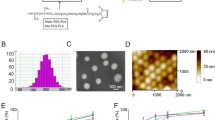
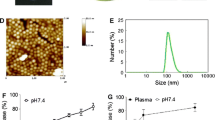
Abstract
Objective
Dysregulation of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway is a hallmark of human cancer, occurring in a majority of tumors. Activation of this pathway is critical for transformation and also for the angiogenic switch, which is a key step for tumor progression. The objective of this study was to engineer a PI3K inhibitor-loaded biodegradable nanoparticle and to evaluate its efficacy.
Methods and results
Here we report that a nanoparticle-enabled targeting of the PI3K pathway results in inhibition of downstream Akt phosphorylation, leading to inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis of B16/F10 melanoma. It, however, failed to exert a similar activity on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, resulting from reduced internalization and processing of nanoparticles in this cell line. Excitingly, the nanoparticle-enabled targeting of the PI3K pathway resulted in inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation and tubulogenesis, two key steps in tumor angiogenesis. Furthermore, it inhibited both B16/F10- and MDA-MB-231-induced angiogenesis in a zebrafish tumor xenotransplant model.
Conclusion
Our study, for the first time, shows that targeting of the PI3K pathway using nanoparticles can offer an attractive strategy for inhibiting tumor angiogenesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Shayesteh L, Lu Y, Kuo WL, Baldocchi R, Godfrey T, Collins C, Pinkel D, Powell B, Mills GB, Gray JW (1999) PIK3CA is implicated as an oncogene in ovarian cancer. Nat Genet 21:99–102
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K, Guimaraes AR, Upadhyay R, Maira M, McNamara K, Perera SA, Song Y, Chirieac LR, Kaur R, Lightbown A, Simendinger J, Li T, Padera RF, García-Echeverría C, Weissleder R, Mahmood U, Cantley LC, Wong KK (2008) Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med 14:1351–1356
Koul D (2008) PTEN signaling pathways in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1321–1325
Petrocelli T, Slingerland JM (2001) PTEN deficiency: a role in mammary carcinogenesis. Breast Cancer Res 3:356–360
Steelman LS, Stadelman KM, Chappell WH, Horn S, Bäsecke J, Cervello M, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Stivala F, Martelli AM, McCubrey JA (2008) Akt as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12:1139–1165
Iwanaga K, Yang Y, Raso MG, Ma L, Hanna AE, Thilaganathan N, Moghaddam S, Evans CM, Li H, Cai WW, Sato M, Minna JD, Wu H, Creighton CJ, Demayo FJ, Wistuba II, Kurie JM (2008) Pten inactivation accelerates oncogenic K-ras-initiated tumorigenesis in a mouse model of lung cancer. Cancer Res 68:1119–1127
Horie Y, Suzuki A, Kataoka E, Sasaki T, Hamada K, Sasaki J, Mizuno K, Hasegawa G, Kishimoto H, Iizuka M, Naito M, Enomoto K, Watanabe S, Mak TW, Nakano T (2004) Hepatocyte-specific Pten deficiency results in steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinomas. J Clin Invest 113:1774–1783
Yuan TL, Choi HS, Matsui A, Benes C, Lifshits E, Luo J, Frangioni JV, Cantley LC (2008) Class 1A PI3K regulates vessel integrity during development and tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9739–9744
Sengupta S, Sellers LA, Li RC, Gherardi E, Zhao G, Watson N, Sasisekharan R, Fan TP (2003) Targeting of mitogen-activated protein kinases and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase inhibits hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced angiogenesis. Circulation 107:2955–2961
Sengupta S, Sasisekharan R (2007) Exploiting nanotechnology to target cancer. Br J Cancer 96(9):1315–1319
Yuan F, Leunig M, Huang SK, Berk DA, Papahadjopoulos D, Jain RK (1994) Microvascular permeability and interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth) liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res 54:3352
Ibrahim NK, Desai N, Legha S, Soon-Shiong P, Theriault RL, Rivera E, Esmaeli B, Ring SE, Bedikian A, Hortobagyi GN, Ellerhorst JA (2002) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of ABI-007, a Cremophor-free, protein-stabilized, nanoparticle formulation of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 8:1038–1044
Stavridi F, Palmieri C (2008) Efficacy and toxicity of nonpegylated liposomal doxorubicin in breast cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8:1859–1869
Basu S, Harfouche R, Soni S, Chimote G, Mashelkar RA, Sengupta S (2009) Nanoparticle-mediated targeting of MAPK signaling predisposes tumor to chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(19):7957–7961
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF (1994) A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 269:5241–5248
Nicoli S, Presta M (2007) The zebrafish/tumor xenograft angiogenesis assay. Nat Protoc 2:2918–2923
Ferrari M (2005) Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nature Rev Cancer 5:161–171
Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R (2007) Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nature Nanotech 2:751–760
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC (2005) Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. FASEB J 19(3):311–330
Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi T, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE (2001) Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Controlled Release 70:1–260
Honorat M, Mesnier A, Di Pietro A, Lin V, Cohen P, Dumontet C, Payen L (2008) Dexamethasone down-regulates ABCG2 expression levels in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 375:308–314
Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Painter GF, Holmes AB, McCormick F, Hawkins PT (1997) Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3, 4, 5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science 277:567–570
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282:1318–1321
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Thomson S, Mulvihill M, Barr S, Brown E, O’Connor M, Yao Y, Pachter J, Miglarese M, Epstein D, Iwata KK, Haley JD, Gibson NW, Ji QS (2008) Feedback mechanisms promote cooperativity for small molecule inhibitors of epidermal and insulin-like growth factor receptors. Cancer Res 68:8322–8332
Grant S (2008) Cotargeting survival signaling pathways in cancer. J Clin Invest 118:3003–3006
She QB, Solit DB, Ye Q, O’Reilly KE, Lobo J, Rosen N (2005) Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 8:287–297
Kinkade CW, Castillo-Martin M, Puzio-Kuter A, Yan J, Foster TH, Gao H, Sun Y, Ouyang X, Gerald WL, Cordon-Cardo C, Abate-Shen C (2008) Targeting AKT/mTOR and ERK MAPK signaling inhibits hormone-refractory prostate cancer in a preclinical mouse model. J Clin Invest 118:3051–3064
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–286
Folkman J (2002) Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 29:15–18
Gasparini G, Longo R, Toi M, Ferrara N (2005) Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:562–577
Sengupta S, Sellers LA, Cindrova T, Skepper J, Gherardi E, Sasisekharan R, Fan TP (2003) Cyclooxygenase-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res 63:8351–8359
Schnell CR, Stauffer F, Allegrini PR, O’Reilly T, McSheehy PM, Dartois C, Stumm M, Cozens R, Littlewood-Evans A, García-Echeverría C, Maira SM (2008) Effects of the dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 on the tumor vasculature: implications for clinical imaging. Cancer Res 68:6598–6607
Stoletov K, Montel V, Lester RD, Gonias SL, Klemke R (2007) High-resolution imaging of the dynamic tumor cell vascular interface in transparent zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:17406–17411
Sengupta S, Eavarone D, Capila I, Zhao G, Watson N, Kiziltepe T, Sasisekharan R (2005) Temporal targeting of tumour cells and neovasculature with a nanoscale delivery system. Nature 436:568–572
Kaul G, Amiji M (2004) Biodistribution and targeting potential of poly(ethylene glycol)-modified gelatin nanoparticles in subcutaneous murine tumor model. J Drug Target 12:585–591
Hood JD, Bednarski M, Frausto R, Guccione S, Reisfeld RA, Xiang R, Cheresh DA (2002) Tumor regression by targeted gene delivery to the neovasculature. Science 296:2404
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Department of Defense BCRP Era of Hope Scholar award [W81XWH-07-1-0482] and Mary Kay Ash Charitable Foundation Grant to SS. DH is supported by an AHA Fellow to Faculty Transition Grant and RH is supported by a CIHR Fellowship. We thank Prof. Joseph Bonventre for access to his laboratory and Nicki Watson, Imaging Facility at Whitehead Institute for Biomedical, for the electron microscopy studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rania Harfouche and Sudipta Basu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10456_2009_9154_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1 Concentration–Effect of NP-LY on viability of cancer cells. a–c Breast adenocarcinoma (MDA-MB-231), Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) and melanoma (B16-F10) cells were plated on 96-well plates in the presence or absence of either free drug (LY) or LY-encapsulated nanoparticles (NP-LY). Cells were subjected to incubation with the drugs in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. At 24 and 72 h, the viability of cells was quantified using the MTS assay. Data represents mean ± SEM from independent triplicates. *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated control cells (ANOVA) (PDF 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harfouche, R., Basu, S., Soni, S. et al. Nanoparticle-mediated targeting of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling inhibits angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 12, 325–338 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-009-9154-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-009-9154-4