Abstract
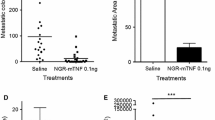
Antiangiogenic agents produce regression in few tumors in clinical trials, but are effective in preventing recurrences. To determine whether the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor is a molecular target to prevent metastatic disease, we utilized a non-specific inhibitor of the VEGF receptor, SU11248. This receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor prevented migration of endothelial cells and markedly attenuated capillary-like tubule formation in endothelial cells in culture. Similarly, this agent prevented blood vessel formation in the tumor vascular window model. VEGF RTK inhibition produced minimal effects on established blood vessels in the tumor vascular window model and little effect on blood flow studied by power Doppler analysis. To determine whether these agents attenuate the development of metastases, Lewis lung carcinoma tumors were resected from the dorsal skin and lung metastases were quantified with and without treatment with SU11248. The RTK inhibitor attenuated the formation of lung metastases following resection of the hind limb tumor. In contrast, these agents did not induce regression of primaries but slowed the progression of tumor growth. These findings suggest that the greatest role for VEGF antagonists may be to prevent the formation of new blood vessels, during and after conventional therapy is given to existing neoplastic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- HMEC:
-
human dermal microvasculature endothelial cells
- HUVEC:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- i.p.:
-
intraperitoneal
- LLC:
-
Lewis lung carcinoma
- RTK:
-
receptor tyrosine kinase
- TKI:
-
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
RS Kerbel (2000) ArticleTitleTumor angionesis: past, present, and near future Carcinogenisis 1 IssueID3 2505–515
DH Ausprunk J Folkman (1977) ArticleTitleMigration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis Microvasc Res 14 53–65
J Folkman (1985) ArticleTitleTumor angiogenesis Adv Cancer Res 43 175–203
R Bos H Zhong CF Hanrahan (2001) ArticleTitleLevels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha during breast carcinogenesis J Natl Cancer Inst 93 309–14
A Giatromanolaki MI Koukourakis E Sivridis et al. (2001) ArticleTitleRelation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and 2 alpha in operable non-small cell lung cancer to angiogenic/molecular profile of tumors and survival Br J Cancer 85 881–90
K Nakayama A Kanzaki K Hata et al. (2002) ArticleTitleHypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1 alpha) gene expression in human ovarian carcinoma Cancer Lett 176 215–23
PH Maxwell GU Dachs JM Gleadle et al. (1997) ArticleTitleHypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94 8104–9
P Carmeliet RK Jain (2000) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis in cancer and other diseases Nature 407 249–57
DE Richard E Berra J Pouyssegur (1999) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis: How a tumor adapts to hypoxia Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266 IssueID3 718–22
D Hanahan (1997) ArticleTitleSignaling vascular morphogenesis and maintenance Science 277 48–50
J Holash PC Maisonpierre D Compton et al. (1999) ArticleTitleVessel cooption, regression and growth in tumors mediated by angiopoietins and VEGF Science 284 1994–8
RK Jain (2002) ArticleTitleTumor angiogenesis and accessibility: role of vascular endothelial growth factor Semin Oncol 29 3–9
N Ferrara HP Gerber J LeCouter (2003) ArticleTitleThe Biology of VEGF and its receptors Nat Med 9 669–76
K Inoue JW Slaton T Karashima et al. (2000) ArticleTitleThe prognostic valie of angiogenesis factor expression for predicting recurrence and metastasis of bladder cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy Clin Cancer Res 6 4866–73
M Niedergethmann R Hildrenbrand B Wostbrook et al. (2002) ArticleTitleHigh expression of vascular endothelial growth factor predicts early recurrence and poor prognosis after curative resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas Pancreas 25 122–9
BR Zetter (1998) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis and tumor metastasis Annu Rev Med 49 407–24
G Bergers K Javaherian KM Lo et al. (1999) ArticleTitleEffects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice Science 284 808–12
N Ferrara (1999) ArticleTitleRole of vascular endothelial growth factor in the regulation of angiogenesis Kidney Int. 56 794–814
