Abstract
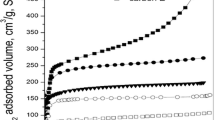
The aim of work is to study the adsorption of a common volatile organic compound such as toluene using activated carbons prepared by chemical activation with phosphoric acid of a lignocellulosic precursor, almond shell, under different conditions. The Impregnation ratio, temperature and time of activation were modified to obtain activated carbons with different characteristics. Regarding the characteristics of the activated carbons, the effects of porous structure and surface chemistry on the toluene adsorption capacity from toluene isotherms have been analysed. Results show that the control of properties of the activated carbons, particularly porous structure, highly dependent on the preparation conditions, plays a decisive role on the toluene adsorption capacity of the activated carbons. Concerning the experiments of toluene adsorption conducted in dynamic mode, activated carbons prepared at low temperatures of activation show higher breakthrough times than those obtained for activated carbons prepared at higher activation temperatures. The amount of toluene adsorbed in presence of water vapor in the gas stream lead to a decrease ranging from 33 to 46 % except for carbons prepared at higher temperatures activated that show only a slight decrease in the amount of toluene adsorbed. Activated carbons can be regenerated with soft heat treatment showing a slight decrease in the adsorption capacity. The high toluene adsorption capacities as well as the high breakthrough times obtained in presence of water vapor make these activated carbons suitable for commercial applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcañiz-Monge, J., Linares-Solano, A., Rand, B.: Water adsorption on activated carbons: study of water adsorption in micro- and mesopores. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 7998–8006 (2001)
Alcañiz-Monge, J., Linares-Solano, A., Rand, B.: Mechanism of adsorption of water in carbon micropores as revealed by a study of activated carbon fiber. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 3209–3216 (2002)
Antal, M.J., Varhegyi, G.: Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: the current state of knowledge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 34, 703–717 (1995)
Babić, B.M., Milonjić, S.K., Polovina, M.J., Kaludierović, B.V.: Point of zero charge and intrinsic equilibrium constants of activated carbon cloth. Carbon 37, 477–481 (1999)
Balci, S., Doğu, T., Yücel, G.: Pyrolysis of lignocellulosic materials. Ind. Chem. Res. 32, 2573–2579 (1993)
Bandosz, T.J., Jagiello, J., Contescu, C., Schwarz, J.A.: Characterization of the surfaces of activated carbons in terms of their acidity constant distribution. Carbon 31(7), 1193–1202 (1993)
Benkheda, J., Jaubert, J.N., Barth, D.: Experimental and modelled results describing the adsorption of toluene onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 45, 653–661 (2000)
Boehm, H.P., Heck, W., Sappok, R., Diehl, E.: Surface oxides of carbon. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 3(10), 669 (1964)
Boehm, H.P.: Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 32, 759–769 (1994)
Bouhamra, W.S., Baker, C.G.J., Elkilani, A.S., Alkandari, A.A., Al-Masour, A.A.A.: Adsorption of toluene and 1,1,1-trichloroethane on selected adsorbents under a range of ambient conditions. Adsorption 15, 461–475 (2009)
Brennan, J.K., Bandosz, T.J., Thomson, K.T., Gubbins, K.E.: Water in porous carbons. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 187, 539–568 (2001)
Caballero, J.A., Conesa, J.A., Font, R., Marcilla, A.: Pyrolysis kinetics of almond shells and olive stones considering their organic fractions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 42, 159–175 (1997)
Cal, M.P., Rood, M.J., Larson, S.M.: Removal of VOCs from humidified gas stream using activated carbon cloth. Gas Sep. Purif. 10(2), 117–121 (1996)
Carrott, P.J.M., Ribeiro Carrott, M.M.L., Estevão Candelas, A.J., Prates Ramalho, J.P.: Numerical simulation of surface ionisation and specific adsorption in a two-site model of a carbon surface. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 91(14), 2179–2184 (1995)
Cossarutto, L., Zimny, T., Kaczmarczyk, J., Siemieniewska, T., Bimer, J., Weber, J.V.: Transport and sorption of water vapour in activated carbons. Carbon 30, 2339–2346 (2001)
Corcho-Corral, B., Olivares-Marín, M., Fernández-González, C., Gómez-Serrano, V., Macías-García, A.: Preparation and textural characterization of activated carbon from vine shoots (Vitis vinifera) by H3PO4-chemical activation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 5961–5966 (2006)
Daifullah, A.M.M., Girgis, B.B.: Impact of surfaces characteristics of activated carbon on adsorption of BTEX. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 214, 181–193 (2003)
Do, D.D., Do, H.D.: A model for water adsorption in activated carbon. Carbon 38(5), 767–773 (2000)
Dubinin, M.M.: Water vapour adsorption and the microporous structures of carbonaceous adsorbents. Carbon 18, 355–364 (1980)
Dubinin, M.M., Serpinsky, V.V.: Isotherm equation for water vapour adsorption by microporous carbonaceous adsorbents. Carbon 19(5), 402–403 (1981)
Dubinin, M.M.: Fundamentals of the theory of adsorption in micropores of carbon adsorbents—characteristics of their adsorption properties and microporous structure. Carbon 27, 457–467 (1989)
