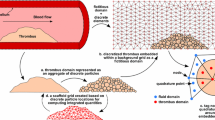
Abstract
Blood clotting under hemodynamic conditions involves numerous multiscale interactions from the molecular scale to macroscopic vessel and systemic circulation scales. Transmission of shear forces to platelet receptors such as GPIbα, P-selectin, α2β1, and α2bβ3 controls adhesion dynamics. These forces also drive membrane tether formation, cellular deformation, and mechanosignaling in blood cells. Blood flow results in red blood cell (RBC) drift towards the center of the vessel along with a near-wall plasma layer enriched with platelets. RBC motions also dramatically enhance platelet dispersion. Trajectories of individual platelets near a thrombotic deposit dictate capture–activation–arrest dynamics as these newly arriving platelets are exposed to chemical gradients of ADP, thromboxane, and thrombin within a micron-scale boundary layer formed around the deposit. If shear forces are sufficiently elevated (>50 dyne/cm2), the largest polymers of von Willebrand Factor may elongate with concomitant shear-induced platelet activation. Finally, thrombin generation enhances platelet recruitment and clot strength via fibrin polymerization. By combination of coarse-graining, continuum, and stochastic algorithms, the numerical simulation of the growth rate, composition, and occlusive/embolic potential of a thrombus now spans multiscale phenomena. These simulations accommodate particular flow geometries, blood phenotype, pharmacological regimen, and reactive surfaces to help predict disease risk or response to therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts, P. A., S. A. van den Broek, G. W. Prins, G. D. Kuiken, J. J. Sixma, and R. M. Heethaar. Blood platelets are concentrated near the wall and red blood cells, in the center in flowing blood. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 8:819–824, 1988.
Bagchi, P. Mesoscale simulation of blood flow in small vessels. Biophys. J. 92:1858–1877, 2007.
Barg, A., R. Ossig, T. Goerge, M. F. Schneider, H. Schillers, H. Oberleithner, and S. W. Schneider. Soluble plasma-derived von Willebrand factor assembles to a halemostatically active filamentous network. Thromb. Haemost. 97:514–526, 2007.
Bathe, M., and R. D. Kamm. A fluid–structure interaction finite element analysis of pulsatile blood flow through a compliant stenotic artery. J. Biomech. Eng. 121:361–369, 1999.
Boyanova, D., S. Nilla, I. Birschmann, T. Dandekar, and M. Dittrich. PlateletWeb: a systems biologic analysis of signaling networks in human platelets. Blood 119:e22–e34, 2011.
Bungay, S. D., P. A. Gentry, and R. D. Gentry. A mathematical model of lipid-mediated thrombin generation. Math. Med. Biol. 20:105–129, 2003.
Chatterjee, M. S., W. S. Denney, H. Jing, and S. L. Diamond. Systems biology of coagulation initiation: kinetics of thrombin generation in resting and activated human blood. PLoS Comput. Biol. 6:e1000950, 2010.
Chatterjee, M. S., J. E. Purvis, L. F. Brass, and S. L. Diamond. Pairwise agonist scanning predicts cellular signaling responses to combinatorial stimuli. Nat. Biotechnol. 28:727–732, 2010.
Chen, H., and A. Alexander-Katz. Polymer-based catch-bonds. Biophys. J. 100:174–182, 2011.
Chintagumpala, M. M., R. L. Hurwitz, J. L. Moake, D. H. Mahoney, and C. P. Steuber. Chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in infants with large von Willebrand factor multimers during remission. J. Pediatr. 120:49–53, 1992.
Colace, T., E. Falls, X. Zheng, and S. Diamond. Analysis of morphology of platelet aggregates formed on collagen under laminar blood flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39:922–929, 2011.
Crowl, L. M., and A. L. Fogelson. Computational model of whole blood exhibiting lateral platelet motion induced by red blood cells. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 26:471–487, 2010.
Delfino, A., N. Stergiopulos, J. E. Moore, Jr., and J. J. Meister. Residual strain effects on the stress field in a thick wall finite element model of the human carotid bifurcation. J. Biomech. 30:777–786, 1997.
Diamond, S. L. Reaction complexity of flowing human blood. Biophys. J. 80:1031–1032, 2001.
Doddi, S. K., and P. Bagchi. Three-dimensional computational modeling of multiple deformable cells flowing in microvessels. Phys. Rev. E 79:046318, 2009.
