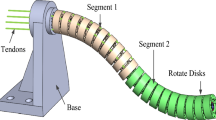
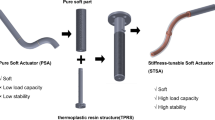
Abstract
In flexible endoscopy, the endoscope needs to be sufficiently flexible to go through the tortuous paths inside the human body and meanwhile be stiff enough to withstand external payloads without unwanted tip bending during operation. Thus, an endoscope whose stiffness can be adjusted on command is needed. This paper presents a novel variable-stiffness manipulator. The manipulator (Ø15 mm) has embedded thermoplastic tubes whose stiffness is tunable through temperature. Temperature is adjusted through joule heat generated by the electrical current supplied to the stainless steel coils and an active air-cooling mechanism. Tests and modeling were conducted to characterize the performance of the design. The manipulator has a high stiffness-changing ratio (22) between rigid and flexible states while that of its commercial Olympus counterpart is only 1.59. The active cooling time is 11.9 s while that of passive ambient cooling is 100.3 s. The thermal insulation layer (Aerogel) keeps the temperature of the outer surface within the safe range (below 41 °C). The models can describe the heating and cooling processes with root mean square errors ranging from 0.6 to 1.3 °C. The results confirm the feasibility of a variable-stiffness endoscopic manipulator with high stiffness-changing ratio, fast mode-switching, and safe thermal insulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alambeigi, F., R. Seifabadi, and M. Armand. A continuum manipulator with phase changing alloy. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 758–764, 2016.
Beasley, R. A. Medical robots: current systems and research directions. J. Robot. 2012:14, 2012.
Blanc, L., A. Delchambre, and P. Lambert. Flexible medical devices: review of controllable stiffness solutions. Actuators 6:23, 2017.
Cao, L., X. Li, P. T. Phan, A. Tiong, J. Liu, and S. Phee. A novel robotic suturing system for flexible endoscopic surgery. In: 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1514–1520, 2019.
Chautems C., A. Tonazzini, D. Floreano, and B. J. Nelson. A variable stiffness catheter controlled with an external magnetic field. In: 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 181–186, 2017.
Chenal, T. P., J. C. Case, J. Paik, and R. K. Kramer. Variable stiffness fabrics with embedded shape memory materials for wearable applications. In: 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2014). IEEE, pp. 2827–2831, 2014.
Cheng, W. B., Y. Y. Di, E. M. Zhang, M. A. Moser, S. Kanagaratnam, L. Y. Korman, N. Sarvazyan, and W. J. Zhang. Modeling and in vitro experimental validation for kinetics of the colonoscope in colonoscopy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41:1084–1093, 2013.
Cheng, W. B., M. A. Moser, S. Kanagaratnam, and W. J. Zhang. Overview of upcoming advances in colonoscopy. Dig. Endosc. 24:1–6, 2012.
Cianchetti, M., T. Ranzani, G. Gerboni, I. De Falco, C. Laschi and A. Menciassi. STIFF-FLOP surgical manipulator: mechanical design and experimental characterization of the single module. In: 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3576–3581, 2013.
De Falco, I., M. Cianchetti, and A. Menciassi. A soft multi-module manipulator with variable stiffness for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 12:056008, 2017.
Degani, A., H. Choset, A. Wolf, and M. Zenati. Highly articulated robotic probe for minimally invasive surgery. In: 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA 2006. Proceedings IEEE, pp. 4167–4172, 2006.
Hu, X., L. Cao, Y. Luo, A. Chen, E. Zhang, and W. J. Zhang. A novel methodology for comprehensive modeling of the kinetic behavior of steerable catheters. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 24:1785–1797, 2019.
Hu, X., and A. Chen. Steerable catheters for minimally invasive surgery: a review and future directions. 23:21–41, 2018.
Kim, Y., S. Cheng, S. Kim, and K. Iagnemma. A stiffness-adjustable hyperredundant manipulator using a variable neutral-line mechanism for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Rob. 30:382–395, 2014.
Kreith, F., R. M. Manglik, and M. S. Bohn. Principles of Heat Transfer. Singapore: Cengage Learning, 2012.
Lai, W., L. Cao, Z. Xu, P. T. Phan, P. Shum and S. J. Phee. Distal end force sensing with optical fiber bragg gratings for tendon-sheath mechanisms in flexible endoscopic robots. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1–5, 2018.
Le, H. M., L. Cao, T. N. Do, and S. J. Phee. Design and modelling of a variable stiffness manipulator for surgical robots. Mechatronics 53:109–123, 2018.
Li, J., X. Li, J. Wang, Y. Xing, S. Wang, and X. Ren. Design and evaluation of a variable stiffness manual operating platform for laparoendoscopic single site surgery (LESS). Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 13(4):e1797, 2017.
Li, X., L. Cao, A. M. H. Tiong, P. T. Phan, and S. J. Phee. Distal-end force prediction of tendon-sheath mechanisms for flexible endoscopic surgical robots using deep learning. Mech. Mach. Theory 134:323–337, 2019.
Loeve, A., P. Breedveld, and J. Dankelman. Scopes too flexible and too stiff. IEEE Pulse 1:26–41, 2010.
Loeve, A. J., D. H. Plettenburg, P. Breedveld, and J. Dankelman. Endoscope shaft-rigidity control mechanism: “FORGUIDE”. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59:542–551, 2012.
Nilsson, J. W., and S. A. Riedel. Electric Circuits. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, p. 1030, 1999.
Olson, G. Medical devices with variable stiffness. Google Patents, 2013.
Phee, S. J., N. Reddy, P. W. Y. Chiu, P. Rebala, G. V. Rao, Z. Wang, Z. Sun, J. Y. Y. Wong, and K. Y. Ho. Robot-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection is effective in treating patients with early-stage gastric neoplasia. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 10:1117–1121, 2012.
Rattner, D., and A. Kalloo. ASGE/SAGES working group on natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery. Surg. Endosc. 20:329–333, 2006.
Tadesse, Y., N. Thayer, and S. Priya. Tailoring the response time of shape memory alloy wires through active cooling and pre-stress. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 21:19–40, 2010.
Vitiello, V., S. L. Lee, T. P. Cundy, and G. Z. Yang. Emerging robotic platforms for minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 6:111–126, 2013.
Wehrmeyer, J. A., J. A. Barthel, J. P. Roth, and T. Saifuddin. Colonoscope flexural rigidity measurement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 36:475–479, 1998.
Yagi, A., K. Matsumiya, K. Masamune, H. Liao, and T. Dohi. Rigid-Flexible Outer Sheath Model Using Slider Linkage Locking Mechanism and Air Pressure for Endoscopic Surgery. Berlin: Springer, pp. 503–510, 2006.
Yalcintas, M., and H. Dai. Magnetorheological and electrorheological materials in adaptive structures and their performance comparison. Smart Mater. Struct. 8:560, 1999.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Singapore through the NRF Investigatorship Grant (NRFI2016-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ka-Wai Kwok oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Electronic supplementary material 1 (MP4 25010 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, H.M., Phan, P.T., Lin, C. et al. A Temperature-Dependent, Variable-Stiffness Endoscopic Robotic Manipulator with Active Heating and Cooling. Ann Biomed Eng 48, 1837–1849 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02495-z