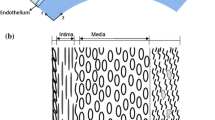
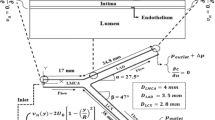
Abstract
Effects of hyperthermia on transport of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) through a stenosed arterial wall are analyzed comprehensively in the present work. The realistic and pertinent aspects of an arterial wall is represented by a multi-layer model, with a proper representation of the thickened intima region due to the atherosclerotic plaque formation. Effects of external and internal hyperthermia on LDL concentration levels are established along with the range of influence of these effects. Various modules of the current work are comprehensively compared with pertinent literature and are found to be in excellent agreement. The effects of external and internal hyperthermia as well as the load level and the axial location of the plaque formation on LDL transport and accumulation for a stenosed artery are established in this work.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area reduction of the stenosis (m2)
- c :
-
LDL concentration (mol/m3)
- \( \bar{c} \) :
-
Intima volume-averaged LDL normalized concentration
- C :
-
Thermal capacity (J/kg K)
- D :
-
LDL diffusivity (m2/s)
- k :
-
First-order reaction coefficient (1/s)
- k T :
-
Thermal-diffusion coefficient
- K :
-
Hydraulic permeability (m2)
- \( \overrightarrow {J} \) :
-
Mass flux (mol/m2 s)
- L :
-
Length of the artery (m)
- M :
-
Molecular weight (g/mol)
- \( \vec{q} \) :
-
Heat flux (W/m2)
- p :
-
Hydraulic pressure (mmHg)
- r :
-
Radial coordinate (m)
- R g :
-
Universal gas constant (J/mol K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u :
-
Velocity vector axial component (m/s)
- v :
-
Velocity vector radial component (m/s)
- \( \overrightarrow {V} \) :
-
Velocity vector (m/s)
- z :
-
Axial coordinate (m)
- z 0 :
-
Distance between center of the stenosis and its beginning (m)
- z st :
-
Axial coordinate at the center of the stenosis (m)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2/s)
- δ :
-
Minimum thickness of the stenosis normalized with lumen radius
- ε :
-
Porosity
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m K)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg/m s)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- σ :
-
Staverman reflection coefficient
- 0:
-
Entrance condition
- eff:
-
Effective property
- f:
-
Fluid (plasma) property
- w:
-
Wall property
- z:
-
Axial component
References
Abraham, J. P., E. M. Sparrow, J. M. Gorman, J. R. Stark, and R. E. Kohler. A mass transfer model of temporal drug deposition in artery walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 58:632–638, 2013.
Abraham, J. P., E. M. Sparrow, and R. D. Lovik. Unsteady, three-dimensional fluid mechanic analysis of blood flow in plaque-narrowed and plaque-free arteries. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 51:5633–5641, 2008.
Abraham, J. P., J. R. Stark, J. M. Gorman, E. M. Sparrow, and R. Kohler. A model of drug deposition within artery walls. J. Med. Dev. 7:020902, 2013.
Ai, L., and K. Vafai. A coupling model for macromolecule transport in a stenosed arterial wall. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 49:1568–1591, 2006.
Alazmi, B., and K. Vafai. Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer interfacial conditions between a porous medium and a fluid layer. Int J. Heat Mass Tran. 44:1735–1749, 2001.
Amiri, A., and K. Vafai. Analysis of dispersion effects and non-thermal equilibrium, non-Darcian, variable porosity incompressible flow through porous media. Int J. Heat Mass Tran. 37:939–954, 1994.
Auer, M., R. Stollberger, P. Regitnig, F. Ebner, and G. A. Holzapfel. 3-D reconstruction of tissue components for atherosclerotic human arteries using ex vivo high-resolution MRI. IEEE T. Med. Imaging 25:345–357, 2006.