Doggett, T. A., G. Girdhar, A. Lawshe, D. W. Schmidtke, I. J. Laurenzi, S. L. Diamond, and T. G. Diacovo. Selectin-like kinetics and biomechanics promote rapid platelet adhesion in flow: the GPIbα-vWF tether bond. Biophys. J. 83:194–205, 2002.
Dong, J.-f., J. L. Moake, L. Nolasco, A. Bernardo, W. Arceneaux, C. N. Shrimpton, A. J. Schade, L. V. McIntire, K. Fujikawa, and J. A. Lopez. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood 100:4033–4039, 2002.
Dopheide, S. M., M. J. Maxwell, and S. P. Jackson. Shear-dependent tether formation during platelet translocation on von Willebrand factor. Blood 99:159–167, 2002.
Dumont, K., J. Vierendeels, R. Kaminsky, G. van Nooten, P. Verdonck, and D. Bluestein. Comparison of the hemodynamic and thrombogenic performance of two bileaflet mechanical heart valves using a CFD/FSI model. J. Biomech. Eng. 129:558–565, 2007.
Eckstein, E. C., and F. Belgacem. Model of platelet transport in flowing blood with drift and diffusion terms. Biophys. J. 60:53–69, 1991.
Fedosov, D. A., B. Caswell, and G. E. Karniadakis. A multiscale red blood cell model with accurate mechanics, rheology, and dynamics. Biophys. J. 98:2215–2225, 2010.
Fedosov, D. A., W. Pan, B. Caswell, G. Gompper, and G. E. Karniadakis. Predicting human blood viscosity in silico. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 108:11772–11777, 2011.
Flamm, M. H., T. Colace, M. S. Chatterjee, H. Jing, S. Zhou, D. Jaegar, L. F. Brass, T. Sinno, and S. L. Diamond. Multiscale prediction of patient-specific platelet function under flow. Blood 2012 (in press).
Flamm, M. H., S. L. Diamond, and T. Sinno. Lattice kinetic Monte Carlo simulations of convective-diffusive systems. J. Chem. Phys. 130:094904, 2009.
Flamm, M. H., T. Sinno, and S. L. Diamond. Simulation of aggregating particles in complex flows by the lattice kinetic Monte Carlo method. J. Chem. Phys. 134:034905, 2011.
Fogelson, A. L., Y. H. Hussain, and K. Leiderman. Blood clot formation under flow: the importance of Factor XI depends strongly on platelet count. Biophys. J. 102:10–18, 2012.
Folie, B. J., and L. V. McIntire. Mathematical analysis of mural thrombogenesis. Concentration profiles of platelet-activating agents and effects of viscous shear flow. Biophys. J. 56:1121–1141, 1989.
Guo, Z., K. M. Bussard, K. Chatterjee, R. Miller, E. A. Vogler, and C. A. Siedlecki. Mathematical modeling of material-induced blood plasma coagulation. Biomaterials 27:796–806, 2006.
Haynes, L. M., Y. C. Dubief, and K. G. Mann. Membrane binding events in the initiation and propagation phases of tissue factor initiated zymogen activation under flow. J. Biol. Chem. 287:5225–5234, 2012.
Haynes, L. M., Y. C. Dubief, T. Orfeo, and K. G. Mann. Dilutional control of prothrombin activation at physiologically relevant shear rates. Biophys. J. 100:765–773, 2011.
Hockin, M. F., K. C. Jones, S. J. Everse, and K. G. Mann. A model for the stoichiometric regulation of blood coagulation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:18322–18333, 2002.
Hubbell, J. A., and L. V. McIntire. Platelet active concentration profiles near growing thrombi. A mathematical consideration. Biophys. J. 50:937–945, 1986.
Hund, S. J., and J. F. Antaki. An extended convection diffusion model for red blood cell-enhanced transport of thrombocytes and leukocytes. Phys. Med. Biol. 54:6415–6435, 2009.
Jadhav, S., C. D. Eggleton, and K. Konstantopoulos. A 3-D computational model predicts that cell deformation affects selectin-mediated leukocyte rolling. Biophys. J. 88:96–104, 2005.
Jesty, J., and E. Beltrami. Positive feedbacks of coagulation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25:2463–2469, 2005.
Kadash, K. E., M. B. Lawrence, and S. L. Diamond. Neutrophil string formation: hydrodynamic thresholding and cellular deformation during cell collisions. Biophys. J. 86:4030–4039, 2004.
