Abstract
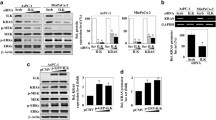
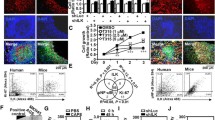
Human pancreatic tumors often overexpress the angiogenesis-promoting factor Interleukin 8 (IL-8), in part due to overexpression of NF-κB, a frequent occurrence in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. In this study, we demonstrate that reducing c-Src kinase activity, through either pharmacologic inhibition or small interfering RNA-targeted reduction of Src expression, significantly decreased IL-8 expression (P < 0.05) without affecting NF-κB-mediated transcription, but by decreasing phosphorylation of STAT3. To ascertain whether Src-mediated expression of IL-8 was dependent on STAT3, we used stable clones expressing a dominant-negative isoform of STAT3 that inhibits endogenous STAT3 phosphorylation and subsequent DNA binding and STAT3-mediated gene expression or a constitutively activated isoform of STAT3. IL-8 expression was significantly lower in clones expressing the dominant-negative isoform and significantly increased in clones expressing the activated isoform (P < 0.05 for both). Pharmacologic inhibition of NF-κB activity significantly reduced basal IL-8 expression and tumor necrosis factor-induced IL-8 expression (P < 0.05 for both), yet NF-κB activity was not dependent on Src. We therefore suggest that Src activation, through phosphorylation of␣STAT3, and NF-κB are all required for expression of IL-8 a critical angiogenic-promoting factor in pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E et al (2005) Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 55:10–30
Ward S, Morris E, Bansback N et al (2001) A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of gemcitabine for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Health Technol Assess 5:1–70
Bramhall SR, Schulz J, Nemunaitis J et al (2002) A double-blind placebo-controlled, randomised study comparing gemcitabine and marimastat with gemcitabine and placebo as first line therapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 87:161–167
Arenberg DA, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL et al (1997) In vitro and in vivo systems to assess role of C-X-C chemokines in regulation of angiogenesis. Methods Enzymol 288:190–220
Takeda A, Stoeltzing O, Ahmad SA et al (2002) Role of angiogenesis in the development and growth of liver metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol 9:610–616
Xie K (2001) Interleukin-8 and human cancer biology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12:375–391
Le X, Shi Q, Wang B et al (2000) Molecular regulation of constitutive expression of interleukin-8 in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Interferon Cytokine Res 20:935–946
Shi Q, Abbruzzese JL, Huang S et al (1999) Constitutive and inducible interleukin 8 expression by hypoxia and acidosis renders human pancreatic cancer cells more tumorigenic and metastatic. Clin Cancer Res 5:3711–3721
Shi Q, Xiong Q, Le X et al (2001) Regulation of interleukin-8 expression by tumor-associated stress factors. J Interferon Cytokine Res 21:553–566
Bruns CJ, Solorzano CC, Harbison MT et al (2000) Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor leads to apoptosis of endothelial cells and therapy of human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 60:2926–2935
Funakoshi M, Sonoda Y, Tago K et al (2001) Differential involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase in the IL-1-mediated NF-kappa B and AP-1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol 1:595–604
Yeh M, Gharavi NM, Choi J et al (2004) Oxidized phospholipids increase interleukin 8 (IL-8) synthesis by activation of the c-src/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)3 pathway. J Biol Chem 279:30175–30181
Summy JM, Gallick GE (2003) Src family kinases in tumor␣progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:337–358
Coppola D (2000) Molecular prognostic markers in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Control 7:421–427
Yezhelyev MV, Koehl G, Guba M et al (2004) Inhibition of SRC tyrosine kinase as treatment for human pancreatic cancer growing orthotopically in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res 10:8028–8036
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ et al (2004) Inhibition of SRC tyrosine kinase impairs inherent and acquired gemcitabine resistance in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 10:2307–2318
Trevino JG, Summy JM, Lesslie DP et al (2006) Inhibition of SRC expression and activity inhibits tumor progression and metastasis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells in an orthotopic nude mouse model. Am J Pathol 168:962–972
