Abstract
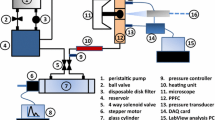
Pulsations in blood flow alter gene and protein expressions in endothelial cells (EC). A computer-controlled system was developed to mimic the common carotid artery flow waveform and shear stress levels or to provide steady flow of the same mean shear stress in a parallel plate flow chamber. The pseudo-steady state shear stress was determined from real-time pressure gradient measurements and compared to the Navier–Stokes equation solution. Following 24 h of steady flow (SF: 13 dyne/cm2), pulsatile arterial flow (AF: average=13 dyne/cm2, range=7–25 dyne/cm2) or static conditions, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and prostaglandin H synthase-2 (PGHS-2) mRNA and protein expressions from human umbilical vein endothelial cells were measured. Relative to steady flow, pulsatile arterial flow significantly attenuated mRNA upregulation of HO-1 (SF: 7.26±2.70-fold over static, AF: 4.84±0.37-fold over static; p < 0.01) and PGHS-2 (SF: 6.11±1.79-fold over static, AF: 3.54±0.79-fold over static; p < 0.001). Pulsatile arterial flow (4.57±0.81-fold over static, p < 0.01) also significantly reduced the steady-flow-induced HO-1 protein upregulation (7.99±1.29-fold over static). These findings reveal that EC can discriminate between different flow patterns of the same average magnitude and respond at the molecular level.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bacabac, R. G., T. H. Smit, S. C. Cowin, J. J. Van Loon, F. T. Nieuwstadt, R. Heethaar, and J. Klein-Nulend. Dynamic shear stress in parallel-plate flow chambers. J. Biomech. 38:159–167, 2005.
Balcells, M., M. Fernandez Suarez, M. Vazquez, and E. R. Edelman. Cells in fluidic environments are sensitive to flow frequency. J. Cell Physiol. 204:329–335, 2005.
Bao, X., C. M. Lu, and J. A. Frangos. Temporal gradient in shear but not steady shear stress induces PDGF-A and MCP-1 expression in endothelial cells: Role of NO, NF kappa B, and egr-1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19:996–1003, 1999.
Blackman, B. R., G. Garcia-Cardena, and M. A. Gimbrone Jr. A new in vitro model to evaluate differential responses of endothelial cells to simulated arterial shear stress waveforms. J. Biomech. Eng. 124:397–407, 2002.
Butler, P. J., T. C. Tsou, J. Y. Li, S. Usami, and S. Chien. Rate sensitivity of shear-induced changes in the lateral diffusion of endothelial cell membrane lipids: A role for membrane perturbation in shear-induced MAPK activation. FASEB J. 16:216–218, 2002.
Chappell, D. C., S. E. Varner, R. M. Nerem, R. M. Medford, and R. W. Alexander. Oscillatory shear stress stimulates adhesion molecule expression in cultured human endothelium. Circ. Res. 82:532–539, 1998.
Chen, X. L., S. E. Varner, A. S. Rao, J. Y. Grey, S. Thomas, C. K. Cook, M. A. Wasserman, R. M. Medford, A. K. Jaiswal, and C. Kunsch. Laminar flow induction of antioxidant response element-mediated genes in endothelial cells. A novel anti-inflammatory mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 278:703–711, 2003.
Curtis, A. S., J. V. Forrester, C. McInnes, and F. Lawrie. Adhesion of cells to polystyrene surfaces. J. Cell Biol. 97:1500–1506, 1983.
Dai, G., M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, S. Natarajan, Y. Zhang, S. Vaughn, B. R. Blackman, R. D. Kamm, G. Garcia-Cardena, and M. A. Gimbrone Jr. Distinct endothelial phenotypes evoked by arterial waveforms derived from atherosclerosis-susceptible and -resistant regions of human vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:14871–14876, 2004.
Dancu, M. B., D. E. Berardi, J. P. Vanden Heuvel, and J. M. Tarbell. Asynchronous shear stress and circumferential strain reduces endothelial NO synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 but induces endothelin-1 gene expression in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:2088–2094, 2004.
De Keulenaer, G. W., D. C. Chappell, N. Ishizaka, R. M. Nerem, R. W. Alexander, and K. K. Griendling. Oscillatory and steady laminar shear stress differentially affect human endothelial redox state: Role of a superoxide-producing NADH oxidase. Circ. Res. 82:1094–1101, 1998.