Kim, J., C.-Z. Zhang, X. Zhang, and T. A. Springer. A mechanically stabilized receptor–ligand flex-bond important in the vasculature. Nature 466:992–995, 2010.
Konstantopoulos, K., T. W. Chow, N. A. Turner, J. D. Hellums, and J. L. Moake. Shear stress-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets. Biorheology 34:57–71, 1997.
Kuharsky, A. L., and A. L. Fogelson. Surface-mediated control of blood coagulation: the role of binding site densities and platelet deposition. Biophys. J. 80:1050–1074, 2001.
Leiderman, K., and A. L. Fogelson. Grow with the flow: a spatial temporal model of platelet deposition and blood coagulation under flow. Math. Med. Biol. 28:47–84, 2011.
Lenoci, L., M. Duvernay, S. Satchell, E. DiBenedetto, and H. E. Hamm. Mathematical model of PAR1-mediated activation of human platelets. Mol. BioSyst. 7:1129–1137, 2010.
Levy, G. G., W. C. Nichols, E. C. Lian, T. Foroud, J. N. McClintick, B. M. McGee, A. Y. Yang, D. R. Siemieniak, K. R. Stark, R. Gruppo, R. Sarode, S. B. Shurin, V. Chandrasekaran, S. P. Stabler, H. Sabio, E. E. Bouhassira, J. D. Upshaw, D. Ginsburg, and H.-M. Tsai. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 413:488–494, 2001.
Li, M. X., J. J. Beech-Brandt, L. R. John, P. R. Hoskins, and W. J. Easson. Numerical analysis of pulsatile blood flow and vessel wall mechanics in different degrees of stenoses. J. Biomech. 40:3715–3724, 2007.
Li, Z., M. K. Delaney, K. A. O’Brien, and X. Du. Signaling during platelet adhesion and activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30:2341–2349, 2010.
Litvinov, R. I., V. Barsegov, A. J. Schissler, A. R. Fisher, J. S. Bennett, J. W. Weisel, and H. Shuman. Dissociation of bimolecular aIIb–b3–fibrinogen complex under a constant tensile force. Biophys. J. 100:165–173, 2011.
Liu, J., N. J. Agrawal, A. Calderon, P. S. Ayyaswamy, D. M. Eckmann, and R. Radhakrishnan. Multivalent binding of nanocarrier to endothelial cells under shear flow. Biophys. J. 101:319–326, 2011.
Lo, K., W. S. Denney, and S. L. Diamond. Stochastic modeling of blood coagulation initiation. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 34:80–90, 2005.
Loth, F., P. F. Fischer, and H. S. Bassiouny. Blood flow in end-to-side anastomoses. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40:367–393, 2008.
Luan, D., M. Zai, and J. D. Varner. Computationally derived points of fragility of a human cascade are consistent with current therapeutic strategies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3:e142, 2007.
Maloney, S. F., L. F. Brass, and S. L. Diamond. P2Y12 or P2Y1 inhibitors reduce platelet deposition in a microfluidic model of thrombosis while apyrase lacks efficacy under flow conditions. Integr. Biol. 2:183–192, 2010.
Moake, J. L., N. A. Turner, N. A. Stathopoulos, L. Nolasco, and J. D. Hellums. Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released from platelets, as well as by exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin. Blood 71:1366–1374, 1988.
Moake, J. L., N. A. Turner, N. A. Stathopoulos, L. H. Nolasco, and J. D. Hellums. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J. Clin. Investig. 78:1456–1461, 1986.
Mody, N. A., and M. R. King. Platelet adhesive dynamics. Part I: Characterization of platelet hydrodynamic collisions and wall effects. Biophys. J. 95:2539–2555, 2008.
Nesbitt, W. S., E. Westein, F. J. Tovar-Lopez, E. Tolouei, A. Mitchell, J. Fu, J. Carberry, A. Fouras, and S. P. Jackson. A shear gradient-dependent platelet aggregation mechanism drives thrombus formation. Nat. Med. 15:665–673, 2009.
Okorie, U. M., W. S. Denney, M. S. Chatterjee, K. B. Neeves, and S. L. Diamond. Determination of surface tissue factor thresholds that trigger coagulation at venous and arterial shear rates: amplification of 100 fM circulating tissue factor requires flow. Blood 111:3507–3513, 2008.
Perktold, K., and D. Hilbert. Numerical simulation of pulsatile flow in a carotid bifurcation model. J. Biomed. Eng. 8:193–199, 1986.