Summy JM, Trevino JG, Baker CH et al (2005) c-Src regulates constitutive and EGF-mediated VEGF expression in pancreatic tumor cells through activation of phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase and p38 MAPK. Pancreas 31:263–274
Trevino JG, Summy JM, Gray MJ et al (2005) Expression and activity of SRC regulate interleukin-8 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells: implications for angiogenesis. Cancer Res 65:7214–7222
Gray MJ, Zhang J, Ellis LM et al (2005) HIF-1alpha, STAT3, CBP/p300 and Ref-1/APE are components of a transcriptional complex that regulates Src-dependent hypoxia-induced expression of VEGF in pancreatic and prostate carcinomas. Oncogene 24:3110–3120
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM, Harrison DA (2004) The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 117:1281–1283
Catlett-Falcone R, Dalton WS, Jove R (1999) STAT proteins as novel targets for cancer therapy. Signal transducer an activator of transcription. Curr Opin Oncol 11:490–496
Silva CM (2004) Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23:8017–8023
Scholz A, Heinze S, Detjen KM et al (2003) Activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) supports the malignant phenotype of human pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 125:891–905
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R et al (1998) Stat3 activation by Src induces specific gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol 18:2545–2552
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS et al (1995) Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science 269: 81–83
Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Kuniyasu H et al (1999) In vivo selection and characterization of metastatic variants from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma by using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Neoplasia 1:50–62
Bromberg J, Darnell JE Jr (2000) The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 19:2468–2473
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G et al (1999) Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98:295–303
Fujioka S, Niu J, Schmidt C et al (2004) NF-kappaB and AP-1 connection: mechanism of NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of AP-1 activity. Mol Cell Biol 24:7806–7819
Summy JM, Trevino JG, Lesslie DP et al (2005) AP23846, a novel and highly potent Src family kinase inhibitor, reduces vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 expression in human solid tumor cell lines and abrogates downstream angiogenic processes. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1900–1911
Yoshida Y, Kumar A, Koyama Y et al (2004) Interleukin 1 activates STAT3/nuclear factor-kappaB cross-talk via a unique T. J Biol Chem 279:1768–1776
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL et al (1992) Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258:1798–1801
Matsuo Y, Sawai H, Funahashi H et al (2004) Enhanced angiogenesis due to inflammatory cytokines from pancreatic cancer cell lines and relation to metastatic potential. Pancreas 28:344–352
Greten FR, Weber CK, Greten TF et al (2002) Stat3 and NF-kappaB activation prevents apoptosis in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 123:2052–2063
Windham TC, Parikh NU, Siwak DR et al (2002) Src activation regulates anoikis in human colon tumor cell lines. Oncogene 21:7797–7807
Staley CA, Parikh NU, Gallick GE (1997) Decreased tumorigenicity of a human colon adenocarcinoma cell line by an antisense expression vector specific for c-Src. Cell Growth Differ 8:269–274
Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY et al (2004) Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science 305:399–401
Acknowledgements
We thank Elizabeth L. Hess, ELS (D), (The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center) for editorial assistance and Dr. James Darnell (The Rockefeller University) for the STAT3-C and STAT3-Y705F plasmids. This work was supported by National Institute of Health (NIH) Grant T32 CA 09599 and the Eleanor B. Pillsbury Fellowship-University of Illinois Hospital (J.G.T.), NIH 2RO-1 CA65527 and NIH U54 CA 090810-01 and U.S. Department of Defense Grant PC020017 (G.E.G.), and the Lockton Foundation (M.J.G. and G.E.G.). M.J.G is the Lockton Fellow for Pancreatic Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jose G. Trevino and Michael J. Gray contributed equally to the work in this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trevino, J.G., Gray, M.J., Nawrocki, S.T. et al. Src activation of Stat3 is an independent requirement from NF-κB activation for constitutive IL-8 expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Angiogenesis 9, 101–110 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-006-9038-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-006-9038-9