Drakos, S. G., C. E. Charitos, A. Ntalianis, J. V. Terrovitis, K. X. Siafakas, P. Dolou, C. Pierrakos, E. Charitos, J. Karelas, and J. N. Nanas. Comparison of pulsatile with nonpulsatile mechanical support in a porcine model of profound cardiogenic shock. ASAIO J. 51:26–29, 2005.
Dusserre, N., N. L'Heureux, K. S. Bell, H. Y. Stevens, J. Yeh, L. A. Otte, L. Loufrani, and J. A. Frangos. PECAM-1 interacts with nitric oxide synthase in human endothelial cells: implication for flow-induced nitric oxide synthase activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:1796–1802, 2004.
Elhadj, S., R. M. Akers, and K. Forsten-Williams. Chronic pulsatile shear stress alters insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) binding protein release in vitro. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:163–170, 2003.
Eskin, S. G., N. A. Turner, and L. V. McIntire. Endothelial cell cytochrome P450 1A1 and 1B1: Up-regulation by shear stress. Endothelium 11:1–10, 2004.
Fish, J. E., C. C. Matouk, A. Rachlis, S. Lin, S. C. Tai, C. D'Abreo, and P. A. Marsden. The expression of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase is controlled by a cell-specific histone code. J. Biol. Chem. 280:24824–24838, 2005.
Florian, J. A., J. R. Kosky, K. Ainslie, Z. Pang, R. O. Dull, and J. M. Tarbell. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a mechanosensor on endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 93:e136–e142, 2003.
Frangos, J. A., L. V. McIntire, and S. G. Eskin. Shear stress induced stimulation of mammalian cell metabolism. Biotech. Bioeng. 32:1053–1060, 1987.
Frangos, J. A., S. G. Eskin, L. V. McIntire, and C. L. Ives. Flow effects on prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Science 227:1477–1479, 1985.
Frye, S. R., A. Yee, S. G. Eskin, R. Guerra, X. Cong, and L. V. McIntire. cDNA microarray analysis of endothelial cells subjected to cyclic mechanical strain: importance of motion control. Physiol. Genom. 21:124–130, 2005.
He, X., D. N. Ku, and J. E. Moore Jr. Simple calculation of the velocity profiles for pulsatile flow in a blood vessel using Mathematica. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 21:45–49, 1993.
Hoffmann, J., S. Dimmeler, and J. Haendeler. Shear stress increases the amount of S-nitrosylated molecules in endothelial cells: Important role for signal transduction. FEBS Lett. 551:153–158, 2003.
Hosoya, T., A. Maruyama, M. I. Kang, Y. Kawatani, T. Shibata, K. Uchida, E. Warabi, N. Noguchi, K. Itoh, and M. Yamamoto. Differential responses of the Nrf2-Keap1 system to laminar and oscillatory shear stresses in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280:27244–27250, 2005.
Hsiai, T. K., S. K. Cho, S. Reddy, S. Hama, M. Navab, L. L. Demer, H. M. Honda, and C. M. Ho. Pulsatile flow regulates monocyte adhesion to oxidized lipid-induced endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21:1770–1776, 2001.
Ishii, T., K. Itoh, S. Takahashi, H. Sato, T. Yanagawa, Y. Katoh, S. Bannai, and M. Yamamoto. Transcription factor Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible genes in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 275:16023–16029, 2000.
Kawahito, S., K. Nakata, K. Nonaka, T. Sato, M. Yoshikawa, T. Takano, T. Maeda, J. Linneweber, S. Schulte-Eistrup, D. Flowers, J. Glueck, and Y. Nose. Analysis of the arterial blood pressure waveform using Fast Fourier Transform technique during left ventricular nonpulsatile assistance: In vitro study. Artif. Organs. 24:580–583, 2000.
Kim, H. K., H. S. Son, Y. H. Fang, P. S. Y. C. M. Hwang, and K. Sun. The effects of pulsatile flow upon renal tissue perfusion during cardiopulmonary bypass: a comparative study of pulsatile and nonpulsatile flow. ASAIO J. 51:30–36, 2005.
Kim, H. P., X. Wang, F. Galbiati, S. W. Ryter, and A. M. Choi. Caveolae compartmentalization of heme oxygenase-1 in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 18:1080–1089, 2004.
