Abstract
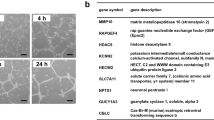
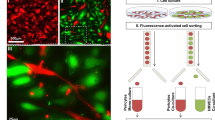
The formation of new tubular structures from a quiescent endothelial lining is one of the hallmarks of sprouting angiogenesis. This process can be mimicked in vitro by inducing capillary-like tubular structures in a three-dimensional (3D) fibrin matrix. We aimed to analyze the differential mRNA expression in two phenotypically distinct cell populations from the same culture, namely in tubule-forming endothelial cells and monolayer endothelial cells not participating in tubule formation. A fibrin-rich 3D matrix derived from human plasma was used to facilitate tubule formation by human foreskin microvascular endothelial cells (hMVEC). After 7 days of stimulation with VEGF, bFGF, and TNF-α, the culture consisted of a monolayer and capillary-like sprouts that had grown into the fibrinous matrix. A method was developed to separate the monolayer and tubule-forming populations of hMVEC, keeping their cellular integrity intact to ensure mRNA extraction and cDNA production. Subsequent array analysis resulted in an inventory of differentially expressed genes that were associated with either tube-forming (angiogenic) or non-angiogenic capacity. Differential gene expression was verified by real-time PCR on the original RNA samples as well as on RNA obtained from laser-capture microdissected cross sections of monolayers and capillary structures in the 3D fibrinous matrix. The expression of CDC42GAP, an inhibitor of active-state small Rho GTPases, was reduced in tubular hMVEC. Overexpression of CDC42GAP in hMVEC attenuated endothelial tubule formation, while its suppression by siRNA slightly enhanced this process. Thus, CDC42GAP was identified as a counter-regulatory mediator for tubule formation






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P (2003) Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med 9:653–660
Ausprunk DH, Folkman J (1977) Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res 14:53–65
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86:353–364
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D, Betsholtz C (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161:1163–1177
van Beijnum JR, Griffioen AW (2005) In silico analysis of angiogenesis associated gene expression identifies angiogenic stage related profiles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1755:121–134
Kahn J, Mehraban F, Ingle G, Xin X, Bryant JE, Vehar G, Schoenfeld J, Grimaldi CJ, Peale F, Draksharapu A, Lewin DA, Gerritsen ME (2000) Gene expression profiling in an in vitro model of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 156:1887–1900
Bell SE, Mavila A, Salazar R, Bayless KJ, Kanagala S, Maxwell SA, Davis GE (2001) Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular differentiation and G-protein signaling. J Cell Sci 114:2755–2773
Hahn CN, Su ZJ, Drogemuller CJ, Tsykin A, Waterman SR, Brautigan PJ, Yu S, Kremmidiotis G, Gardner A, Solomon PJ, Goodall GJ, Vadas MA, Gamble JR (2005) Expression profiling reveals functionally important genes and coordinately regulated signaling pathway genes during in vitro angiogenesis. Physiol Genomics 22:57–69
Gerritsen ME, Soriano R, Yang S, Ingle G, Zlot C, Toy K, Winer J, Draksharapu A, Peale F, Wu TD, Williams PM (2002) In silico data filtering to identify new angiogenesis targets from a large in vitro gene profiling data set. Physiol Genomics 10:13–20
Sun XT, Zhang MY, Shu C, Li Q, Yan XG, Cheng N, Qiu YD, Ding YT (2005) Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in a microcarrier-based three-dimensional in vitro model of angiogenesis with focus on chemokines and chemokine receptors. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2283–2290
Grove AD, Prabhu VV, Young BL, Lee FC, Kulpa V, Munson PJ, Kohn EC (2002) Both protein activation and gene expression are involved in early vascular tube formation in vitro. Clin Cancer Res 8:3019–3026
St Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, Traverso G, Romans KE, Montgomery E, Lal A, Riggins GJ, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (2000) Genes expressed in human tumor endothelium. Science 289:1197–1202
van Beijnum JR, Dings RP, van der Linden E, Zwaans BM, Ramaekers FC, Mayo KH, Griffioen AW (2006) Gene expression of tumor angiogenesis dissected: specific targeting of colon cancer angiogenic vasculature. Blood 108:2339–2348
Schoenfeld J, Lessan K, Johnson NA, Charnock-Jones DS, Evans A, Vourvouhaki E, Scott L, Stephens R, Freeman TC, Saidi SA, Tom B, Weston GC, Rogers P, Smith SK, Print CG (2004) Bioinformatic analysis of primary endothelial cell gene array data illustrated by the analysis of transcriptome changes in endothelial cells exposed to VEGF-A and PlGF. Angiogenesis 7:143–156
Dvorak HF, Harvey VS, Estrella P, Brown LF, McDonagh J, Dvorak AM (1987) Fibrin containing gels induce angiogenesis. Implications for tumor stroma generation and wound healing. Lab Invest 57:673–686
Koolwijk P, van Erck MG, de Vree WJ, Vermeer MA, Weich HA, Hanemaaijer R, van Hinsbergh VWM (1996) Cooperative effect of TNFalpha, bFGF, and VEGF on the formation of tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in a fibrin matrix. Role of urokinase activity. J Cell Biol 132:1177–1188
Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Lupu F, Broxterman HJ, van der Valk P, Kakkar AK, Pinedo HM (2000) Platelet and coagulation activation with vascular endothelial growth factor generation in soft tissue sarcomas. Clin Cancer Res 6:166–171
van Hinsbergh VWM, Collen A, Koolwijk P (2001) Role of fibrin matrix in angiogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci 936:426–437
Kroon ME, Koolwijk P, van Goor H, Weidle UH, Collen A, van der Pluijm G, van Hinsbergh VWM (1999) Role and localization of urokinase receptor in the formation of new microvascular structures in fibrin matrices. Am J Pathol 154:1731–1742
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Koolwijk P, Versteilen A, van Hinsbergh VWM (2003) Involvement of RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:211–217
van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Beckers CM, Achekar ID, Zeeman S, Musters RJ, van Hinsbergh VW (2007) Involvement of Rho kinase in endothelial barrier maintenance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2332–2339
Barfod ET, Zheng Y, Kuang WJ, Hart MJ, Evans T, Cerione RA, Ashkenazi A (1993) Cloning and expression of a human CDC42 GTPase-activating protein reveals a functional SH3-binding domain. J Biol Chem 268:26059–26062
Van Hinsbergh VWM, Sprengers ED, Kooistra T, (1987) Effect of thrombin on the production of plasminogen activators and PA inhibitor-1 by human foreskin microvascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemostas 57:176-182
Defilippi P, van Hinsbergh V, Bertolotto A, Rossino P, Silengo L, Tarone G (1991) Differential distribution and modulation of expression of alpha 1/beta 1 integrin on human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 114:855–863
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Low BC, Seow KT, Guy GR (2000) The BNIP-2 and Cdc42GAP homology domain of BNIP-2 mediates its homophilic association and heterophilic interaction with Cdc42GAP. J Biol Chem 275:37742–37751
Gerhardt H, Betsholtz C (2005) How do endothelial cells orientate? EXS 94:3–15
Riento K, Villalonga P, Garg R, Ridley A (2005) Function and regulation of RhoE. Biochem Soc Trans 33:649–651
Fujioka Y, Taira T, Maeda Y, Tanaka S, Nishihara H, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Nagashima K, Ariga H (2001) MM-1, a c-Myc-binding protein, is a candidate for a tumor suppressor in leukemia/lymphoma and tongue cancer. J Biol Chem 276:45137–45144
Folkman J (1996–1997) Endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis. Harvey Lect 92:65–82
Marneros AG, Olsen BR (2005) Physiological role of collagen XVIII and endostatin. FASEB J 19:716–728
Autiero M, De Smet F, Claes F, Carmeliet P (2005) Role of neural guidance signals in blood vessel navigation. Cardiovasc Res 65:629–638
Eichmann A, Le Noble F, Autiero M, Carmeliet P (2005) Guidance of vascular and neural network formation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:108–115
Hashizume A, Ueno T, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Nakanishi Y, Hieda Y (2004) Expression patterns of claudin family of tight junction membrane proteins in developing mouse submandibular gland. Dev Dyn 231:425–431
Shi Y, Reitmaier B, Regenbogen J, Slowey RM, Opalenik SR, Wolf E, Goppelt A, Davidson JM (2005) CARP, a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is up-regulated during wound healing and induces angiogenesis in experimental granulation tissue. Am J Pathol 166:303–312
Schwartz M (2004) Rho signalling at a glance. J Cell Sci 117:5457–5458
Bayless KJ, Davis GE (2002) The Cdc42 and Rac1 GTPases are required for capillary lumen formation in three-dimensional extracellular matrices. J Cell Sci 115:1123–1136
Bishop AL, Hall A (2000) Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem J 348:241–255
Zhang B, Zheng Y (1998) Regulation of RhoA GTP hydrolysis by the GTPase-activating proteins p190, p50RhoGAP, Bcr, and 3BP-1. Biochemistry 37:5249–5257
Zhang B, Chernoff J, Zheng Y (1998) Interaction of Rac1 with GTPase-activating proteins and putative effectors. A comparison with Cdc42 and RhoA. J Biol Chem 273:8776–8782
Su ZJ, Hahn CN, Goodall GJ, Reck NM, Leske AF, Davy A, Kremmidiotis G, Vadas MA, Gamble JR (2004) A vascular cell-restricted RhoGAP, p73RhoGAP, is a key regulator of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12212–12217
Aitsebaomo J, Wennerberg K Der CJ, Zhang C, Kedar V, Moser M, Kingsley-Kallesen ML, Zeng GQ, Patterson C (2004) p68RacGAP is a novel GTPase-activating protein that interacts with vascular endothelial zinc finger-1 and modulates endothelial cell capillary formation. J Biol Chem 279:17963–17972
Fryer BH, Field J (2005) Rho, Rac, Pak and angiogenesis: old roles and newly identified responsibilities in endothelial cells. Cancer Lett 229:13–23
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants of ZON-MW (902-90-017) and the European Vascular Genomics Network (LSHM-CT-2003-503254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelse, M.A., Laurens, N., Verloop, R.E. et al. Differential gene expression analysis of tubule forming and non-tubule forming endothelial cells: CDC42GAP as a counter-regulator in tubule formation. Angiogenesis 11, 153–167 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-007-9086-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-007-9086-9