrogen peroxide and Ca2+ in TGF-β1-induced IL-6 expression. J Immunol 165:2190–2197
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386:671–674
Klagsbrun M (1991) Regulators of angiogenesis: stimulators, inhibitors, and extracellular matrix. J Cell Biochem 47:199–200
Li J, Cubbon RM, Wilson LA, Amer MS, McKeown L, Hou B, Majeed Y, Tumova S, Seymour VA, Taylor H, Stacey M, O’Regan D, Foster R, Porter KE, Kearney MT, Beech DJ (2011) Orai1 and CRAC channel dependence of VEGF-activated Ca2+ entry and endothelial tube formation. Circ Res 108:1190–1198
Rousseau S, Houle F, Kotanides H, Witte L, Waltenberger J, Landry J, Huot J (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-driven actin-based motility is mediated by VEGFR2 and requires concerted activation of stress-activated protein kinase 2 (SAPK2/p38) and geldanamycin-sensitive phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem 275:10661–10672
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J (1997) Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 388:190–195
Maelfait J, Beyaert R (2008) Non-apoptotic functions of caspase-8. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1365–1373
Tavora B, Batista S, Reynolds LE, Jadeja S, Robinson S, Kostourou V, Hart I, Fruttiger M, Parsons M, Hodivala-Dilke KM (2010) Endothelial FAK is required for tumour angiogenesis. EMBO Mol Med 2:516–528
Gervais FG, Thornberry NA, Ruffolo SC, Nicholson DW, Roy S (1998) Caspases cleave focal adhesion kinase during apoptosis to generate a FRNK-like polypeptide. J Biol Chem 273:17102–17108
Ganapathy S, Chen Q, Singh KP, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2010) Resveratrol enhances antitumor activity of TRAIL in prostate cancer xenografts through activation of FOXO transcription factor. PLoS ONE 5:e15627
Jo M, Kim TH, Seol DW, Esplen JE, Dorko K, Billiar TR, Strom SC (2000) Apoptosis induced in normal human hepatocytes by tumor necrosis factorrelated apoptosis-inducing ligand. Nat Med 6:564–567
Lawrence D, Shahrokh Z, Marsters S, Achilles K, Shih D, Mounho B, Hillan K, Totpal K, DeForge L, Schow P, Hooley J, Sherwood S, Pai R, Leung S, Khan L, Gliniak B, Bussiere J, Smith CA, Strom SS, Kelley S, Fox JA, Thomas D, Ashkenazi A (2001) Differential hepatocyte toxicity of recombinant Apo2L/TRAIL versions. Nat Med 7:383–385
Martin JL, Charboneau R, Barke RA, Roy S (2010) Chronic morphine treatment inhibits LPS-induced angiogenesis: implications in wound healing. Cell Immunol 265:139–145
Kang YC, Kim KM, Lee KS, Namkoong S, Lee SJ, Han JA, Jeoung D, Ha KS, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2004) Serum bioactive lysophospholipids prevent TRAIL-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt-dependent cFLIP expression and Bad phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ 11:1287–1298
Han SH, Kim M, Park K, Kim TH, Seol DW (2008) Blockade of processing/activation of caspase-3 by hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 375:684–788
Raleigh JA, Calkins-Adams DP, Rinker LH, Ballenger CA, Weissler MC, Fowler WC Jr, Novotny DB, Varia MA (1998) Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human squamous cell carcinomas using pimonidazole as a hypoxia marker. Cancer Res 58:3765–3768
Zhang XD, Nguyen T, Thomas WD, Sanders JE, Hersey P (2000) Mechanisms of resistance of normal cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis vary between different cell types. FEBS Lett 482:193–199
Varfolomeev EE, Schuchmann M, Luria V, Chiannilkulchai N, Beckmann JS, Mett IL, Rebrikov D, Brodianski VM, Kemper OC, Kollet O, Lapidot T, Soffer D, Sobe T, Avraham KB, Goncharov T, Holtmann H, Lonai P, Wallach D (1998) Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity 9:267–276
Sakamaki K, Inoue T, Asano M, Sudo K, Kazama H, Sakagami J, Sakata S, Ozaki M, Nakamura S, Toyokuni S, Osumi N, Iwakura Y, Yonehara S (2002) Ex vivo whole-embryo culture of caspase-8-deficient embryos normalize their aberrant phenotypes in the developing neural tube and heart. Cell Death Differ 9:1196–1206
Scharner D, Rössig L, Carmona G, Chavakis E, Urbich C, Fischer A, Kang TB, Wallach D, Chiang YJ, Deribe YL, Dikic I, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2009) Caspase-8 is involved in neovascularization-promoting progenitor cell functions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:571–578
Finlay D, Howes A, Vuori K (2009) Critical role for caspase-8 in epidermal growth factor signaling. Cancer Res 69:5023–5029
When LP, Fahrni JA, Troie S, Guan JL, Orth K, Rosen GD (1997) Cleavage of focal adhesion kinase by caspases during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:26056–26061
Kornberg LJ, Shaw LC, Spoerri PE, Caballero S, Grant MB (2004) Focal adhesion kinase overexpression induces enhanced pathological retinal angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:4463–4469
Zhao Y, Sui X, Ren H (2010) From procaspase-8 to caspase-8: revising structural functions of caspase-8. J Cell Physiol 225:316–320
Finlay D, Vuori K (2007) Novel noncatalytic role for caspase-8 in promoting SEC-mediated adhesion and Erk signaling in neurobalstoma cells. Cancer Res 67:11704–11711
Cursi S, Rufini A, Stagni V, Condò I, Matafora V, Bachi A, Bonifazi AP, Coppola L, Superti-Furga G, Testi R, Barilà D (2006) Src kinase phosphorylates caspase-8 on Tyr380: a novel mechanism of apoptosis suppression. EMBO J 25:1895–1905
Senft J, Helfer B, Frisch SM (2007) Caspase-8 interacts with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to regulate cell adhesion and motility. Cancer Res 67:11505–11509
Barbero S, Barilà D, Mielgo A, Stagni V, Clair K, Stupack D (2008) Identification of a critical tyrosine residue in caspase 8 that promotes cell migration. J Biol Chem 283:13031–13034
Engelman JS (2009) Targeting PI3K signing in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 9:550–562
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP, Novotny W (2004) Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:391–400
Shojaei F (2012) Anti-angiogenesis therapy in cancer: current challenges and further perspectives. Cancer Lett 320:130–137
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (NRF-2011-0028790). We thank Dr. Elaine Por for helpful comments and critical reading of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hee-Jun Na and Jong-Yun Hwang have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, HJ., Hwang, JY., Lee, KS. et al. TRAIL negatively regulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis via caspase-8-mediated enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions. Angiogenesis 17, 179–194 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9387-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9387-0