Abstract
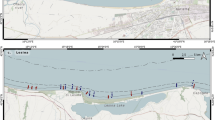
The influence of a passive shrimp fishing gear on benthic communities was studied at Laguna Estuarine System (South Brazil), a shallow choked coastal lagoon. The gear is composed by a group of fyke nets (25 mm mesh size) set in contact to the bottom, fixed with stakes forming a cage-like structure (around 30 m2). Samplings were conducted in the two main fishery areas of the estuarine system, Mirim (sand bottoms) and Imaruí (muddy bottoms) lagoon, in May 2005. In each area, 10 fyke net enclosures and 10 nearby sites without nets (control) were sampled. Microphytobenthos biomass (chlorophyll a and phaeopigments), number of taxa/species, density, Hill’s number N 1 and N 2, and estimated number of species (ES100) were used as community attributes. For the nematodes, values of the maturity index and abundance of Wieser’s feeding type were used as well. The effects of the small-scale passive shrimp fishing gear on the coastal lagoon bottoms were dependent on the benthic component analyzed and the type of sediment. Whereas macrofauna was not affected by the net enclosures, meiofauna and nematodes, particularly from the mud sites were. At the sand site, the fyke net enclosures caused a decrease in the microphytobenthos biomass and changed the relative abundances of non-selective deposit feeding and epigrowth-feeding nematodes. The results indicated that small-scale static nets, such as the studied fyke enclosures, produced low intensity levels of disturbance. However, the enclosed area by nets at Laguna had already reached around 25,000 m2. Given the large proportion of the coastal population involved and the area closed by nets, management policies should consider site-specific differences within the same estuarine system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi DM (1990) The ecology of tropical soft-bottom benthic ecosystems. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 28:381–496
Angonesi LG (2005) Dinâmica de curto prazo da macrofauna bentônica em uma enseada estuarna da Lagoa dos Patos: efeitos antrópicos e mecanismos de persistêncai e resistência. PhD thesis Universidade do Rio Grande, Rio Grande
Arias M, Drake P (1994) Structure and production of the benthic macroinvertebrate community in a shallow lagoon in the Bay of Cadiz. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 115:151–167
Austen MC, Widdicombe S (2006) Comparison of the response of meio- and macrobenthos to disturbance and organic enrichment. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 330:96–104
Austen MC, Widdicombe S, Villano-Pitacco N (1998) Effects of biological disturbance on diversity and structure of meiobenthic nematode communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 174:233–246
Bemvenuti CE (1997) Benthic invertebrates. In: Seeliger U, Odebrecht C, Castello JP (eds) Subtropical convergence environments. the coast and sea in the southwestern Atlantic. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 43–46
Bemvenuti CE, Netto SA (1998) Distribution and seasonal patterns of the sublittoral benthic macrofauna of Patos Lagoon (south Brazil). Rev Bras Biol 58:211–221
Blaber SJM, Cyrus DP, Albaret JJ, Ching CV, Day JW, Elliott M, Fonseca MS, Hoss DE, Orensanz J, Potter IC, Silvert W (2000) Effects of fishing on the structure and functioning of estuarine and nearshore ecosystems. ICES J Mar Sci 57:590–602
Bland JM, Altman DG (1995) Multiple significance tests: the Bonferroni method. BMJ Stat Note 310:170
Bongers T (1990) The maturity index: an ecological measure of environmental disturbance based on nematode species composition. Oecologia 83:14–19
Bongers T, Alkemade R, Yeates GW (1991) Interpretation of disturbance-induced maturity decrease in marine nematode assemblages by means of the Maturity Index. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 76:135–142
Bongers T, de Goede RGM, Korthals GW, Yeates GW (1995) Proposed changes of c-p classification for nematodes. Russ J Nematol 3:61–62
Cahoon LB, Nearhoof JE, Tilton CL (1999) Sediment grain size effect on benthic microalgal biomass in shallow aquatic ecosystems. Estuaries 22:735–741
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Ainsworth M (1993) A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92:205–219
Clarke KR, Green RH (1988) Statistical design and analysis for a ‘biological effects’ study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 46:226–231
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1994) Changes in marine communities: an approach to statistical analyses and interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, United Kingdom