Auer, M., R. Stollberger, P. Regitnig, F. Ebner, and G. A. Holzapfel. In vitro angioplasty of atherosclerotic human femoral arteries: analysis of the geometrical changes in the individual tissues using MRI and image processing. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:1276–1287, 2010.
Chapman, S., and T. G. Cowling. The Mathematical Theory of Non-uniform Gases: An Account of the Kinetic Theory of Viscosity, Thermal Conduction and Diffusion in Gases. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 431, 1952.
Chung, S., and K. Vafai. Effect of the fluid-structure interactions on low-density lipoprotein transport within a multi-layered arterial wall. J. Biomech. 45:371–381, 2012.
Chung, S., and K. Vafai. Low-density lipoprotein transport within a multi-layered arterial wall: effect of the atherosclerotic plaque/stenosis. J. Biomech. 46:574–585, 2013.
Chung, S., and K. Vafai. Mechanobiology of low-density lipoprotein transport within an arterial wall-impact of hyperthermia and coupling effects. J. Biomech. 47:137–147, 2014.
Cilla, M., E. Peña, and M. A. Martinez. 3D computational parametric analysis of eccentric atheroma plaque: influence of axial and circumferential residual stresses. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 11:1001–1013, 2012.
Cilla, M., E. Peña, and M. A. Martinez. Mathematical modelling of atheroma plaque formation and development in coronary arteries. J. R. Soc. Interface 11:20130866, 2014.
Colton, C. K., S. Friedman, D. E. Wilson, and R. S. Lees. Ultrafiltration of lipoproteins through a synthetic membrane. Implications for the filtration theory of atherogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 51:2472–2481, 1972.
Cullen, S. A., and R. I. Hill. Aviation pathology and toxicology. In: Ethics and Mental Health: The Patient, Profession and Community, edited by D. J. Rainford, and D. P. Gradwell. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2006, pp. 517–533.
Darcy, H. Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon. Exposition et Application des Principes à Suivre et des Formules à Employer dans les Questions de Distribution d’Eau. Paris: Victor Dalmont, 1856.
Duck, F. A. Physical Properties of Tissues: A Comprehensive Reference Book. San Diego: Academic Press Inc, p. 336, 1990.
Eslamian, M. Advances in thermodiffusion and thermophoresis (Soret effect) in liquid mixtures. FHMT 2:043001, 2011.
Finegold, J. A., P. Asaria, and D. P. Francis. Mortality from ischaemic heart disease by country, region, and age: statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations. Int. J. Cardiol. 168:934–945, 2013.
Gupta, P. K., J. Singh, and K. N. Rai. Numerical simulation for heat transfer in tissues during thermal therapy. J. Therm. Biol. 35:295–301, 2010.
Hao, W., and A. Friedman. The LDL-hdl profile determines the risk of atherosclerosis: a mathematical model. PLoS ONE 9:e90497, 2014.
Hossain, S. S., S. F. A. Hossainy, Y. Bazilevs, V. M. Calo, and T. J. R. Hughes. Mathematical modeling of coupled drug and drug-encapsulated nanoparticle transport in patient-specific coronary artery walls. Comput. Mech. 49:213–242, 2012.
Huang, Y., D. Rumschitzki, S. Chien, and S. Weinbaum. A fiber matrix model for the filtration through fenestral pores in a compressible arterial intima. Am. J. Physiol. 272:H2023–H2039, 1997.
Huysmans, M., and A. Dassargues. Review of the use of Péclet numbers to determine the relative importance of advection and diffusion in low permeability environments. Hydrogeol. J. 13:895–904, 2005.
Jung, H., J. W. Choni, and C. G. Park. Asymmetric flows of non-Newtonian fluids in symmetric stenosed artery. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 16:101–108, 2004.
Kaazempur-Mofrad, M. R., S. Wada, J. G. Myers, and C. R. Ethier. Mass transport and fluid flow in stenotic arteries: axisymmetric and asymmetric models. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 48:4510–4517, 2005.
