Abstract
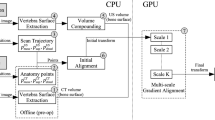
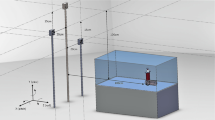
Posterior spinal fusion surgery requires careful insertion of screws into the spine to avoid neurologic injury. While current systems use CT-scans, three-dimensional ultrasound (3DUS) could provide guidance by reconstructing the vertebral surface, and then registering a pre-operative vertebral model to that surface for localization. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and processing time of a custom CT-3DUS registration algorithm. A phantom human vertebra was 3D-printed and scanned with a motion capture-based 3D ultrasound (3DUS) system. Image registration was performed that included a pre-alignment phase using vertebral symmetry information, and then comparing Gaussian pyramid intensity-based registration with iterative-closest-point registration for final transformations. Image registration was performed 192 times while surgical registration between CT and real-world position was performed 84 times. The accuracy of image registration (CT-to-3DUS) was 0.3 ± 0.2 mm and 0.9 ± 0.8° completed in 13.3 ± 2.9 s. The surgical navigation accuracy (CT model to real-world position) of the system was 1.2 ± 0.5 mm and 2.2 ± 2.0° completed in 16.2 ± 3.0 s. Both meet accuracy thresholds of < 2 mm and < 5° required for the surgery. A feasibility study on porcine spine qualitatively showed appropriate overlapping anatomy in CT-3DUS registrations. The usage of 3D ultrasound for navigation has demonstrated accuracy to provide radiation-free image guidance for spine surgery.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C. H., J. R. Bergen, P. J. Burt, and J. M. Ogden. Pyramid Methods in Image Processing. RCA engineer 29(6):33–41, 1984.
Atlas, H.-E. Atlas of ultrasound-guided procedures in interventional pain management [electronic resource]. New York: Springer, 2011.
Bærentzen, J. A., J. Gravesen, F. Anton, and H. Aanæs. Guide to Computational Geometry Processing: Foundations, Algorithms, and Methods. London: Springer-Verlag, 2012.
Basques, B. A., A. M. Lukasiewicz, A. M. Samuel, M. L. Webb, D. D. Bohl, B. G. Smith, and J. N. Grauer. which pediatric orthopaedic procedures have the greatest risk of adverse outcomes? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 37:429–434, 2017.
Chan, A., J. Aguillon, D. Hill, and E. Lou. Precision and accuracy of consumer-grade motion tracking system for pedicle screw placement in pediatric spinal fusion surgery. Med. Eng. Phys. 46:33–43, 2017.
Chan, A., E. Parent, and E. Lou. Reconstruction and positional accuracy of 3D ultrasound on vertebral phantoms for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis spinal surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-1894-4.
Chan, A., E. Parent, J. Wong, K. Narvacan, C. San, and E. Lou. Does image guidance decrease pedicle screw-related complications in surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review update and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-06219-3.
Chen, T. K., P. Abolmaesumi, A. D. Thurston, and R. E. Ellis. Automated 3D freehand ultrasound calibration with real-time accuracy contro. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv. MICCAI Int. Conf. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv 9:899–906, 2006.
Chen, F., D. Wu, and H. Liao. Registration of CT and Ultrasound Images of the Spine with Neural Network and Orientation Code Mutual Information. Cham: Springer, 2016.
Chen, Z., B. Wu, X. Zhai, Y. Bai, X. Zhu, B. Luo, X. Chen, C. Li, M. Yang, K. Xu, C. Liu, C. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Wei, K. Chen, W. Yang, D. Ta, and M. Li. Basic study for ultrasound-based navigation for pedicle screw insertion using transmission and backscattered methods. PloS One 10:e0122392, 2015.
Coe, J. D., V. Arlet, W. Donaldson, S. Berven, D. S. Hanson, R. Mudiyam, J. H. Perra, and C. I. Shaffrey. Complications in spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the new millennium. A report of the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Spine 31:345–349, 2006.
Cuartas, E., A. Rasouli, M. O’Brien, and H. L. Shufflebarger. Use of all-pedicle-screw constructs in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 17:550–561, 2009.
De Lorenzo, D., A. Vaccarella, G. Khreis, H. Moennich, G. Ferrigno, and E. De Momi. Accurate calibration method for 3D freehand ultrasound probe using virtual plane. Med. Phys. 38:6710–6720, 2011.
Fitzpatrick, J. M. Fiducial registration error and target registration error are uncorrelated. New York: Springer, 2009.
Gueziri, H.-E., and D. L. Collins. Fast Registration of CT with Intra-operative Ultrasound Images for Spine Surgery. New York: Springer, 2019.