Purvis, J. E., M. S. Chatterjee, L. F. Brass, and S. L. Diamond. A molecular signaling model of platelet phosphoinositide and calcium regulation during homeostasis and P2Y1 activation. Blood 112:4069–4079, 2008.
Purvis, J. E., R. Radhakrishnan, and S. L. Diamond. Steady-state kinetic modeling constrains cellular resting states and dynamic behavior. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5:e1000298, 2009.
Ruggeri, Z. M., J. N. Orje, R. Habermann, A. B. Federici, and A. J. Reininger. Activation-independent platelet adhesion and aggregation under elevated shear stress. Blood 108:1903–1910, 2006.
Schneider, S. W., S. Nuschele, A. Wixforth, C. Gorzelanny, A. Alexander-Katz, R. R. Netz, and M. F. Schneider. Shear-induced unfolding triggers adhesion of von Willebrand factor fibers. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 104:7899–7903, 2007.
Shankaran, H., P. Alexandridis, and S. Neelamegham. Aspects of hydrodynamic shear regulating shear-induced platelet activation and self-association of von Willebrand factor in suspension. Blood 101:2637–2645, 2003.
Shim, K., P. J. Anderson, E. A. Tuley, E. Wiswall, and J. Evan Sadler. Platelet–VWF complexes are preferred substrates of ADAMTS13 under fluid shear stress. Blood 111:651–657, 2008.
Sorensen, E. N., G. W. Burgreen, W. R. Wagner, and J. F. Antaki. Computational simulation of platelet deposition and activation: I. Model development and properties. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27:436–448, 1999.
Sorensen, E. N., G. W. Burgreen, W. R. Wagner, and J. F. Antaki. Computational simulation of platelet deposition and activation: II. Results for Poiseuille flow over collagen. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27:449–458, 1999.
Steppich, D. M., J. I. Angerer, K. Sritharan, S. W. Schneider, S. Thalhammer, A. Wixforth, A. Alexander-Katz, and M. F. Schneider. Relaxation of ultralarge VWF bundles in a microfluidic–AFM hybrid reactor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 369:507–512, 2008.
Stuhne, G. R., and D. A. Steinman. Finite-element modeling of the hemodynamics of stented aneurysms. J. Biomech. Eng. 126:382–387, 2004.
Taylor, C. A., T. J. R. Hughes, and C. K. Zarins. Finite element modeling of three-dimensional pulsatile flow in the abdominal aorta: relevance to atherosclerosis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 26:975–987, 1998.
Turitto, V. T., A. M. Benis, and E. F. Leonard. Platelet diffusion in flowing blood. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 11:216–223, 1972.
Vincentelli, A., S. Susen, T. Le Tourneau, I. Six, O. Fabre, F. Juthier, A. Bauters, C. Decoene, J. Goudemand, A. Prat, and B. Jude. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome in aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 349:343–349, 2003.
Xu, Z., N. Chen, M. M. Kamocka, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. A multiscale model of thrombus development. J. R. Soc. Interface 5:705–722, 2008.
Xu, Z., N. Chen, S. C. Shadden, J. E. Marsden, M. M. Kamocka, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. Study of blood flow impact on growth of thrombi using a multiscale model. Soft Matter 5:769–779, 2009.
Xu, Z., J. Lioi, J. Mu, M. M. Kamocka, X. Liu, D. Z. Chen, E. D. Rosen, and M. Alber. A multiscale model of venous thrombus formation with surface-mediated control of blood coagulation cascade. Biophys. J. 98:1723–1732, 2010.
Yago, T., J. H. Wu, C. D. Wey, A. G. Klopocki, C. Zhu, and R. P. McEver. Catch bonds govern adhesion through L-selectin at threshold shear. J. Cell Biol. 166:913–923, 2004.
Yeh, C., and E. C. Eckstein. Transient lateral transport of platelet-sized particles in flowing blood suspensions. Biophys. J. 66:1706–1716, 1994.
Zhao, H., and E. S. G. Shaqfeh. Shear-induced platelet margination in a microchannel. Phys. Rev. E 83:061924, 2011.
Zhuo, R., C. A. Siedlecki, and E. A. Vogler. Competitive-protein adsorption in contact activation of blood Factor XII. Biomaterials 28:4355–4369, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Michael R. King oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flamm, M.H., Diamond, S.L. Multiscale Systems Biology and Physics of Thrombosis Under Flow. Ann Biomed Eng 40, 2355–2364 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0557-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0557-9