Abstract
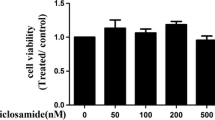
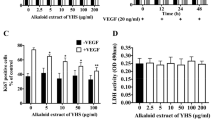
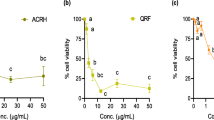
Sinomenine is an alkaloid extracted from the Chinese medicinal plant, Sinomenium acutum, which has been utilized to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in China for over 2000 years. Sinomenine has been shown to mediate a wide range of pharmacological actions which includes anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects. RA has been classified as a chronic immune-mediated disease that exhibits overlapping manifestation of inflammatory, abnormal cellular and hormonal immune responses with synovial hyperplasia. Since, angiogenesis is recognized to play a critical role in the development of RA and anti-angiogenic therapy has been proposed as a new therapeutic strategy for treatment of RA, we would like to see if sinomenine possesses anti-angiogenic property. In this study, sinomenine inhibited bFGF-induced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and arrested its cell cycle in G1 phase. Sinomenine disrupted tube formation of HUVEC on Matrigel and suppressed the chemotaxis of HUVEC. In addition, sinomenine reduced neovascularization in Matrigel plug assay as well as microvascular outgrowth in rat aorta ring sprouting assay. These results suggest that sinomenine inhibited bFGF-induced angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. As the leukocytes–endothelial adhesive interactions also play an important role in inflammation, we found that sinomenine reduced the transmigration of granulocytic differentiated HL60 cells across IL-1β activated HUVEC monolayer. Therefore, the inhibition of leukocytes migration across blood vessel walls and the anti-angiogenic effect of sinomenine may contribute towards its therapeutic mechanisms in alleviating the pathogenesis of RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L Liu J Riese K Rasch V Kaever (1994) ArticleTitleImpairment of macrophage eicosanoid and nitric oxide production by an alkaloid from Sinomenium acutum Arzneimittel–Forschung/Drug Res 44 1223–6
L Liu K Resch V Kaever (1994) ArticleTitleInhibition of lymphocytes proliferation by the anti-arthritic drug sinomenine Int J Immunopharmacol 16 685–91 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0192-0561(94)90142-2 Occurrence Handle7989137
SS Chang SX Fu YS Li NC Wang (1964) ArticleTitleThe pharmacology of sinomenine. I. The analgesic and anti-phlogistic actions and acute toxicity Yao Xue Xue Bao 4 177–80
HR Hua XP Chen (1989) ArticleTitleStudy on the mechanisms of sinomenine on analgesic and anti-inflammtory actions J Xian Med Univ 4 346–9
L Liu E Buchner D Beitze et al. (1996) ArticleTitleAmelioration of rat experimental arthritis by treatment with the alkaloid sinomenine Int J Immunopharmacol 18 529–43 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0192-0561(96)00025-2 Occurrence Handle9080247
XY Ke MX Siu (1986) ArticleTitleTreatment of rheumatoid arthritis by sinomenine Beijing Yi Xue 3 186–7
PM Shi ZX Ma WZ Zhang (1986) ArticleTitleTherapeutic efficacy of sinomenine of 60 rheumatoid arthritis cases Xien Yi Xue 3 292–3
GS Panayi (1994) The pathogenesis of Rreumatoid arthritis F Wolfe T Pincus (Eds) Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pathogenesis Assessment Outcome and Treatment Marcel Dekker New York, Basel, Hong Kong 75–100
NJ Olsen PP Chen (1997) Rheumatoid factor F Wolfe T Pincus (Eds) Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pathogenesis, Assessment, Outcome and Treatment Marcel Dekker New York, Basel, Hong Kong 101–14
ED Harris (1997) Rheumatoid synovium: Complex, and more than the sum of its parts. In Rheumatoid Arthritis W.B. Saunders Company Philadelphia 126
ED Harris (1997) Cartilage and the mechanisms of destruction. In Rheumatoid Arthritis W.B. Saunders Company Philadelphia 150–54
ED Harris (1997) Clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. In Rheumatoid Arthritis W.B. Saunders Company Philadelphia 215–21
J Folkman Y Shing (1992) ArticleTitleMinireview. Angiogenesis J Biol Chem 267 IssueID16 10931–4 Occurrence Handle1375931
DA Walsh (1999) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis and arthritis Rheumatology 38 103–12 Occurrence Handle10.1093/rheumatology/38.2.103 Occurrence Handle10342621
EM Paleolog (2002) ArticleTitleSupplementary review: Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Res Suppl 3 81–90 Occurrence Handle10.1186/ar575
J Folkman (1995) ArticleTitleReview: Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases Nat Med 1 27–31 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0195-27 Occurrence Handle7584949
J Favier P Corvol (2001) ArticleTitlePhysiological angiogenesis. [abstract] Therapie 56 455–63 Occurrence Handle11806281
J Folkman M Klangburn (1987) ArticleTitleAngiogenic factor Science 235 442–7 Occurrence Handle2432664
W Risau (1997) ArticleTitleMechanism of angiogenesis Nature 386 671–4 Occurrence Handle10.1038/386671a0 Occurrence Handle9109485