Dayton PK, Thrush SF, Agardy MT, Hofman RJ (1995) Environmental effects of marine fishing. Aquat Conserv Mar Freshwat Ecosyst 5:205–232
De Jonge VN, Bouwman LA (1977) A simple density separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Mar Biol 42:143–148
Dean WE (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. J Sed Petrol 44:242–248
Dernie KM, Kaiser MJ, Richardson EA, Warwick RM (2003) Recovery of soft sediment communities and habitats following physical disturbance. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 285:415–434
EPAGRI (2007) Empresa de Pesquisa Agronômica e Extensão Rural de Santa Catarina. Centro Integrado de Meteorologia e Recursos Hídricos de Santa Catarina. http://www.epagri.rct-sc.br
Essink K, Keidel H (1998) Changes in estuarine nematode communities following a decrease of organic pollution. Aquat Ecol 32:195–202
FAO (2007) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: essential documents, statistics, maps and multimedia resources. http://www.fao.org
Fonseca G, Netto SA (2006) Shallow sublittoral benthic communities of the Laguna Estuarine System, South Brazil. Braz J Oceanogr 54:41–54
Gallucci F, Netto SA (2004) Effects of the passage of cold fronts over a coastal site: an ecosystem approach. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 281:79–92
Guiral D, Gourbault N, Helleouet MN (1995) Etude sédimentologique et méiobenthos d’un écosystème lagunaire modifié par un récif artificiel à vocation aquacole: l’acadja. Oceanol Acta 18:543–555
Gray JS (1974) Animal-sediment relationships. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 12:223–261
Hall SJ (1994) Physical disturbance and marine benthic communities: life in unconsolidated sediments. Oceanogr Mar Biol Ann Rev 32:179–239
Hendelberg M, Jensen P (1993) Vertical distribution of the nematode fauna in coastal sediment influenced by seasonal hypoxia in the bottom water. Ophelia 37:83–94
Hill MO (1973) Diversity and evenness: a unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 54:427–432
Hurlbert SH (1971) The nonconcept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 52:577–586
Jawad LA (2006) Fishing gear and methods of the lower Mesopotamian plain with reference to fishing management. Mar Mesop Online 1:1–37
Jones JB (1992) Environmental impact of trawling on the seabed: a review. NZ J Mar Freshwat Res 26:59–67
Kaiser MJ, Collie JS, Hall SJ, Jennings S, Poiner IR (2002) Modification of marine habitats by trawling activities: prognosis and solutions. Fish Fisher 3:114–136
Kaiser MJ, Clarke KR, Hinz H, Austen MCV, Somerfield PJ, Karakassis I (2006) Global analysis of response and recovery of benthic biota to fishing. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 311:1–14
Kjerfve B (1994) Coastal Lagoons. In: Kjerfve B (ed) Coastal lagoon processes. Elsevier-Oceanographic Series 60, New York, pp 1–8
Kromkamp J, Peene J, Van Rijswijk P, Sandee A, Goosen N (1995) Nutrients, light and primary production by phytoplankton and microphytobenthos in eutrophic, turbid Westerschelde estuary (The Netherlands). Hydrobiology 311:9–19
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Determination of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: spectrometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr 12:343–346
McClanahan TR, Mangi SC (2004) Gear-based management of a tropical artisanal fishery based on species selectivity and capture size. Fish Manage Ecol 11:51–60
McIntyre CD, Amspoker MC (1986) Effects of sediment properties on benthic primary production in the Columbia River estuary. Aquat Bot 24:249–267
McLusky DS (1989) The estuarine ecosystem, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, New York
Meurer AZ, Netto SA (2007) Seasonal dynamics of benthic communities in a shallow sublitoral site of Laguna Estuarine System (South, Brazil). Braz J Aquat Sci Tech 11(2):53–62
Moens T, Vincx M (1997) Observations on the feeding ecology of estuarine nematodes. J Mar Biol Ass UK 77:211–227
Nedelec C, Prado J (1990) Definition and classification of fishing gear categories. FAO, Roma
Paterson DM, Hagerthey SE (2001) Microphytobenthos in contrasting coastal ecosystems: biology and dynamics. In: Reise K (ed) Ecological comparisons of sedimentary shores. Ecological Studies 151 Springer, 105–126 pp
Pereira TJ, Netto SA (2005) Rejeitos da pesca de camarão no Sistema Estuarino de Laguna (Shrimp fishery bycatch at the Laguna Estuarine System). In: II Brazilian Conference of Oceanography, Espirito Santo Federal University, Vitória, 9–12 October 2005
Perneger TV (1998) What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. BMJ 316:1236–1238