Hacihaliloglu, I., A. Rasoulian, R. N. Rohling, and P. Abolmaesumi. Local phase tensor features for 3-D ultrasound to statistical shape + pose spine model registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:2167–2179, 2014.
Holly, L. T., O. Bloch, and J. P. Johnson. Evaluation of registration techniques for spinal image guidance. J. Neurosurg. Spine 4:323–328, 2006.
Konieczny, M. R., H. Senyurt, and R. Krauspe. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 7:3–9, 2013.
Koo, T. K., and W. E. Kwok. A non-ionizing technique for three-dimensional measurement of the lumbar spine. J. Biomech. 49:4073–4079, 2016.
Lou, E. H., D. L. Hill, A. Donauer, M. Tilburn, D. Hedden, and M. Moreau. Results of ultrasound-assisted brace casting for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 12:23, 2017.
Maruyama, T., and K. Takeshita. Surgical treatment of scoliosis: a review of techniques currently applied. Scoliosis 3:6, 2008.
Mujagić, M., H. J. Ginsberg, and R. S. C. Cobbold. Development of a method for ultrasound-guided placement of pedicle screws. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 55:1267–1276, 2008.
Parker, S. L., M. J. McGirt, S. H. Farber, A. G. Amin, A.-M. Rick, I. Suk, A. Bydon, D. M. Sciubba, J.-P. Wolinsky, Z. L. Gokaslan, and T. F. Witham. Accuracy of free-hand pedicle screws in the thoracic and lumbar spine: analysis of 6816 consecutive screws. Neurosurgery 68:170–178, 2011; ((Discussion 178)).
Perna, F., R. Borghi, F. Pilla, N. Stefanini, A. Mazzotti, and M. Chehrassan. Pedicle screw insertion techniques: an update and review of the literature. Musculoskelet. Surg. 100:165–169, 2016.
Puvanesarajah, V., J. A. Liauw, S. Lo, I. A. Lina, and T. F. Witham. Techniques and accuracy of thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement. World J. Orthop. 5:112–123, 2014.
Rampersaud, Y. R., D. A. Simon, and K. T. Foley. Accuracy requirements for image-guided spinal pedicle screw placement. Spine 26:352–359, 2001.
Reames, D. L., J. S. Smith, K.-M. G. Fu, D. W. Polly, C. P. Ames, S. H. Berven, J. H. Perra, S. D. Glassman, R. E. McCarthy, R. D. Knapp, R. Heary, C. I. Shaffrey, and Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality Committee. Complications in the surgical treatment of 19,360 cases of pediatric scoliosis: a review of the Scoliosis Research Society Morbidity and Mortality database. Spine 36:1484–1491, 2011.
Richards, B. S., R. M. Bernstein, C. R. D’Amato, and G. H. Thompson. Standardization of criteria for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace studies: SRS Committee on Bracing and Nonoperative Management. Spine 30:2068–2075, 2005; ((Discussion 2076–2077)).
Takahashi, J., H. Hirabayashi, H. Hashidate, N. Ogihara, and H. Kato. Accuracy of multilevel registration in image-guided pedicle screw insertion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 35:347–352, 2010.
Tamura, Y., N. Sugano, T. Sasama, Y. Sato, S. Tamura, K. Yonenobu, H. Yoshikawa, and T. Ochi. Surface-based registration accuracy of CT-based image-guided spine surgery. Eur. Spine J. 14:291–297, 2005.
Yan, C. X. B., B. Goulet, D. Tampieri, and D. L. Collins. Ultrasound-CT registration of vertebrae without reconstruction. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 7:901–909, 2012.
Zheng, Y.-P., T. Lee, K. Lai, B. Yip, G. Zhou, W.-W. Jiang, J. Cheung, M.-S. Wong, B. Ng, J. Cheng, and T.-P. Lam. A reliability and validity study for Scolioscan: a radiation-free scoliosis assessment system using 3D ultrasound imaging. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 11:13, 2016.
Zindrick, M. R., G. W. Knight, M. J. Sartori, T. J. Carnevale, A. G. Patwardhan, and M. A. Lorenz. Pedicle morphology of the immature thoracolumbar spine. Spine 25:2726–2735, 2000.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the finical support from the Alberta Spine Foundation, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the Alberta Innovates Technology Future. We also like to thank Dr. Kumaradevan Punithakumar for guidance on image registration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Arash Kheradvar oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, A., Coutts, B., Parent, E. et al. Development and Evaluation of CT-to-3D Ultrasound Image Registration Algorithm in Vertebral Phantoms for Spine Surgery. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 310–321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02546-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02546-5