Karner, G., and K. Perktold. Effect of endothelial injury and increased blood pressure on albumin accumulation in the arterial wall: a numerical study. J. Biomech. 33:709–715, 2000.
Karner, G., K. Perktold, and H. P. Zehentner. Computational modeling of macromolecule transport in the arterial wall. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 4:491–504, 2001.
Katz, M. A. New formulation of water and macromolecular flux which corrects for non-ideality: theory and derivation, predictions, and experimental results. J. Theor. Biol. 112:369–401, 1985.
Kays, W. M., and M. E. Crawford. Convective Heat and Mass Transfer. New York: Mcgraw-Hill, p. 512, 1993.
Kedem, O., and A. Katchalsky. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 27:229–246, 1958.
Keller, B., F. Clubb Jr., and G. Dubini. A review of atherosclerosis and mathematical transport models. In: IFMBE Proceedings, Vol. 36, edited by S. Vlad, and R. V. Ciupa. Berlin: Springer, 2011, pp. 338–343.
Kenjereš, S., and A. de Loor. Modelling and simulation of low-density lipoprotein transport through multi-layered wall of an anatomically realistic carotid artery bifurcation. J. R. Soc. Interface 11:20130941, 2014.
Khakpour, M., and K. Vafai. Effects of gender-related geometrical characteristics of aorta-iliac bifurcation on hemodynamics and macromolecule concentration distribution. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 51:5542–5551, 2008.
Khakpour, M., and K. Vafai. Critical assessment of arterial transport models. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 51:807–822, 2008.
Khamdaengyodtai, P., K. Vafai, P. Sakulchangsatjatai, and P. Terdtoon. Effects of pressure on arterial failure. J. Biomech. 45:2577–2588, 2012.
Kiousis, D. E., T. C. Gasser, and G. A. Holzapfel. A numerical model to study the interaction of vascular stents with human atherosclerotic lesions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35:1857–1869, 2007.
Kolios, M. C., M. D. Sherar, and J. W. Hunt. Large blood vessel cooling in heated tissues: a numerical study. Phys. Med. Biol. 40:477–494, 1995.
Liu, X., Y. Fan, and X. Deng. Effect of the endothelial glycocalyx layer on arterial LDL transport under normal and high pressure. J. Theor. Biol. 283:71–81, 2011.
Mahjoob, S., and K. Vafai. Analytical characterization of heat transport through biological media incorporating hyperthermia treatment. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 52:1608–1618, 2009.
Malvè, M., C. Serrano, E. Peña, R. Fernández-Parra, F. Lostalé, M. A. De Gregorio, and M. A. Martinez. Modelling the air mass transfer in a healthy and a stented rabbit trachea: CT-images, computer simulations and experimental study. Int. Commun Heat. Mass 53:1–8, 2014.
Mandal, D. K., N. K. Manna, and S. Chakrabarti. Influence of different bell-shaped stenoses on the progression of the disease, atherosclerosis. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 25:1933–1947, 2011.
Meyer, G., R. Merval, and A. Tedqui. Effects of pressure-induced stretch and convection on low-density lipoprotein and albumin uptake in the rabbit aortic wall. Circ. Res. 79:532–540, 1996.
Misra, J. C., and G. C. Shit. Blood flow through arteries in a pathological state: a theoretical study. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 44:662–671, 2006.
Olgac, U., V. Kurtcuoglu, and D. Poulikakos. Computational modeling of coupled blood-wall mass transport of LDL: effects of local wall shear stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 294:H909–H919, 2008.
Platten, J. K. The Soret effect: a review of recent experimental results. J. Appl. Mech. 73:5–15, 2006.
Prosi, M., P. Zunino, K. Perktold, and A. Quarteroni. Mathematical and numerical models for transfer of low-density lipoproteins through the arterial walls: a new methodology for the model set up with applications to the study of disturbed lumenal flow. J. Biomech. 38:903–917, 2005.