Koneru, P., and C. W. Leffler. Role of cGMP in carbon monoxide-induced cerebral vasodilation in piglets. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 286:H304–H309, 2004.
Ku, D. N., D. P. Giddens, D. J. Phillips, and D. E. Strandness Jr. Hemodynamics of the normal human carotid bifurcation: In vitro and in vivo studies. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 11:13–26, 1985.
Levonen, A. L., A. Landar, A. Ramachandran, E. K. Ceaser, D. A. Dickinson, G. Zanoni, J. D. Morrow, and V. M. Darley-Usmar. Cellular mechanisms of redox cell signalling: Role of cysteine modification in controlling antioxidant defences in response to electrophilic lipid oxidation products. Biochem. J. 378:373–382, 2004.
Li Volti, G., F. Seta, M. L. Schwartzman, A. Nasjletti, and N. G. Abraham. Heme oxygenase attenuates angiotensin II-mediated increase in cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human femoral endothelial cells. Hypertension 41:715–719, 2003.
Lieu, D. K., P. A. Pappone, and A. I. Barakat. Differential membrane potential and ion current responses to different types of shear stress in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 286:C1367–C1375, 2004.
Long, Q., X. Y. Xu, K. V. Ramnarine, and P. Hoskins. Numerical investigation of physiologically realistic pulsatile flow through arterial stenosis. J. Biomech. 34:1229–1242, 2001.
Mattart, M., L. Mazzolai, C. Chambaz, D. Hayoz, H. R. Brunner, and P. Silacci. ET-1 and NOS III gene expression regulation by plaque-free and plaque-prone hemodynamic conditions. Biorheology 40:289–297, 2003.
Mazzag, B. M., J. S. Tamaresis, and A. I. Barakat. A model for shear stress sensing and transmission in vascular endothelial cells. Biophys. J. 84:4087–4101, 2003.
McCormick, S. M., S. G. Eskin, L. V. McIntire, C. L. Teng, C. M. Lu, C. G. Russell, and K. K. Chittur. DNA microarray reveals changes in gene expression of shear stressed human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98:8955–8960, 2001.
McCormick, S. M., P. A. Whitson, K. K. Wu, and L. V. McIntire. Shear stress differentially regulates PGHS-1 and PGHS-2 protein levels in human endothelial cells. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 28:824–833, 2000.
Mesana, T. G. Rotary blood pumps for cardiac assistance. Artif. Organs. 28:218–225, 2004.
Mills, C. J., I. T. Gabe, J. H. Gault, D. T. Mason, J. Ross Jr., E. Braunwald, and J. P. Shillingford. Pressure-flow relationships and vascular impedance in man. Cardiovasc. Res. 4:405–417, 1970.
Nguyen, K. T., S. G. Eskin, C. Patterson, M. S. Runge, and L. V. McIntire. Shear stress reduces protease activated receptor-1 expression in human endothelial cells. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29:145–152, 2001.
Nishikawa, Y., D. W. Stepp, D. Merkus, D. Jones, and W. M. Chilian. In vivo role of heme oxygenase in ischemic coronary vasodilation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 286:H2296–H2304, 2004.
Passerini, A. G., D. C. Polacek, C. Shi, N. M. Francesco, E. Manduchi, G. R. Grant, W. F. Pritchard, S. Powell, G. Y. Chang, C. J. Stoeckert Jr., and P. F. Davies. Coexisting proinflammatory and antioxidative endothelial transcription profiles in a disturbed flow region of the adult porcine aorta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:2482–2487, 2004.
Perktold, K., and G. Rappitsch. Computer simulation of local blood flow and vessel mechanics in a compliant carotid artery bifurcation model. J. Biomech. 28:845–856, 1995.
Poulos, T. L. Structural and functional diversity in heme monooxygenases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 33:10–18, 2005.
Samijo, S. K., J. M. Willigers, P. J. Brands, R. Barkhuysen, R. S. Reneman, P. J. Kitslaar, and A. P. Hoeks. Reproducibility of shear rate and shear stress assessment by means of ultrasound in the common carotid artery of young human males and females. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 23:583–590, 1997.