Figueiredo, J.L., Pereira, M.F.R., Freitas, M.M.A., Órfão, J.J.M.: Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 37, 1379–1389 (1999)
Font, R., Marcilla, A., Verdú, E., Devesa, J.: Thermogravimetric kinetic study of the pyrolysis of almond shells and almond shells impregnated with CoCl2. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 21, 249–264 (1991)
Girgis, B.B., Hendawy, A.A.N.: Porosity development in activated carbons obtained from date pits under chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 52, 105–117 (2002)
González, J.F., Román, S., Encinar, J.M., Martínez, G.: Pyrolysis of various biomass residues and char utilization for the production of activated carbons. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 85, 134–141 (2009)
Izquierdo, M.T., Martínez de Yuso, A., Rubio, B., Pino, M.R.: Conversion of almond shell to activated carbons: methodical study of the chemical activation based on an experimental design and relationship with their characteristics. Biomass Bioenergy 35, 1235–1244 (2011)
Jones, A.P.: Indoor air quality and health. In: Austin, J., Brimblecombe, P., Sturges, W. (eds.) Developments in Environmental Science. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2002)
Macías-Pérez, M.C., Lillo-Ródenas, M.A., Bueno-López, A., Salinas-Martínez de Lecea, C., Linares-Solano, M.: SO2 retention on CaO/activated carbon sorbents. Part II: effect of the activated carbon support. Fuel 87, 2544–2550 (2008)
Menéndez, J.A., Illán-Gómez, M.J., León y León, C.A., Radovic, L.R.: On the difference between the isoelectric point and the point of zero charge of carbons. Carbon 33(11), 1655–1659 (1995)
Lagorsse, S., Campo, M.C., Magalhaes, F.D., Mendes, A.: Water adsorption on carbon molecular sieve membranes: experimental data and isotherm model. Carbon 43, 2769–2779 (2005)
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40, 1361–1402 (1918)
Lavanchi, A., Stoeckli, F.: Dynamic adsorption, in active carbon beds, of vapour mixtures corresponding to miscible and immiscible liquids. Carbon 37(2), 315–321 (1999)
Lillo-Rodenas, M.A., Cazorla-Amoros, D., Linares-Solano, A.: Behaviour of activated carbons with different pore size distributions and surface oxygen groups for benzene and toluene adsorption at low concentration. Carbon 43, 1758–1767 (2005)
Naono, H., Hakuman, M.: Analysis of porous texture by means of water vapour adsorption isotherm with particular attention to lower limit of hysteresis loop. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 158, 19–26 (1993)
Neimark, A.V., Lin, Y., Ravikovitch, P.I., Thommes, M.: Quenched solid density functional theory and pore size analysis of micro-mesoporous carbons. Carbon 47, 1617–1628 (2009)
Noh, J.S., Schwarz, J.A.: Estimation of the point of zero charge of simple oxides by mass titration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 130(1), 157–164 (1988)
Noh, J.S., Schwarz, J.A.: Effect of HNO3 treatment on the surface acidity of activated carbons. Carbon 28(5), 675–682 (1990)
Ouensanga, A., Largitte, L., Arsene, M.A.: The dependence of char yield on the amounts of components in precursors for pyrolysed tropical fruit stones and seeds. Micorporous Mesorporous Mater. 59, 85–91 (2003)
Puziy, A.M., Poddubnaya, O.I., Martínez-Alonso, A., Suárez-García, F., Tascón, J.M.D.: Synthetic carbons activated with phosphoric acid I. Surface chemistry and ion binding properties. Carbon 40, 1493–1505 (2002)
Puziy, A.M., Poddubnaya, O.I., Martínez-Alonso, A., Suárez-García, F., Tascón, J.M.D.: Surface chemistry of phosphorus-containing carbons of lignocellulosic origin. Carbon 43, 2857–2868 (2005)
Ruddy, E.N., Carroll, L.A.: Select the best VOC control strategy. Chem. Eng. Prog. 89, 28–35 (1993)
Salame, I.I., Bandosz, T.J.: Experimental study of water adsorption on activated carbons. Langmuir 15, 587–593 (1999a)
Salame, I.I., Bandosz, T.J.: Study of water adsorption on activated carbons with different degrees of surface oxidation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 210, 367–374 (1999b)
Sillman, S.: Tropospheric ozone and photochemical smog. In: Heinrich, D., Hollan, Karl K. (eds.) Treatise on Geochemistry, vol 9, pp. 407–431. Elsevier, Turekian (2003)
Silvestre-Albero, A., Silvestre-Albero, J., Sepúlveda-Escribano, A., Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.: Ethanol removal using activated carbon: effect of porous structure and surface chemistry. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 120, 62–68 (2009)
Suárez-García, F., Martínez-Alonso, A., Tascón, J.M.D.: Activated carbon fibers from Nomex by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Carbon 42, 1419–1426 (2004)
Valente Nabais, J.M., Laginhas, C.E.C., Carrott, P.J.M., Ribeiro Carrott, M.M.L.: Production of activated carbons from almond shell. Fuel Process. Technol. 92, 234–240 (2011)
Werner, M.D.: The effects of relative humidity on the vapour phase adsorption of trichloroethylene by activated carbon. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 46(10), 585–590 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez de Yuso, A., Izquierdo, M.T., Rubio, B. et al. Adsorption of toluene and toluene–water vapor mixture on almond shell based activated carbons. Adsorption 19, 1137–1148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9540-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-013-9540-5