Abstract
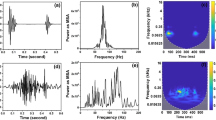
Carotid Artery Doppler Signals were recorded from 114 subjects, 60 of whom had Atherosclerosis disease while the rest were healthy controls. Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis from Carotid Artery Doppler Signals was conducted using Fuzzy weighted pre-processing and Least Square Support Vector Machine (LSSVM). First, in order to determine the LSSVM inputs, spectral analysis of Carotid Artery Doppler Signals was performed via Autoregressive (AR) modeling. Then, fuzzy weighted pre-processing based is proposed expert system, applied to inputs obtained from spectral analysis of Carotid Artery Doppler Signals. LSSVM was used to detect Atherosclerosis from Carotid Artery Doppler Signals. All data set were obtained from Carotid Artery Doppler Signals of healthy subjects and subjects suffering from Atherosclerosis disease. The employed expert system has achieved 100% classification accuracy using a 10-fold Cross Validation (CV) method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H., (1974), A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control AC-19:716–723
Baird R. N., Bird D. R., Clifford P. C., Lusby R. J., Skidmore R., Woodcock J. P. (1980) Upstream stenosis: diagnosis by Doppler signals from the femoral artery. Arch. Surg. 115(11):1316 –1322
Cheung, N. 2001. Machine learning techniques for medical analysis. BSc thesis, School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, University of Queenland
Currie I. C., Wilson Y. G., Baird R. N., Lamont P. M. (1995) Postocclusive hyperaemic duplex scan: a new method of aortoiliac assessment. Br. J. Surg. 82:1226–1229
Dart, A. M., F. Lacombe, J. K. Yeoh, J. D. Cameron, G. L. Jennings, E. Laufer, and D. S. Esmore. Aortic distensibility in patients with isolated hyper-cholesterolaemia, coronary artery disease, or cardiac transplant. Lancet 338:270–273, 1991
Dean Forbes A. (1995). Classification-algorithm evaluation: five performance measures based onconfusion matrices. J. Clin. Monitor. Comput. 11(3):189–206
Delen D., Walker G., Kadam A., (2004). Predicting breast cancer survivability: a comparison of three data mining methods. Artific. Intell. Med. 34(2):113–127
Evans D. (2000) Doppler signal analysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 26(Supplement 1):S13–S15
Evans, D. H., W. N. McDicken, R. Skidmore, and J. P. Woodcock. Doppler Ultrasound: Physics, Instrumentation and Clinical Applications. Wiley, Chichester, 1989
Gosling R. G., King D. H. (1974), Continuous wave ultrasound as an alternative and complement to X-rays in vascular examination. In: Reneman R. S. (eds) Cardiovascular Applications of Ultrasound. Amsterdam, North-Holland pp 266 –282
Hirai, T., S. Sasayama, T. Kawasaki, and S. Yagi. Stiffness of systemic arteries in patients with myocardial infarction. A noninvasive method to predict severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation, 80:78–86, 1989
Jeff Schneider’s Home Page, http://www.cs.cmu.edu/∼schneide/tut5/node42.html (last accessed: May, 30, 2006)
Kaluzynski K. (1989) Order selection in Doppler blood flow signal spectral analysis using autoregressive modeling. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 27:89–92
Kara, S. A study of mitral and tricuspid valve blood flows by autoregressive spectral analysis method and Doppler unit. Thesis of Doctorate, Institute of Science of Erciyes University Press, 1995
Kay S. M., Marple S. L. (1981) Spectrum analysis – a modern perspective. Proc. IEEE, 69(11):1380–1419
Macpherson D. S., Evans D. H., Bell P. R. F. (1984) Common femoral artery Doppler waveforms: a comparison of three methods of objective analysis with direct pressure measurements. Br. J. Surg. 71:46–49
Muller M., Ciccotti P., Reiche W., Hagen T. (2001) Comparison of color flow Doppler scanning, power Doppler scanning, and frequency shift for assessment of carotid artery stenosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 34:1090–1095
Planiol T., Pourcelot L. (1973), Doppler Effect Study of the Carotid Circulation. Ultrasonics in Medicine. Elsevier, New York
Polat K., Şahan S., Güneş S. (2006). A new method to medical diagnosis: artificial immune recognition system (AIRS) with fuzzy weighted pre-processing and application to ECG arrhythmia. Expert Syst. Appl. 31(2):264–269
Saini, V. D., N. C. Nanda, and D. Maulik. Basic principles of ultrasound and Doppler effect. In: Doppler Echocardiography, edited by N. C. Nanda. London: Lea & Febiger, 1993
Schlindwein F.S., Evans D.H., (1990), Selection of the order of autoregressive models for spectral analysis of Doppler ultrasound signals. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 16(1): 81–91
Sigel B. (1998) A brief history of Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of peripheral vascular disease. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 24:169–176
Stefanadis, C., C. Stratos, H. Boudoulas, C. Kourouklis, and P. Toutouzas. Distensibility of the ascending aorta, comparison of invasive and non-invasive techniques in healthy men and in men with coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. 11:990–996, 1990
Suykens J. A. K., Vandewalle J. (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 9(3):293–300
Tsujinishi, D., and S. Abe. Fuzzy least squares support vector machines for multi-class problems. Neural Netw. 16:785–792, 2003
Vaitkus P. J., Cobbold R. S. C., Johnston K. W. (1988) A comparative study and assessment of Doppler ultrasound spectral estimation techniques part II: methods and results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 14:673–688
Van Asten W. N., Beijneveld W. J., Pieters B. R., et al. (1991) Assessment of aortoiliac obstructive disease by Doppler spectrum analysis of blood flow velocities in the common femoral artery at rest and during reactive hyperemia. Surgery 109:633–639
Vapnik V. (1995) The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. Springer, New York
Wang X., Paliwal K. K. (2003). Feature extraction and dimensionality reduction algorithms and their applications in vowel recognition. Pattern Recognit. 36:2429– 2439
Yeh C. K., Li P. C. (2002) Doppler Angle estimation of pulsatile flows using AR modeling. Ultrason. Imaging 24:135–146
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by the Scientific Research Projects of Selcuk University (project no. 05401069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polat, K., Kara, S., Latifoğlu, F. et al. Pattern Detection of Atherosclerosis from Carotid Artery Doppler Signals using Fuzzy Weighted Pre-Processing and Least Square Support Vector Machine (LSSVM). Ann Biomed Eng 35, 724–732 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9289-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-007-9289-7