Abstract
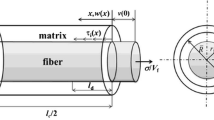
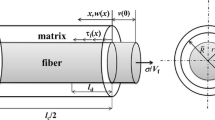
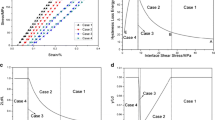
In this paper, the fatigue hysteresis loops of fiber-reinforced ceramic-matrix composites (CMCs) under multiple loading stress levels considering interface wear has been investigated using micromechanical approach. Under fatigue loading, the fiber/matrix interface shear stress decreases with the increase of cycle number due to interface wear. Upon increasing of fatigue peak stress, the interface debonded length would propagate along the fiber/matrix interface. The difference of interface shear stress existed in the new and original debonded region would affect the interface debonding and interface frictional slipping between the fiber and the matrix. Based on the fatigue damage mechanism of fiber slipping relative to matrix in the interface debonded region upon unloading and subsequent reloading, the interface slip lengths, i.e., the interface debonded length, interface counter-slip length and interface new-slip length, are determined by fracture mechanics approach. The fatigue hysteresis loops models under multiple loading stress levels have been developed. The effects of single/multiple loading stress levels and different loading sequences on fatigue hysteresis loops have been investigated. The fatigue hysteresis loops of unidirectional C/SiC composite under multiple loading stress levels have been predicted.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naslain, R.: Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: an overview. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 155–170 (2004). doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00230-6
Schmidt, S., Beyer, S., Knabe, H., Immich, H., Meistring, R., Gessler, A.: Advanced ceramic matrix composite materials for current and future propulsion system applications. Acta Astronaut. 55, 409–420 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2004.05.052
DiCarlo, J.A., Van Roode, M.: Ceramic composite development for gas turbine hot section components. Proc. ASME Turbo Expo: Power for Land Sea Air 2, 221–231 (2006)
Stephen, T.: General Electric primes CMC for turbine blades. Flight International. (2010). http://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/general-electric-primes-cmc-for-turbine-blades-349834/
Zhang, L.T., Cheng, L.F., Luan, X.G., Mei, H., Xu, Y.D.: Environmental performance testing system for thermostructure materials applied in aeroengines. Key Eng. Mater. 313, 183–190 (2006). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.313.183
Evans, A.G., Zok, F.W., McMeeking, R.M.: Fatigue of ceramic matrix composites. Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 859–875 (1995). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(94)00304-Z
Holmes, J.W., Cho, C.D.: Experimental observation of frictional heating in fiber-reinforced ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 929–938 (1992). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1992.tb04162.x
Reynaud, P.: Cyclic fatigue of ceramic-matrix composites at ambient and elevated temperatures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 56, 809–814 (1996). doi:10.1016/0266-3538(96)00025-5
Fantozzi, G., Reynaud, P.: Mechanical hysteresis in ceramic matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 521–522, 18–23 (2009). doi:10.1016/jmsea.2008.09.128
Kotil, T., Holmes, J.W., Comninou, M.: Origin of hysteresis observed during fatigue of ceramic matrix composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1879–1883 (1990). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1990.tb05239.x
Pryce, A.W., Smith, P.A.: Matrix cracking in unidirectional ceramic matrix composites under quasi-static and cyclic loading. Acta Metall. Mater. 41, 1269–1281 (1993). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(93)90178-U
Ahn, B.K., Curtin, W.A.: Strain and hysteresis by stochastic matrix cracking in ceramic matrix composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 45, 177–209 (1997)
Solti, J.P., Mall, S., Robertson, D.D.: Modeling damage in unidirectional ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 54, 55–66 (1995). doi:10.1016/0266-3538(95)00041-0
Solti, J.P., Mall, S., Robertson, D.D.: Modeling of fatigue in cross-ply ceramic matrix composites. J. Compos. Mater. 31, 1921–1943 (1997). doi:10.1177/002199839703101903
Vagaggini, E., Domergue, J.M., Evans, A.G.: Relationships between hysteresis measurements and the constituent properties of ceramic matrix composites: I, theory. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 2709–2720 (1995). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1995.tb08046.x
Hutchison, J.W., Jensen, H.M.: Models of fiber debonding and pullout in brittle composites with friction. Mech. Mater. 9, 139–163 (1990). doi:10.1016/0167-6636(90)90037-G
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Z.G.: Influence of interface de-bonding on the fatigue hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. Chin. J. Solid. Mech. 30, 8–14 (2009)
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Z.G.: Effect of fiber poisson contraction on fatigue hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. J. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 41, 181–186 (2009)
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D.: Effect of fiber failure on quasi-static unloading/reloading hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. Trans. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 28, 94–102 (2011)
Li, L.B.: Modeling fatigue hysteresis behavior of unidirectional C/SiC ceramic-matrix composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 66, 466–474 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.06.014
Li, L.B.: Modeling hysteresis behavior of cross-ply C/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 53, 36–45 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.04.029
Li, L.B.: Fatigue hysteresis behavior of cross-ply C/SiC ceramic matrix composites at room and elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 586, 160–170 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.msea.2013.08.017
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D.: An approach to estimate interface shear stress of ceramic matrix composites from hysteresis loops. Appl. Compos. Mater. 17, 309–328 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10443-009-9122-6
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Y.C.: Estimate interface shear stress of unidirectional C/SiC ceramic matrix composites from hysteresis loops. Appl. Compos. Mater. 20, 693–707 (2012). doi:10.1007/s10443-012-9297-0
Li, L.B.: Estimate interface shear stress of woven ceramic matrix composites from hysteresis loops. Appl. Compos. Mater. 20, 993–1005 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10443-013-9314-y
Budiansky, B., Hutchinson, J.W., Evans, A.G.: Matrix fracture in fiber-reinforced ceramics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 34, 167–189 (1986). doi:10.1016/0022-5096(86)90035-9
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province for the funding that made this research study possible. The author would also thank Prof. Pwter W.R. Beaumont for his valuable comments on an earlier version of the paper.
Funding
This study has received the support from the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province through the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20140813).
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longbiao, L. Modeling for Fatigue Hysteresis Loops of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Ceramic-Matrix Composites under Multiple Loading Stress Levels. Appl Compos Mater 22, 945–959 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-015-9444-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-015-9444-5