G Bergers LE Benjamin (2003) ArticleTitleReviews: Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch Nat Rev 3 401–10 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrc1093 Occurrence Handle12778130
PJ Polverini (2002) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis in health and disease: Insights into basic mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities J Dent Educ 66 962–75 Occurrence Handle12214844
R Longo R Sarmieto M. Fanelli et al. (2002) ArticleTitleReview: Anti-angiogenic therapy: Rationale, challenges, and clinical studies Angiogenesis 5 237–56 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1024532022166 Occurrence Handle12906317
ED Harris (1997) The pannus-cartilage junction: Focus of the destructive process. In Rheumatoid Arthritis W.B. Saunders Company Philadelphia 158–73
MJ Elices LY Osborn C Takada et al. (1996) ArticleTitleVCAM–1 on activated endothelium interacts with leukocytes intergrins VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibonlectin binding sites Cell 60 557–84
M Ebisawa BS Bovhner SN Georas RP Schlemier (1992) ArticleTitleEosinophil transendothelial migration induced by cytokines. I. Role of endothelial and Eosinophil adhesion molecules in IL-1β-induced transendothelial migration J Immunol 149 4021–8 Occurrence Handle1460288
L Zhang D Yu M Hu et al. (2000) ArticleTitleWild-type p53 suppresses angiogenesis in human leiomyosarcoma and synovial sarcoma by transcriptional suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression Cancer Res 60 IssueID13 3655–61 Occurrence Handle10910082
N Ferrara HP Gerber J LeCounter (2003) ArticleTitleThe biology of VEGF and its receptors Nat Med 9 669–76 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0603-669 Occurrence Handle12778165
Y Kubota HK Kleinman GR Matrin TJ Lawley (1998) ArticleTitleRole of laminin and basement membrane in the morphological differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures J Cell Biol 107 1589–98 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.107.4.1589
A Passaniti RM Taylor R. Pili et al. (1992) ArticleTitleMethod in laboratory investigation. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor Lab Invest 67 519–28 Occurrence Handle1279270
RF Nicosia A Ottinetti (1990) ArticleTitleGrowth of microvessels in serum-free matrix culture of rat aorta. A quantitative assay of angiogenesis in vitro Lab Invest 63 115–22 Occurrence Handle1695694
RF Nicosia A Ottinetti (1990) ArticleTitleModulation of microvascular growth and morphogenesis by reconstituted basement membrane gel in three-dimensional cultures of rat aorta: A comparative study of angiogenesis in Matrigel, collagen, fibrin, and plasma clot. In vitro Cell Dev Biol 26 119–28 Occurrence Handle1690206
DH Adam M Yanelli SuffixJr W Newman et al. (1997) ArticleTitleAdhesion of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes to endothelium. A phenotypic and functional analysis Br J Cancer 75 1421–31 Occurrence Handle9166933
MB Furie MJ Burns MCA Tancinco et al. (1992) ArticleTitleE-selectin (endothelial–leukocyte adhesion molecules-1) is not required for the migration of neutrophils across IL-1 stimulated endothelial in vitro J Immunol 148 2395–404 Occurrence Handle1373167
DS Milstone D Fukamura RC Padgett et al. (1998) ArticleTitleMice lacking E-selectin show normal number of rolling leukocytes but reduce leukocytes stable arrest on cytokine-activated microvascular endothelium Microcirculation 5 153–71 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.mn.7300023 Occurrence Handle9789256
M Yoshida BE Szente JM Kiely et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePhospharylation of the cytoplamic domain of E-selectin is regulated during leukocytes–endothelial adhesion J Immunol 161 933–47 Occurrence Handle9670972
PR Colivelle-Nash DL Scott (1992) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis and rheumatoid arthritis: Pathologic and therapeutic implication Ann Rhem Dis 51 1919–25
PEC Brenchley (2001) ArticleTitleAntagonising angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis Ann Rheum Dis 60 70–4
P Carmeliet (2003) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis in health and disease Nat Sci 9 653–60 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nm0603-653
P Carmeliet RK Jain (2000) ArticleTitleInsight review articles: Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases Nature 407 249–57 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35025220 Occurrence Handle11001068
G Steiner JS Smolen (2003) ArticleTitleTherapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis Nat Rev 2 473–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kok, T.W., Yue, P.Y.K., Mak, N.K. et al. The Anti-Angiogenic Effect of Sinomenine. Angiogenesis 8, 3–12 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-005-2892-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-005-2892-z