Abstract
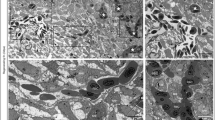
The role of Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) as a regulator of blood vessel endothelium is complicated and controversial, and the mechanisms by which TGF-β is able to induce angiogenesis in vivo are not well understood. Here we show that TGF-β causes in vivo a massive recruitment of tissue infiltrating hematopoietic cells. Concurrently, TGF-β induces strong vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production in the recruited hematopoietic cells, resulting in activated angiogenesis and vascular remodeling. TGF-β also promoted abnormalities of α-smooth muscle actin-expressing pericytes on angiogenic capillaries. TGF-β-induced angiogenic effect was inhibited by a systemic treatment with VEGF-neutralizing antibodies. When studied in isolated human hematopoietic cells, physiological concentrations of TGF-β stimulated VEGF mRNA and protein expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner. This induction was p38 and p44/p42 mitogen activated kinase dependent. p38 and p44/p42 activation was also observed in vivo in TGF-β–treated angiogenic murine tissues. Taken together, our results provide a dual action mechanism by which TGF-β promotes angiogenesis in vivo via recruitment of paracrine VEGF-expressing hematopoietic effector cells. This mechanism may activate vascular growth and remodeling during inflammatory conditions and tumor growth when TGF-β activity is upregulated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rifkin DB et al (1993) TGF-beta: structure, function, and formation. Thromb Haemost 70(1):177–179
Dickson MC et al (1995) Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1 knock out mice. Development 121(6):1845–1854
Pardali E, Goumans MJ, ten Dijke P (2010) Signaling by members of the TGF-beta family in vascular morphogenesis and disease. Trends Cell Biol 20(9):556–567
Phillips GD et al (1993) Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) stimulation of angiogenesis: an electron microscopic study. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 25(2):149–155
Roberts AB et al (1986) Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83(12):4167–4171
van Royen N et al (2002) Exogenous application of transforming growth factor beta 1 stimulates arteriogenesis in the peripheral circulation. FASEB J 16(3):432–434
Yang EY, Moses HL (1990) Transforming growth factor beta 1-induced changes in cell migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. J Cell Biol 111(2):731–741
Ferrari G et al (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) induces angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 219(2):449–458
Ferrari G et al (2006) VEGF, a prosurvival factor, acts in concert with TGF-beta1 to induce endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(46):17260–17265
Pepper MS et al (1991) Chondrocytes inhibit endothelial sprout formation in vitro: evidence for involvement of a transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Physiol 146(1):170–179
Pollman MJ, Naumovski L, Gibbons GH (1999) Vascular cell apoptosis: cell type-specific modulation by transforming growth factor-beta1 in endothelial cells versus smooth muscle cells. Circulation 99(15):2019–2026
Tsukada T et al (1995) Transforming growth factor beta 1 induces apoptotic cell death in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells with down-regulated expression of bcl-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 210(3):1076–1082
Yan Q, Sage EH (1998) Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces apoptotic cell death in cultured retinal endothelial cells but not pericytes: association with decreased expression of p21waf1/cip1. J Cell Biochem 70(1):70–83
Kim KJ et al (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 362(6423):841–844
Weidner N et al (1993) Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol 143(2):401–409
Tischer E et al (1991) The human gene for vascular endothelial growth factor. Multiple protein forms are encoded through alternative exon splicing. J Biol Chem 266(18):11947–11954
Houck KA et al (1991) The vascular endothelial growth factor family: identification of a fourth molecular species and characterization of alternative splicing of RNA. Mol Endocrinol 5(12):1806–1814
Pertovaara L et al (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced in response to transforming growth factor-beta in fibroblastic and epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 269(9):6271–6274
Jeon SH et al (2007) Mechanisms underlying TGF-beta1-induced expression of VEGF and Flk-1 in mouse macrophages and their implications for angiogenesis. J Leukoc Biol 81(2):557–566
Nam EH, Park SR, Kim PH (2010) TGF-beta1 induces mouse dendritic cells to express VEGF and its receptor (Flt-1) under hypoxic conditions. Exp Mol Med 42(9):606–613
Salven P et al (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor in squamous cell head and neck carcinoma: expression and prognostic significance. Mod Pathol 10(11):1128–1133
Salven P, Heikkila P, Joensuu H (1997) Enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in metastatic melanoma. Br J Cancer 76(7):930–934
Salven P et al (2002) Interleukin-1alpha promotes angiogenesis in vivo via VEGFR-2 pathway by inducing inflammatory cell VEGF synthesis and secretion. FASEB J 16(11):1471–1473
Rajantie I et al (2004) Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells. Blood 104(7):2084–2086
Purhonen S et al (2008) Bone marrow-derived circulating endothelial precursors do not contribute to vascular endothelium and are not needed for tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(18):6620–6625
Salven P et al (2001) Endotoxins induce and interferon alpha suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. FASEB J 15(7):1318–1320
Murdoch C et al (2008) The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):618–631
Coffelt SB, Hughes R, Lewis CE (2009) Tumor-associated macrophages: effectors of angiogenesis and tumor progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1796(1):11–18
Jain RK, Duda DG (2003) Role of bone marrow-derived cells in tumor angiogenesis and treatment. Cancer Cell 3(6):515–516
De Palma M, Naldini L (2006) Role of haematopoietic cells and endothelial progenitors in tumour angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1766(1):159–166
Nozawa H, Chiu C, Hanahan D (2006) Infiltrating neutrophils mediate the initial angiogenic switch in a mouse model of multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(33):12493–12498
Shojaei F, Ferrara N (2008) Refractoriness to antivascular endothelial growth factor treatment: role of myeloid cells. Cancer Res 68(14):5501–5504
Fang S, Salven P (2011) Stem cells in tumor angiogenesis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50(2):290–295
Wartiovaara U et al (1998) Peripheral blood platelets express VEGF-C and VEGF which are released during platelet activation. Thromb Haemost 80(1):171–175
Salven P, Orpana A, Joensuu H (1999) Leukocytes and platelets of patients with cancer contain high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 5(3):487–491
Ezaki T et al (2001) Time course of endothelial cell proliferation and microvascular remodeling in chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol 158(6):2043–2055
Morikawa S et al (2002) Abnormalities in pericytes on blood vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am J Pathol 160(3):985–1000
Teicher BA (2001) Malignant cells, directors of the malignant process: role of transforming growth factor-beta. Cancer Metastasis Rev 20(1–2):133–143
Assoian RK, Sporn MB (1986) Type beta transforming growth factor in human platelets: release during platelet degranulation and action on vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol 102(4):1217–1223
Gaengel K et al (2009) Endothelial-mural cell signaling in vascular development and angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(5):630–638
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shentong Fang and Nalle Pentinmikko contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, S., Pentinmikko, N., Ilmonen, M. et al. Dual action of TGF-β induces vascular growth in vivo through recruitment of angiogenic VEGF-producing hematopoietic effector cells. Angiogenesis 15, 511–519 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9278-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9278-9