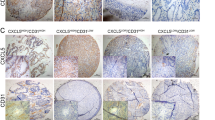
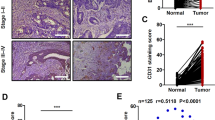
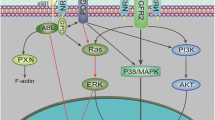
Abstract
Vascular growth factor (VEGF) is an important mediator of angiogenesis. PI3K plays essential roles in angiogenesis; however, the mechanisms and specific functions of individual isoforms of PI3K members in tumor angiogenesis regulation are still not fully understood. In this study, we evaluate the role of p55PIK, a PI3K regulatory subunit encoded by PIK3R3 gene, in tumor angiogenesis. We reported that overexpression of p55PIK in cancer cells up-regulated HIF-1α expression and increased VEGF expression. Furthermore, overexpression of p55PIK increased tumor angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Moreover, data indicated enhanced HIF-1α expression by p55PIK-PI3K depended on its ability to activate NF-кB signaling pathways, especially to increase the phosphorylation of p65 subunits of NF-κB. Our study suggested that p55PIK-PI3K was essential in regulating cancer cell-mediated angiogenesis and contributed to tumor growth and that the p55PIK provides a potential and specific target for new anti-angiogenesis drug development.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DH (2010) p85 Plays a critical role in controlling flux through the PI3K/PTEN signaling axis through dual regulation of both p110 (PI3K) and PTEN. Cell Cycle 9:2055–2056
Berenjeno IM, Vanhaesebroeck B (2009) PI3K regulatory subunits lose control in cancer. Cancer Cell 16:449–450
Bergers G, Benjamin LE (2003) Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer 3:401–410
Bikfalvi A (2006) Angiogenesis: health and disease. Ann Oncol 17(Suppl 10):x65–x70
Bunney TD, Katan M (2010) Phosphoinositide signalling in cancer: beyond PI3K and PTEN. Nat Rev Cancer 10:342–352
Carmeliet P (2003) Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med 9:653–660
Cook KM, Figg WD (2010) Angiogenesis inhibitors: current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J Clin 60:222–243
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB, Engelman JA (2010) The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1075–1083
Dayan F, Bilton RL, Laferriere J et al (2009) Activation of HIF-1alpha in exponentially growing cells via hypoxic stimulation is independent of the Akt/mTOR pathway. J Cell Physiol 218:167–174
Du J, Xu R, Hu Z et al (2011) PI3K and ERK-induced Rac1 activation mediates hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS One 6:e25213
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8:579–591
Eltzschig HK, Carmeliet P (2011) Hypoxia and inflammation. N Engl J Med 364:656–665
Fang J, Ding M, Yang L et al (2007) PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling regulates prostate tumor angiogenesis. Cell Signal 19:2487–2497
Foukas LC, Berenjeno IM, Gray A et al (2010) Activity of any class IA PI3K isoform can sustain cell proliferation and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:11381–11386
Grothey A, Galanis E (2009) Targeting angiogenesis: progress with anti-VEGF treatment with large molecules. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:507–518
Hamada K, Sasaki T, Koni PA et al (2005) The PTEN/PI3K pathway governs normal vascular development and tumor angiogenesis. Genes Dev 19:2054–2065
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Hu J, Liu S, Wang J et al (2005) Overexpression of the N-terminal end of the p55gamma regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase blocks cell cycle progression in gastric carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 26:1321–1327
Hu J, Xia X, Cheng A et al (2008) A peptide inhibitor derived from p55PIK phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit: a novel cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3719–3728
Hubbard J, Grothey A (2010) Antiangiogenesis agents in colorectal cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 22:374–380
Jia S, Liu Z, Zhang S et al (2008) Essential roles of PI(3)K-p110beta in cell growth, metabolism and tumorigenesis. Nature 454:776–779
Jiang BH, Liu LZ (2009) PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Adv Cancer Res 102:19–65
Karar J, Maity A (2011) PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci 4:51
Kerbel RS (2008) Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 358:2039–2049
Kloo B, Nagel D, Pfeifer M et al (2011) Critical role of PI3K signaling for NF-kappaB-dependent survival in a subset of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:272–277
Lawrence T, Bebien M, Liu GY et al (2005) IKKalpha limits macrophage NF-kappaB activation and contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature 434:1138–1143
Marone R, Cmiljanovic V, Giese B et al (2008) Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:159–185
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM et al (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:8104–8109
Menakuru SR, Brown NJ, Staton CA et al (2008) Angiogenesis in pre-malignant conditions. Br J Cancer 99:1961–1966
Mitchell DC, Bryan BA (2010) Anti-angiogenic therapy: adapting strategies to overcome resistant tumors. J Cell Biochem 111:543–553
Mylonis I, Chachami G, Paraskeva E et al (2008) Atypical CRM1-dependent nuclear export signal mediates regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by MAPK. J Biol Chem 283:27620–27627
Okumura N, Yoshida H, Kitagishi Y et al (2012) PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling as a molecular target in leukemia angiogenesis. Adv Hematol 2012:843085
Pufe T, Lemke A, Kurz B et al (2004) Mechanical overload induces VEGF in cartilage discs via hypoxia-inducible factor. Am J Pathol 164:185–192
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K et al (2004) Large-scale meta-analysis of cancer microarray data identifies common transcriptional profiles of neoplastic transformation and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9309–9314
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K et al (2004) ONCOMINE: a cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia 6:1–6
Sakurai H, Chiba H, Miyoshi H et al (1999) IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 274:30353–30356
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C (T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Skrzypczak M, Goryca K, Rubel T et al (2010) Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical reliability. Plos One 5:e13091
Tian T, Nan KJ, Wang SH et al (2010) PTEN regulates angiogenesis and VEGF expression through phosphatase-dependent and -independent mechanisms in HepG2 cells. Carcinogenesis 31:1211–1219
Tsuzuki Y, Fukumura D, Oosthuyse B et al (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) modulation by targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha–> hypoxia response element–> VEGF cascade differentially regulates vascular response and growth rate in tumors. Cancer Res 60:6248–6252
Van Uden P, Kenneth NS, Rocha S (2008) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by NF-kappaB. Biochem J 412:477–484
Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M et al (2010) The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 11:329–341
Wang G, Deng Y, Cao X et al (2012) Blocking p55PIK Signaling inhibits proliferation and induces differentiation of leukemia cells. Cell Death Differ 19:1870–1879
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira SM et al (2008) PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:13057–13062
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR et al (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Winder T, Lenz HJ (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor signaling pathways as therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 138:2163–2176
Xia X, Cheng A, Akinmade D et al (2003) The N-terminal 24 amino acids of the p55 gamma regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase binds Rb and induces cell cycle arrest. Mol Cell Biol 23:1717–1725
Yuan TL, Cantley LC (2008) PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene 27:5497–5510
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N et al (2007) Integrative genomic analysis of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase family identifies PIK3R3 as a potential therapeutic target in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:5314–5321
Zhao L, Vogt PK (2008) Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 27:5486–5496
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants of foundation of “973” Program (No. 2009CB521802), National Natural Science foundation (No. 30872472, No.30973496, No.81172512, No.81272278, and No.31000612). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guihua Wang and Cheng Chen contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Chen, C., Yang, R. et al. p55PIK-PI3K stimulates angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cell by activating NF-κB pathway. Angiogenesis 16, 561–573 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9336-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9336-y