Silacci, P., A. Desgeorges, L. Mazzolai, C. Chambaz, and D. Hayoz. Flow pulsatility is a critical determinant of oxidative stress in endothelial cells. Hypertension 38:1162–1166, 2001.
Simmons, D. L., R. M. Botting, and T. Hla. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: the biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 56:387–437, 2004.
Smith, W. L., D. L. DeWitt, and R. M. Garavito. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69:145–182, 2000.
Soares, M. P., M. P. Seldon, I. P. Gregoire, T. Vassilevskaia, P. O. Berberat, J. Yu, T. Y. Tsui, and F. H. Bach. Heme oxygenase-1 modulates the expression of adhesion molecules associated with endothelial cell activation. J. Immunol. 172:3553–3563, 2004.
Sorescu, G. P., H. Song, S. L. Tressel, J. Hwang, S. Dikalov, D. A. Smith, N. L. Boyd, M. O. Platt, B. Lassegue, K. K. Griendling, and H. Jo. Bone morphogenic protein 4 produced in endothelial cells by oscillatory shear stress induces monocyte adhesion by stimulating reactive oxygen species production from a nox1-based NADPH oxidase. Circ. Res. 95:773–779, 2004.
Tai, S. C., G. B. Robb, and P. A. Marsden. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: a new paradigm for gene regulation in the injured blood vessel. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:405–412, 2004.
Takatani, S. Beyond implantable first generation cardiac prostheses for treatment of end-stage cardiac patients with clinical results in a multicenter. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 8:253–263, 2002.
Topper, J. N., J. Cai, D. Falb, and M. A. J. Gimbrone. Identification of vascular endothelial genes differentially responsive to fluid mechanical stimuli: Cyclooxygenase-2, manganese superoxide dismutase, and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase are selectively up-regulated by steady laminar shear stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:10417–10422, 1996.
VanderLaan, P. A., C. A. Reardon, and G. S. Getz. Site specificity of atherosclerosis: Site-selective responses to atherosclerotic modulators. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:12–22, 2004.
Wieselthaler, G. M., H. Schima, M. Hiesmayr, R. Pacher, G. Laufer, G. P. Noon, M. DeBakey, and E. Wolner. First clinical experience with the DeBakey VAD continuous-axial-flow pump for bridge to transplantation. Circulation. 101:356–359, 2000.
Wittstein, I. S., W. Qiu, R. C. Ziegelstein, Q. Hu, and D. A. Kass. Opposite effects of pressurized steady versus pulsatile perfusion on vascular endothelial cell cytosolic pH: Role of tyrosine kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Circ. Res. 86:1230–1236, 2000.
Womersley, J. R. Method for the calculation of velocity, rate of flow and viscous drag in arteries when the pressure gradient is known. J. Physiol. 127:553–563, 1955.
Wunder, C., R. W. Brock, S. D. McCarter, A. Bihari, K. Harris, O. Eichelbronner, and R. F. Potter. Inhibition of haem oxygenase activity increases leukocyte accumulation in the liver following limb ischaemia-reperfusion in mice. J. Physiol. 540:1013–1021, 2002.
Yet, S. F., M. D. Layne, X. Liu, Y. H. Chen, B. Ith, N. E. Sibinga, and M. A. Perrella. Absence of heme oxygenase-1 exacerbates atherosclerotic lesion formation and vascular remodeling. FASEB J. 17:1759–1761, 2003.
Younis, H. F., M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, R. C. Chan, A. G. Isasi, D. P. Hinton, A. H. Chau, L. A. Kim, and R. D. Kamm. Hemodynamics and wall mechanics in human carotid bifurcation and its consequences for atherogenesis: investigation of inter-individual variation. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 3:17–32, 2004.
Zhao, S. Z., B. Ariff, Q. Long, A. D. Hughes, S. A. Thom, A. V. Stanton, and X. Y. Xu. Inter-individual variations in wall shear stress and mechanical stress distributions at the carotid artery bifurcation of healthy humans. J. Biomech. 35:1367–1377, 2002.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by HL-18672 from the NIH. We thank Drs. George Sorescu and Hanjoong Jo of Emory University School of Medicine for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yee, A., Sakurai, Y., Eskin, S.G. et al. A Validated System for Simulating Common Carotid Arterial Flow In Vitro: Alteration of Endothelial Cell Response. Ann Biomed Eng 34, 593–604 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-006-9078-8