Quinn GP, Keough MJ (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Reizopoul S, Nicolaidou A (2004) Benthic diversity of coastal brackish-water lagoons in western Greece. Aquat Conserv: Mar Freshwat Ecosyst 14:93–1024
Sanders HL (1968) Marine benthic diversity: A comparative study. Am Nat 102:243–282
Schratzberger M, Jennings S (2002) Impacts of chronic trawling disturbance on meiofaunal communities. Mar Biol 141:991–1000
Schratzberger M, Warwick RM (1999) Effects of physical disturbance on nematode communities in sand and mud: a microcosm experiment. Mar Biol 130:643–650
Schratzberger M, Dinmore TA, Jennings S (2002) Impacts of trawling on the diversity, biomass and structure of meiofauna assemblages. Mar Biol 140:83–93
Snelgrove PVR, Butman CA (1994) Animal–sediment relationships revisited: cause versus effect. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 32:111–177
Soetaert K, Heip C (1990) Nematode assemblages of deep-sea and shelf break sites in the North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 125:171–83
Soetaert K, Vincx M, Wittoeck J, Tulkens M (1995) Meiobenthic distribution and nematode community structure in five European estuaries. Hydrobiologia 311:185–206
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1997) Biometry. WH Freeman and Company, New York
Somerfield PJ, Warwick RM (1996) Meiofauna in marine pollution programmes. A laboratory manual. MAFF Directorate of Fisheries Research, Lowestoft
Stergiou KI, Petrakis G, Politou CY (1996) Small-scale fisheries in the South Euboikos Gulf (Greece): species composition and gear competition. Fish Res 26:325–336
Steyaert M, Vanaverbeke J, Vanreusel A, Barranguet C, Lucas C, Vincx M, (2003) The importance of fine-scale, vertical profiles in characterising nematode community structure. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 58:353–366
Strickland JHD, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa
Suguio K (1973) Introdução à sedimentologia. Editora. Blücher, São Paulo
Sunye PS (2006) Diagnóstico da pesca no litoral do estado de Santa Catarina. In: Isaac VJ, Martins AS, Haimovici M, Andriguetto JM (eds) A Pesca Marinha e Estuarina do Brasil no Início do Século XXI: Recursos, Tecnologias, Aspectos Socioeconômicos e Institucionais. Editora Universitária UFPA, Belém, pp 141–156
Vanhove S, Arntz W, Vincx M (1999) Comparative study of nematode communities of southeastern Weddel Sea shelf and slope (Antarctica). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 181:237–256
Vieira JP, Vasconcellos MC, Silva RE, Fischer LG (1996) A rejeição da pesca do camarão rosa (Penaeus paulensis) no estuário da Lagoa dos Patos, RS, Brasil. Atlântica 18:123–142
Walsh HJ, Peters DS, Cyrus DP (1999) Habitat utilization by small flatfishes in a North Carolina estuary. Estuaries 22:803–813
Warwick RM, Platt HM, Clarke KR, Agard J, Gobin J (1990) Analysis of macrobenthic and meiobenthic community structure in relation to pollution and disturbance in Hamilton Harbour, Bermuda. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 138:119–142
Wasmund N (2007) Production and distribution of the microphytobenthos in sediment of Lake Mikolajskie. Int Reveu ges Hydrobiol 69:215–229
Wieser W (1953) Die Beziehung zwishen Mundhöhlengestalt, Ernährungsweise und Vorkommen bei freilebenden marine Nematoden—eine ökologischmorphologische Studie. Ark Zool 4:439–483
Widdicombe S, Austen MC (2005) Setting diversity and community structure in subtidal sediments: The importance of biological disturbance. In: Kostka J, Haese R, Kristensen E (eds) Interactions between macro- and microorganisms in marine sediments, AGU, New York, pp 217–231
Zajac R (2003) Macrofaunal responses to pit–mound patch dynamics in an intertidal mudflat: local versus patch-type effects. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 313:2297–315
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all fishermen who allowed us to onboard a scientific observer, despite the great restrictions imposed by the boat size. We also thank Gustavo Fonseca and Fabiane Gallucci for their help in the field. Dr Patricia Sunye (EPAGRI), Dr. Axayácatl Rocha-Olivares and Mc. Ruth Gingold (CISESE) are thanked for commenting the manuscript. This study was founded by the Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC). Finally, we thank three anonymous referees for their contribution in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Netto, S.A., Pereira, T.J. Benthic community response to a passive fishing gear in a coastal lagoon (South Brazil). Aquat Ecol 43, 521–538 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-008-9177-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-008-9177-8