J Folkman (2002) ArticleTitleRole of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis Semin Oncol 29 15–8
T Annie T Fong K Laura et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor(Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types Cancer Res 59 99–106
DB Mendel AD Laird BD Smolich et al. (2000) ArticleTitleDevelopment of SU5416, a selective small molecule inhibitor of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase activity, as an anti-angiogenesis agent Anti-Cancer Drug Design 15 29–41
AJ Schueneman E Himmelfarb L Geng et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSU11248 Maintenance therapy prevents tumor regrowth after fractioned irradiation of murine tumor models Cancer Res 63 4009–16
L Sun N Tran F Tang et al. (1998) ArticleTitleSynthesis and biological evaluations of 3-substituted indolin-2-ones: A novel class of tyrosine kinase inhibitors that exhibit selectively toward particular receptor tyrosine kinases J Med Chem 41 2588–603
DB Mendel AD Laird X Xin et al. (2003) ArticleTitleIn vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and plateletderived growth factor receptors: Determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship Clin Cancer Res 9 327–37
S Dimmeler E Dernbach AM Zeiher (2000) ArticleTitlePhosphorylation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase at Ser-1177 is required for VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration FEBS 477 258–62
P Sonveaux A Brouet X Havaux et al. (2003) ArticleTitleIrradiation-induced angiogenesis through the up-regulation of the nitric oxide pathway: Implications for tumor radiatherapy Cancer Research 63 1012–19
Y Kureishi Z Luo I Shiojima et al. (2000) ArticleTitleThe HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin activates the protein kinase Akt and promotes angiogenesis in normocholesterolemic animals Nat Med 6 1004–10
A Abdollahi KE Lipson X Han et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSU5416 and SU6668 Attenuate the angiogenic effects of radiation-induced tumor cell growth factor production and amplify the direct anti-endothelial action of radiation in vitro Cancer Res 63 3755–63
L Geng E Donnelly G McMahon et al. (2001) ArticleTitleInhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling leads to reversal of tumor resistance to radiotherapy Cancer Res 61 2413–19
T Kilic JA Alberta PR Zdunek et al. (2000) ArticleTitleIntracranial inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-mediated glioblastoma cell growth by an orally active kinase inhibitor of the 2-phenylaminopyrimidine class Cancer Research 60 5143–50
MS O’Reilly L Holmgren Y Shing et al. (1994) ArticleTitleAngiostatin: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma Cell 79 315–8
K Camphausen MA Moses WD Beecken et al. (2001) ArticleTitleRadiation therapy to a primary tumor accelerates metastatic growth in mice Cancer Res 61 2207–11
M Shibuya S Yamaguchi A Yamane et al. (1990) ArticleTitleNucleotide sequence and expression of a novel human receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene (flt) closely related to the fms family Oncogene 5 519–24
BI Terman ME Carrion E Kovacs et al. (1991) ArticleTitleIdentification of a new endothelial cell growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase Oncogene 6 1677–83
C Vries Particlede JA Escobedo H Ueno et al. (1992) ArticleTitleThe fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor Science 255 989–91
N Ferrara (2002) ArticleTitleVEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors Nat Rev Cancer 2 795–803
J LeCouter R Lin N Ferrara (2002) ArticleTitleEndocrine gland-derived VEGF and the emerging hypothesis of organ-specific regulation of angiogenesis Nat Med 8 913–7
R. Kerbel J Folkman (2002) ArticleTitleClinical translation of angiogenesis inhibitors Nat Rev Cancer 2 727–39
T Asahara D Chen T Takashi et al. (1998) ArticleTitleTie2 receptor ligands, angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2, modulate VEGF-induced postnatal neovascularization Circ Res 83 IssueID3 233–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osusky, K.L., Hallahan, D.E., Fu, A. et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU11248 impedes endothelial cell migration, tubule formation, and blood vessel formation in vivo, but has little effect on existing tumor vessels. Angiogenesis 7, 225–233 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-004-3149-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-004-3149-y