Rahman, M. A., and M. Z. Saghir. Thermodiffusion or Soret effect: historical review. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 73:693–705, 2014.
Sáez, P., E. Peña, M. A. Martínez, and E. Kuhl. Computational modeling of hypertensive growth in the human carotid artery. Comput. Mech. 53:1183–1196, 2014.
Seeley, B. D., and D. F. Young. Effect of geometry on pressure losses across models of arterial stenosis. J. Biomech. 9:447–448, 1976.
Stangeby, D. K., and C. R. Ethier. Computational analysis of coupled blood-wall arterial LDL transport. J. Biomech. Eng. 124:1–8, 2002.
Stark, J. R., J. M. Gorman, E. M. Sparrow, J. P. Abraham, and R. E. Kohler. Controlling the rate of penetration of therapeutic drug into the wall of an artery by means of a pressurized balloon. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 6:527–532, 2013.
Steiner, R. Laser-tissue interactions. In: Laser and IPL Technology in Dermatology and Aesthetic Medicine, edited by S. Karsai, and C. Raulin. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011.
Sun, N., R. Torii, N. B. Wood, A. D. Hughes, S. A. Thom, and X. Y. Xu. Computational modeling of LDL and albumin transport in an in vivo CT image-based human right coronary artery. J. Biomech. Eng. 131:021003, 2009.
Sun, N., N. B. Wood, A. D. Hughes, S. A. M. Thom, and X. Y. Xu. Effects of transmural pressure and wall shear stress on LDL accumulation in the arterial wall: a numerical study using a multilayered model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 292:H3148–H3157, 2007.
Tada, S., and J. M. Tarbell. Interstitial flow through the internal elastic lamina affects shear stress on arterial smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 278:H1589–H1597, 2000.
Tarbell, J. M. Mass transport in arteries and the localization of atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 5:79–118, 2003.
Taylor, F., M. D. Huffman, A. F. Macedo, T. H. Moore, M. Burke, G. Davey Smith, K. Ward, and S. Ebrahim. Statins for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 1:CD004816, 2013.
Vafai, K., and C. L. Tien. Boundary and inertia effects on flow and heat transfer in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 24:195–203, 1981.
Wada, S., and T. Karino. Computational study on LDL transfer from flowing blood to arterial walls. In: Clinical Application of Computational Mechanics to the Cardiovascular System, edited by T. Yamaguchi. Tokyo: Springer Japan, 2000, pp. 157–173.
Wakeham, W. A., A. Nagashima, and J. V. Sengers. Experimental Thermodynamics, Vol. III, Measurement of the Transport Properties of Fluids, Vol. III. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1991.
Xie, X., J. Tan, D. Wei, D. Lei, T. Yin, J. Huang, X. Zhang, J. Qiu, C. Tang, and G. Wang. In vitro and in vivo investigations on the effects of low-density lipoprotein concentration polarization and haemodynamics on atherosclerotic localization in rabbit and zebrafish. J. R. Soc. Interface 10:20121053, 2013.
Yang, F., G. Holzapfel, C. Schulze-Bauer, R. Stollberger, D. Thedens, L. Bolinger, A. Stolpen, and M. Sonka. Segmentation of wall and plaque in in vitro vascular MR images. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 19:419–428, 2003.
Yang, N., and K. Vafai. Modeling of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transport in the artery—effects of hypertension. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 49:850–867, 2006.
Young, D. F., and F. Y. Tsai. Flow characteristics in models of arterial stenoses: I. Steady flow. J. Biomech. 6:395–410, 1973.
Acknowledgments
The financial support by UniNA and Compagnia di San Paolo, through Programme STAR, is greatly appreciated.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest. This manuscript has not been submitted to anywhere else.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Estefanía Peña oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iasiello, M., Vafai, K., Andreozzi, A. et al. Effects of External and Internal Hyperthermia on LDL Transport and Accumulation Within an Arterial Wall in the Presence of a Stenosis. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 1585–1599 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1196-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1196-0